178 | Border Gateway Protocol
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Route Reflectors
Route Reflectors reorganize the iBGP core into a hierarchy and allows some route advertisement rules.
Route reflection divides iBGP peers into two groups: client peers and nonclient peers. A route reflector and
its client peers form a route reflection cluster. Since BGP speakers announce only the best route for a given
prefix, route reflector rules are applied after the router makes its best path decision.
• If a route was received from a nonclient peer, reflect the route to all client peers.
• If the route was received from a client peer, reflect the route to all nonclient and all client peers.
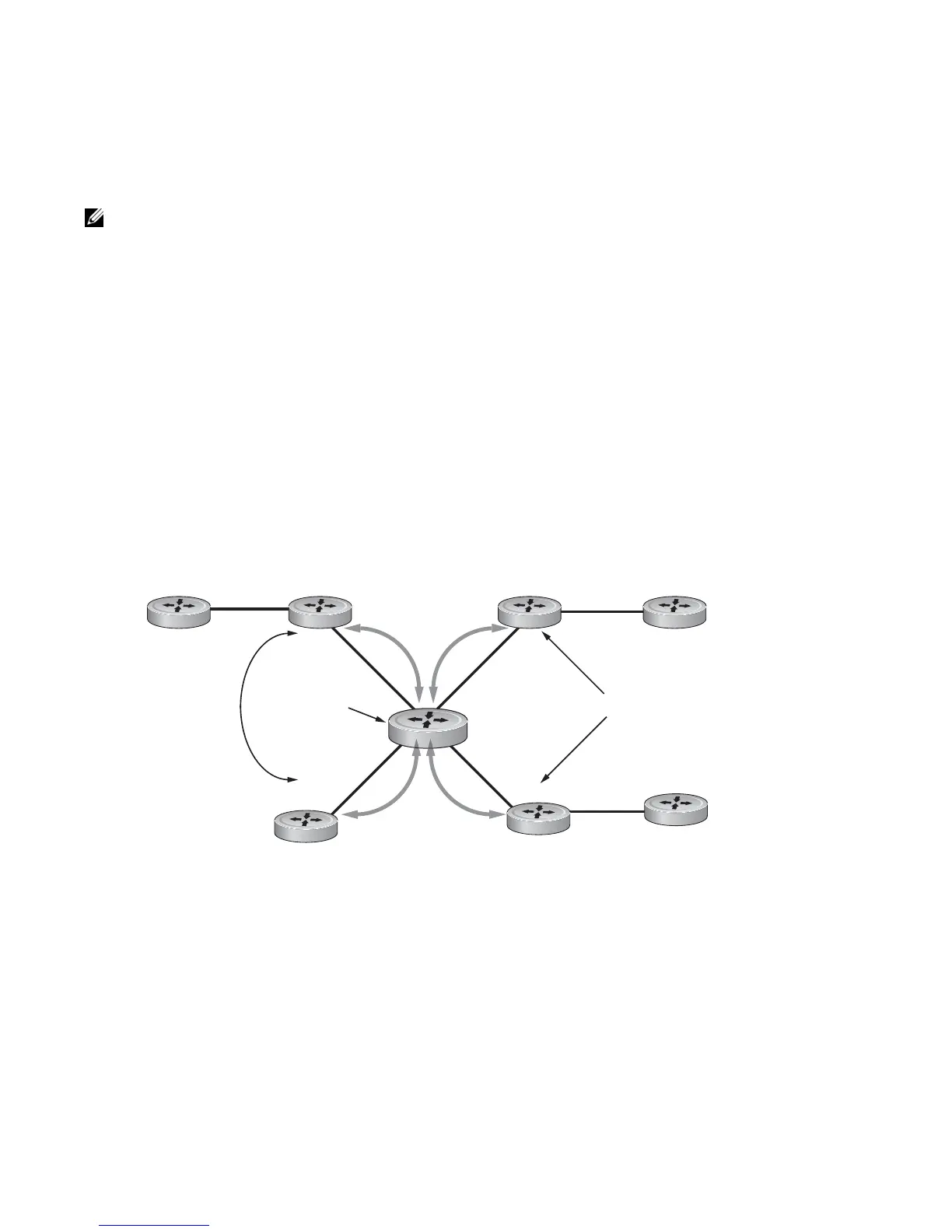
To illustrate how these rules affect routing, see Figure 9-3 and the following steps. Routers B, C, D, E, and
G are members of the same AS - AS100. These routers are also in the same Route Reflection Cluster,
where Router D is the Route Reflector. Router E and H are client peers of Router D; Routers B and C and
nonclient peers of Router D.
Figure 9-3. Route Reflection Example
1. Router B receives an advertisement from Router A through eBGP. Since the route is learned through
eBGP, Router B advertises it to all its iBGP peers: Routers C and D.
2. Router C receives the advertisement but does not advertise it to any peer because its only other peer is
Router D, an iBGP peer, and Router D has already learned it through iBGP from Router B.
3. Router D does not advertise the route to Router C because Router C is a nonclient peer and the route
advertisement came from Router B who is also a non-client peer.
4. Router D does reflect the advertisement to Routers E and G because they are client peers of Router D.
5. Routers E and G then advertise this iBGP learned route to their eBGP peers Routers F and H.
Note: Route Reflectors (RRs) should not be used in the forwarding path. In iBGP, hierarchal RRs
maintaining forwarding plane RRs could create routing loops.
Router A Router B
Router C
Router D
Router E
Router G
Router F
Router H
eBGP Route
eBGP Route
eBGP Route
Route Reflector
Route Reflector Client Peers
iBGP Route
iBGP Routes
iBGP Routes

 Loading...
Loading...











