1098 | Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
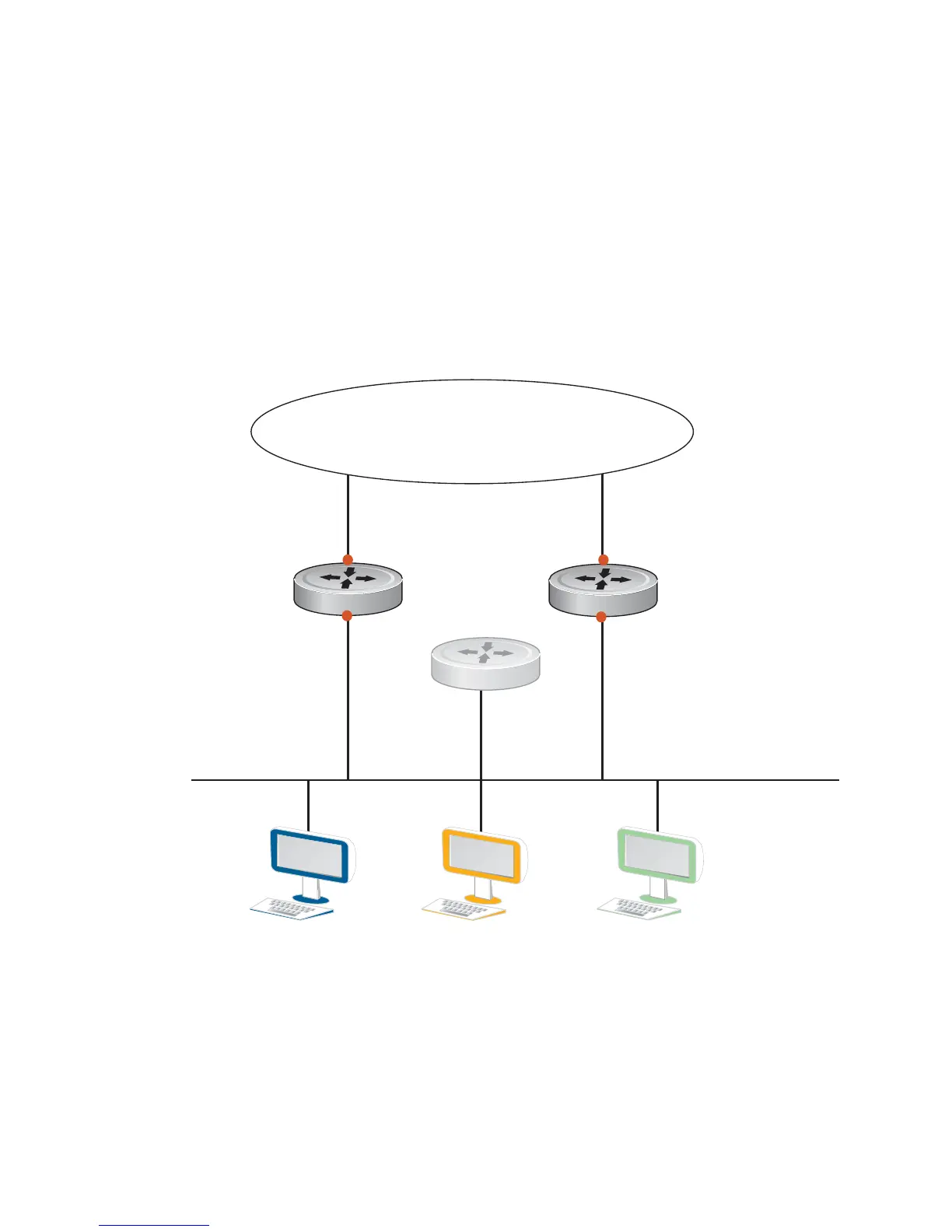
In Figure 55-1 below, Router A is configured as the MASTER router. It is configured with the IP address
of the virtual router and sends any packets addressed to the virtual router through interface GigabitEthernet
1/1 to the Internet. As the BACKUP router, Router B is also configured with the IP address of the virtual
router. If for any reason Router A becomes unavailable, VRRP elects a new MASTER Router. Router B
assumes the duties of Router A and becomes the MASTER router. At that time, Router B responds to the
packets sent to the virtual IP address.
All workstations continue to use the IP address of the virtual router to address packets destined to the
Internet. Router B receives and forwards them on interface GigabitEthernet 10/1. Until Router A resumes
operation, VRRP allows Router B to provide uninterrupted service to the users on the LAN segment
accessing the Internet.
Figure 55-1. Basic VRRP Configuration
For more detailed information on VRRP, refer to RFC 2338, Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol.
10.10.10.4
10.10.10.5
10.10.10.6
10.10.10.0/24
LAN Segment
Interface gi 1/0
10.10.10.1
Virtual IP Address
10.10.10.3
Router A
Master Router
Virtual IP 10.10.10.3
Priority 255
Router B
Backup Router
Virtual IP 10.10.10.3
Priority 100
Interface gi 10/0
10.10.10.2
Interface gi 1/1
63.62.154.23
Interface gi 10/1
204.1.78.37
INTERNET
IP Addresses
Default Gateway
10.10.10.3 10.10.10.3 10.10.10.3
FN0001_lp
Virtual Router

 Loading...
Loading...











