Debug support (DBG) RM0401
742/771 RM0401 Rev 3
26.8 SW debug port
26.8.1 SW protocol introduction
This synchronous serial protocol uses two pins:
• SWCLK: clock from host to target
• SWDIO: bidirectional
The protocol allows two banks of registers (DPACC registers and APACC registers) to be
read and written to.
Bits are transferred LSB-first on the wire.
For SWDIO bidirectional management, the line must be pulled-up on the board (100 KΩ
recommended by Arm
®
).
Each time the direction of SWDIO changes in the protocol, a turnaround time is inserted
where the line is not driven by the host nor the target. By default, this turnaround time is one
bit time, however this can be adjusted by configuring the SWCLK frequency.
26.8.2 SW protocol sequence
Each sequence consist of three phases:
1. Packet request (8 bits) transmitted by the host
2. Acknowledge response (3 bits) transmitted by the target
3. Data transfer phase (33 bits) transmitted by the host or the target
Refer to the Cortex
®
-M4 with FPU r0p1 TRM for a detailed description of DPACC and
APACC registers.
The packet request is always followed by the turnaround time (default 1 bit) where neither
the host nor target drive the line.
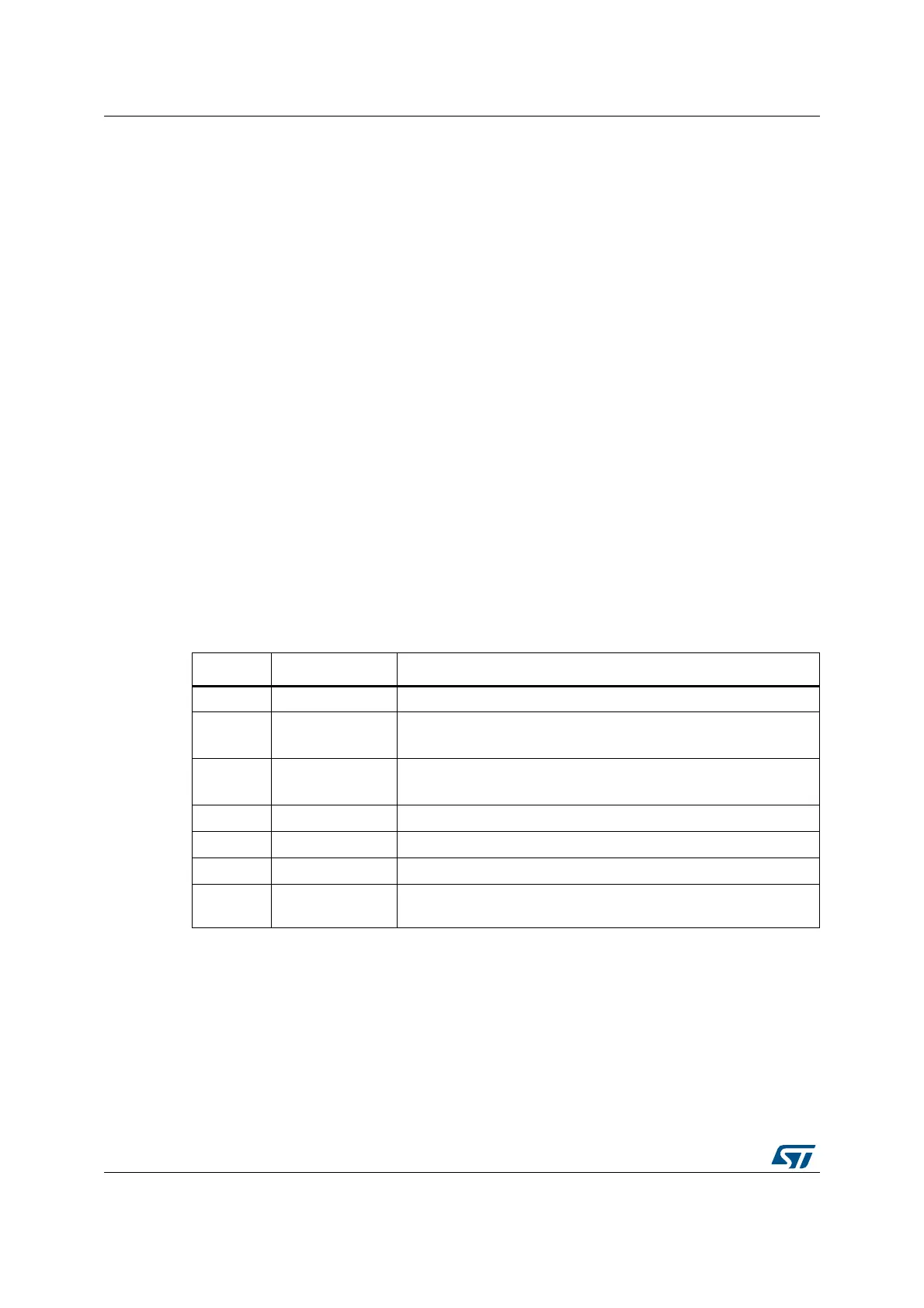
Table 133. Packet request (8-bits)
Bit Name Description
0 Start Must be “1”
1 APnDP
0: DP Access
1: AP Access
2RnW
0: Write Request
1: Read Request
4:3 A[3:2] Address field of the DP or AP registers (refer to Table 132)
5 Parity Single bit parity of preceding bits
6Stop 0
7Park
Not driven by the host. Must be read as “1” by the target because of
the pull-up

 Loading...
Loading...