Multiple-axis machining | The PLANE function: Tilting the working plane (option 8)
Comparison of the tilting orders:
Tilting order A-B-C:
1 Tilt about the non-tilted X axis of the workpiece coordinate
system
2 Tilt about the non-tilted Y axis of the workpiece coordinate
system
3 Tilt about the non-tilted Z axis of the workpiece coordinate
system
Tilting order C-B-A:
1 Tilt about the non-tilted Z axis of the workpiece coordinate
system
2 Tilt about the tilted Y axis
3 Tilt about the tilted X axis
Programming notes:
You must always define all three spatial angles SPA,
SPB and SPC, even if one or more have the value 0.
Depending on the machine, Cycle 19 requires you to
enter spatial angles or axis angles. If the configuration
(machine parameter setting) allows the input of
spatial angles, the angle definition is the same in Cycle
19 and in the PLANE SPATIAL function.
You can select the desired positioning behavior.
Further information: "Defining the positioning
behavior of the PLANE function", Page 450
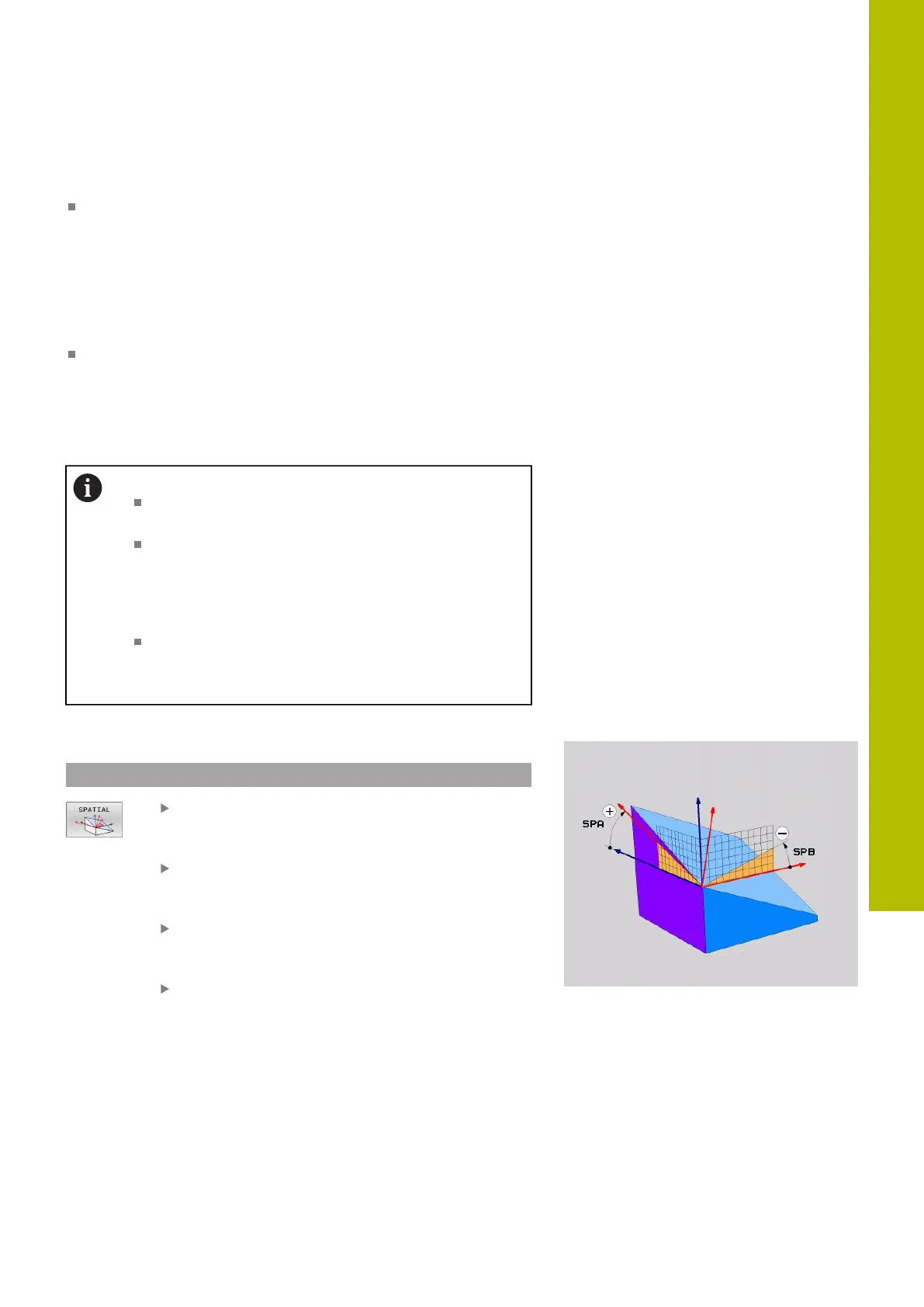
Input parameters
Example
5 PLANE SPATIAL SPA+27 SPB+0 SPC+45 .....
Spatial angle A?: Rotational angle SPA about the
(non-tilted) X axis. Input range from -359.9999 to
+359.9999
Spatial angle B?: Rotational angle SPB about the
(non-tilted) Y axis. Input range from -359.9999 to
+359.9999
Spatial angle C?: Rotational angle SPC about the
(non-tilted) Z axis. Input range from -359.9999 to
+359.9999
Continue with the positioning properties
Further information: "Defining the positioning
behavior of the PLANE function", Page 450
11
HEIDENHAIN | TNC620 | Klartext Programming User's Manual | 01/2022
437

 Loading...
Loading...