Chapter 15 Tips/FAQ/Troubleshooting
15-2-2
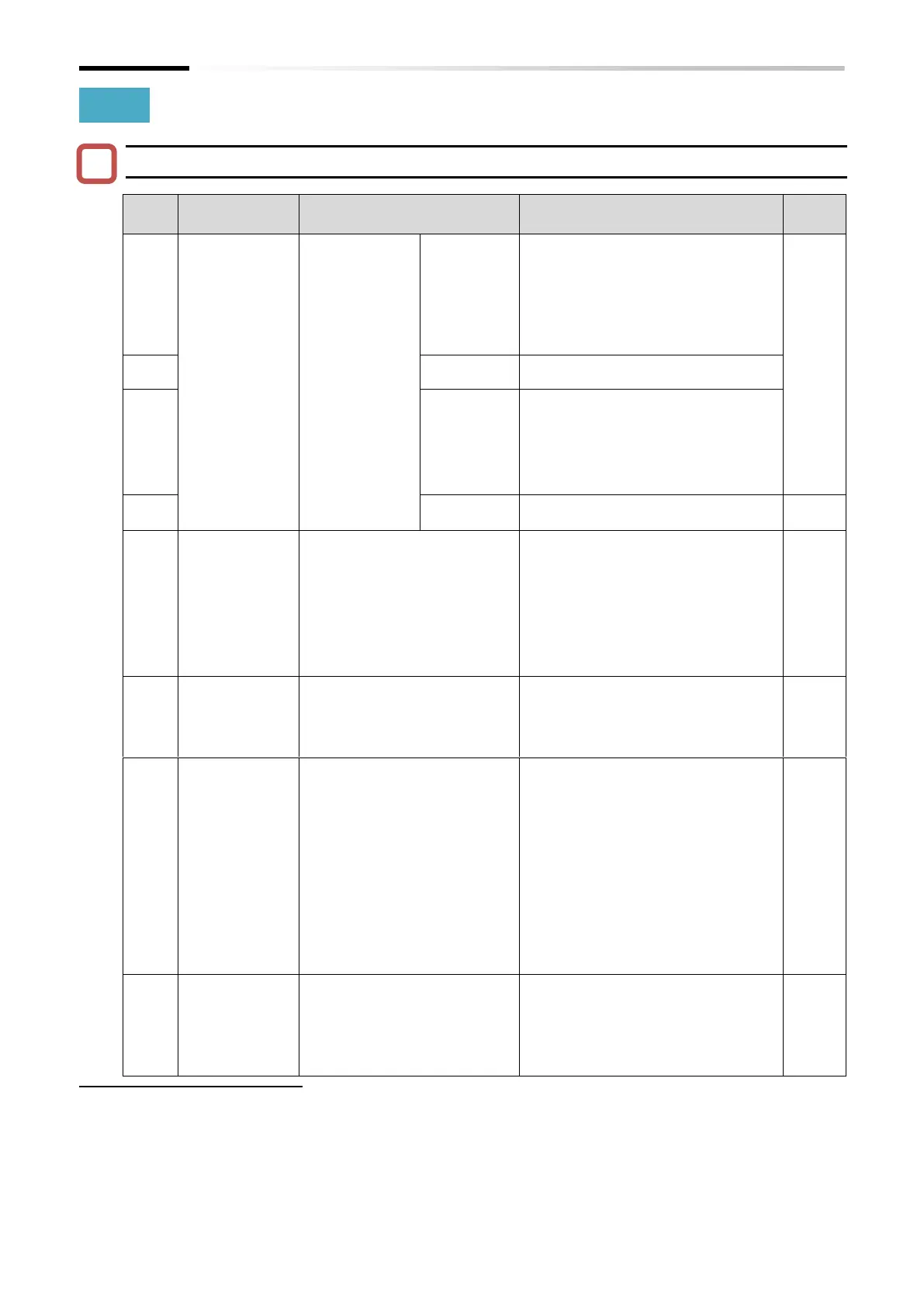
15.2.2 Error Code List and Countermeasures
List of error codes, descriptions, possible causes, and countermeasures
Possible causes and countermeasures
If the motor is
fixed or rapidly
accelerated or
decelerated, a
large current
flows through
the inverter,
which may
cause a failure.
For this reason,
the protection
circuit operates
and trips at
approximately
200% of the
inverter rated
output current.
Is there a steep load change?
→ Eliminate load fluctuation.
Is there an output short circuit?
→ Check the output line.
Is there a ground fault?
→ Check the output wires and
motor.
Rapid deceleration → Increase the
deceleration time.
Rapid acceleration
→ Increase the acceleration time.
Is motor locked?
→ Check the motor and wiring.
Is the torque boost high?
→ Decrease the boost value.
Is DC braking high?
→ Decrease the DC braking force.
The built-in electronic thermal
function monitors the output
current of the inverter and
when an overload is detected,
the inverter trips.
When "Electronic thermal
decrease function enable
[b910]" ≠ 00, it operates as
motor overload protection.
Is the acceleration torque
insufficient?
→ Increase the acceleration time.
Is the load too heavy?
→ Lower the load factor.
Is thermal level correct?
→ Set to the proper level.
Braking resistor
overload error
When the use ratio of inverter's
braking resistor operation
circuit (BRD) exceeds the use
ratio set in [b090], the inverter
trips.
Is it decelerating rapidly?
→ Increase the deceleration time.
Is the operation cycle short?
→ Increase the operating cycle.
Too high voltage between P
and N terminals results in a
failure. Therefore, if the voltage
between P and N terminals
exceeds approx. 400 VDC
(200 V class) or 800 VDC (400
V class) due to regenerative
energy from the motor or an
increase in the power supply
voltage, the inverter trips.
Is it decelerating rapidly?
→ Increase the deceleration time.
Is there a ground fault?
→ Check the output wires and
motor.
Is the motor rotated from the load
side?
→ Reduce the regeneration amount.
Is the power supply voltage rising?
→ Lower the power supply voltage,
suppress power fluctuations, or
insert an AC reactor into the
input.
When an error occurs in the
built-in memory due to
external noise or abnormal
temperature rise, etc., the
inverter trips. (In some cases, a
CPU error will occur.)
Is there a large noise source nearby?
→ Noise suppression.
Is the cooling efficiency lowered?
→ Check for clogging of the cooling
fins and clean it, and replace the
cooling fans.
*1. When it is not in the subtraction mode ([b910] = 00), the reset operation is not accepted until 10 seconds have
elapsed after a trip occurs.
In the subtraction mode ([b910] ≠ 00), resetting is possible immediately after a trip occurs, but the
accumulated overload value is not cleared. Therefore, if restarting immediately after reset, the
accumulated overload may immediately reach 100% and [E05] trip may occur again. In this case, wait
a while before restarting.
*2. When these errors occur, the reset operation is not accepted. Turn off the power once. If the same error occurs
the next time the power is turned on, there is a possibility of failure. Please contact your supplier or local Hitachi
sales office.

 Loading...
Loading...











