Advanced-control timers (TIM1) RM0401
306/771 RM0401 Rev 3
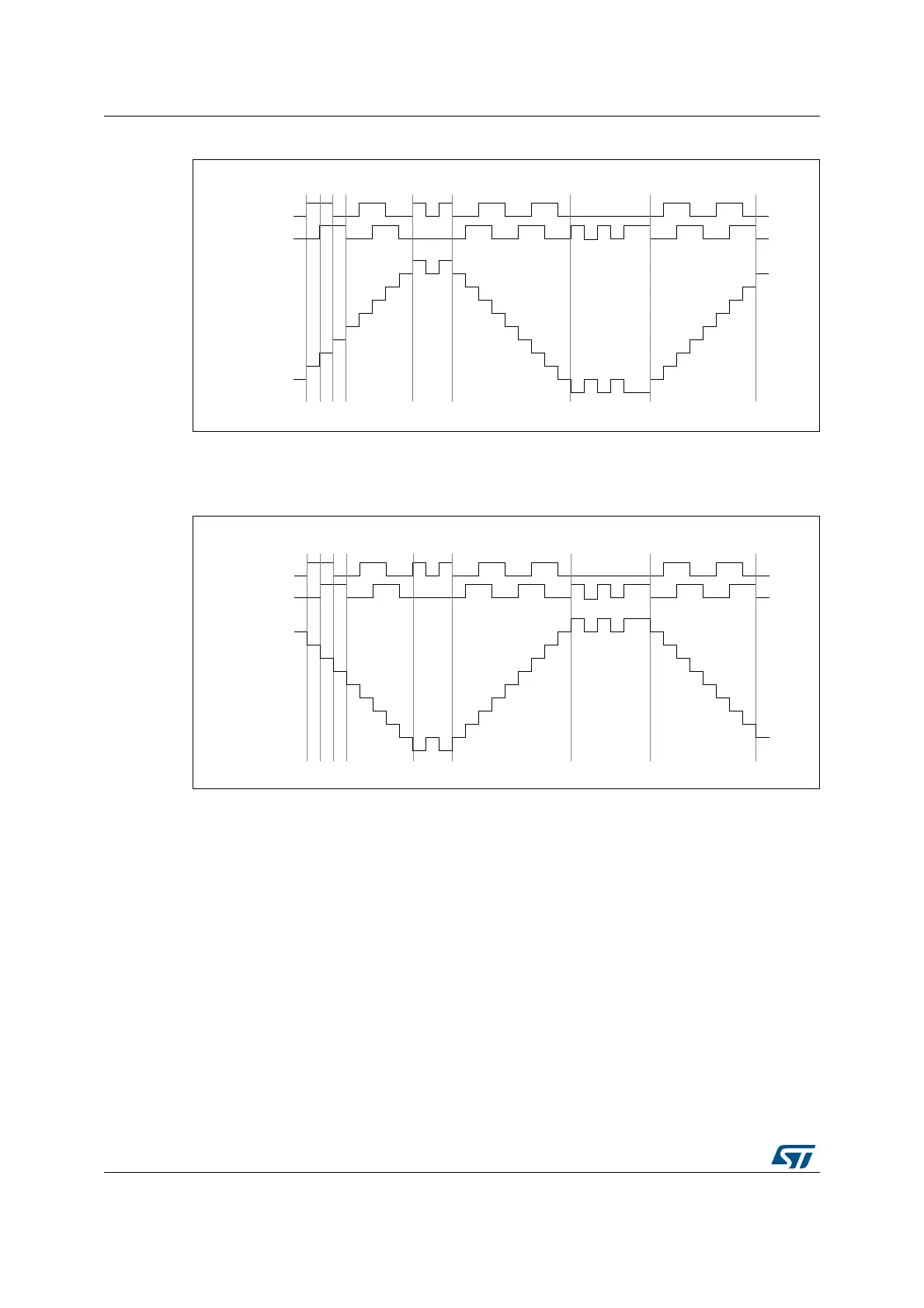
Figure 90. Example of counter operation in encoder interface mode.
Figure 91 gives an example of counter behavior when TI1FP1 polarity is inverted (same
configuration as above except CC1P=’1’).
Figure 91. Example of encoder interface mode with TI1FP1 polarity inverted.
The timer, when configured in Encoder Interface mode provides information on the sensor’s
current position. Dynamic information can be obtained (speed, acceleration, deceleration)
by measuring the period between two encoder events using a second timer configured in
capture mode. The output of the encoder which indicates the mechanical zero can be used
for this purpose. Depending on the time between two events, the counter can also be read
at regular times. This can be done by latching the counter value into a third input capture
register if available (then the capture signal must be periodic and can be generated by
another timer). when available, it is also possible to read its value through a DMA request
generated by a real-time clock.
7,
EDFNZDUGMLWWHU MLWWHU
XS GRZQ XS
7,
&RXQWHU
IRUZDUG IRUZDUG
069
7,
EDFNZDUGMLWWHU MLWWHU
XSGRZQ
7,
&RXQWHU
IRUZDUG IRUZDUG
069
GRZQ

 Loading...
Loading...