Chapter 9 Inverter Functions
9-9-19
■ Instantaneous power failure non-stop function, mode selection,
"Voltage controlled deceleration-stop " ([b050] = 02, 03)
When an instantaneous power failure or undervoltage error occurs during operation and the P-N
voltage falls to or below [b051], the inverter automatically decelerates the motor while
maintaining the P-N voltage at the "Instantaneous power failure non-stop function, target
voltage level [b052]".
When the duration of the instantaneous power failure is short, the operation is able to continue
without shutting off the output. However, when an instantaneous power failure also causes an
undervoltage error, the output is immediately shut off, ending the operation of this function.
After the instantaneous power failure and operation resumption, the "Restart mode selection
after instantaneous power failure/undervoltage error [b001]" determines the subsequent
operation. For details, refer to "9.9.6 Restarting after Instantaneous Power Failure/
Undervoltage".
When [b050] is set to "Voltage controlled deceleration-stop (with recovery) (03)", if the power is
restored before the output is shut off, normal operation can be resumed. However, depending
on the setting of [b052], the inverter may decelerate the motor to stop. Details are as follows:
02
(Voltage controlled deceleration-
stop (without recovery))
[b052] > Vre (P-N voltage when the power
is received/restored)
Deceleration stop (constant DC voltage control)
(Example 1)
[b052] < Vre (P-N voltage when the power
is received/restored)
Deceleration stop (normal operation)
(Example 2)
03
(Voltage controlled deceleration-
stop (with recovery))
[b052] > Vre (P-N voltage when the power
is received/restored)
Deceleration stop (constant DC voltage control)
(Example 1)
[b052] < Vre (P-N voltage when the power
is received/restored)
Operation (normal operation)
(Example 2)
If the difference between "Instantaneous power failure non-stop function, start voltage level
[b051]" and "Instantaneous power failure non-stop function, target voltage level [b052]" is great,
when the value specified for "Constant DC voltage control P gain [b133]" is too large, it may
quickly accelerate immediately after this function starts, resulting in an overcurrent error.
Use "Constant DC bus voltage control P gain [b133]" and "Constant DC bus voltage control I
gain [b134]" to adjust this function. Setting a larger proportional gain ([b133]) or a shorter
integral gain ([b134]) speeds up the response but make it more likely to trip. Setting a smaller
proportional gain ([b133]) on the other hand, an undervoltage error may occur due to a voltage
drop immediately after this function starts.
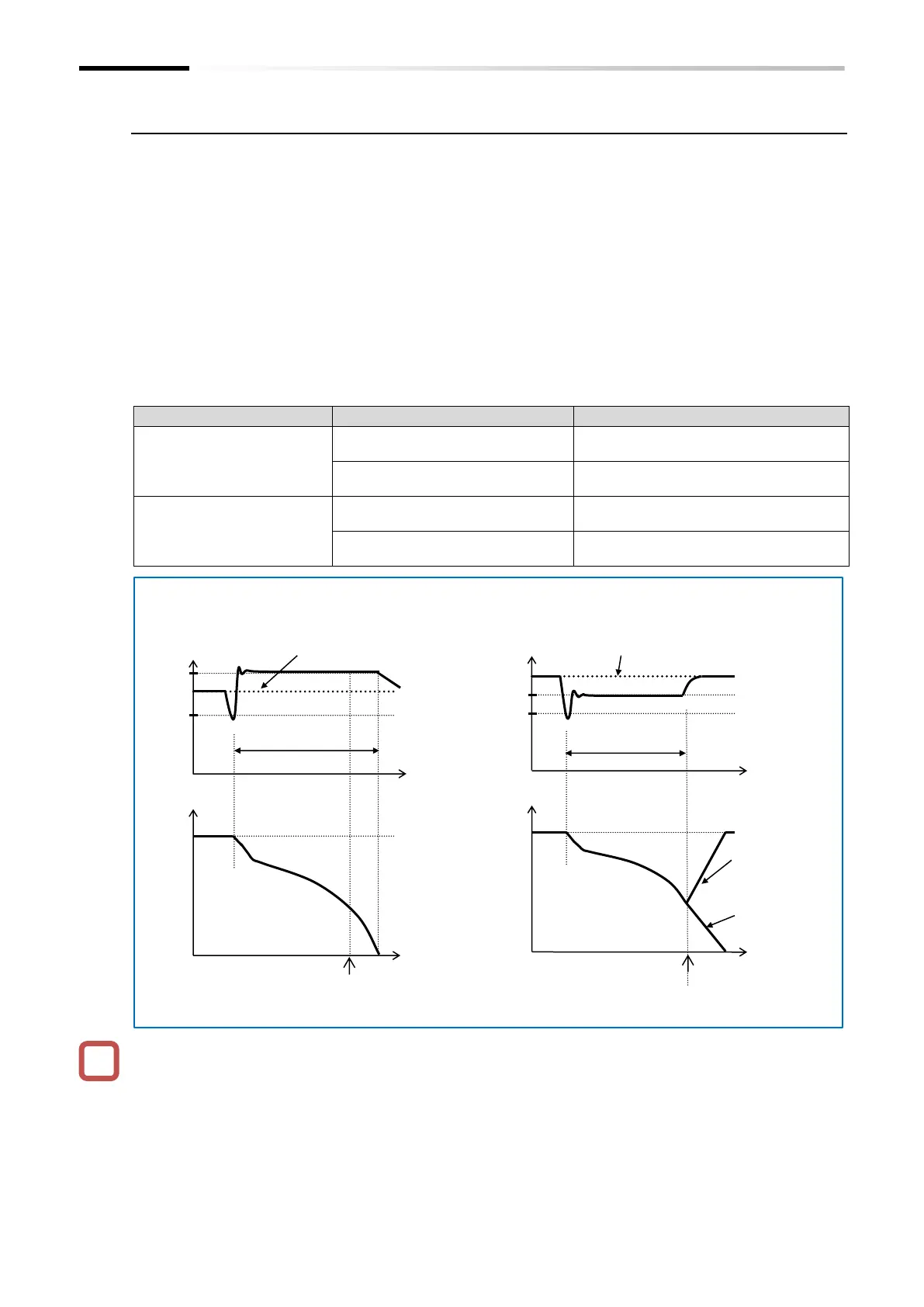
■ (Example 1) [b052] is greater than the P-N
voltage when the power is received/restored
Under constant DC
voltage control
[b050] =
"Operation
resumed (03)"
[b050] =
"Operation not
resumed (02)"
Vre (P-N voltage when the
power is received/restored)
Under constant DC
voltage control
[b050] = 02, 03
(deceleration stop)
Power is received/restored
Vre (P-N voltage when the
power is received/restored)
Power is received/restored
■ (Example 2) [b052] is smaller than the P-N
voltage when the power is received/restored
(Note) Depending on the proportional gain ([b133]) or integral gain ([b134]) setting of the constant DC voltage
control, the P-N voltage may be lower than that of [b052].

 Loading...
Loading...











