Operation Principles D2 Series Servo Drive User Manual
3-4 HIWIN MIKROSYSTEM CORP.
(2) Use PWM command
The drive converts the PWM signal to the current command to control the force or torque of motor
movement. It can set the command current correspond to “Full PWM”.
3.1.4 Stand-alone mode
There is one high-speed DSP on the inside of drive. Therefore, the drive can plan the motion profile by
itself. If the drive needs to do test alone or without any host controller (e.g. only the servo motor and
drive), the stand-alone mode can be selected to let drive be responsible for all control loops.
3.2 Encoder type
The encoder usually plays an important role in the servo motor control. It provides the information of drive
position or angle to realize the servo-loop control. There are two types of commonly used encoder: digital
type and analog type. D2-series drives only support the digital encoder presently, but not analog encoder.
(1) Digital type
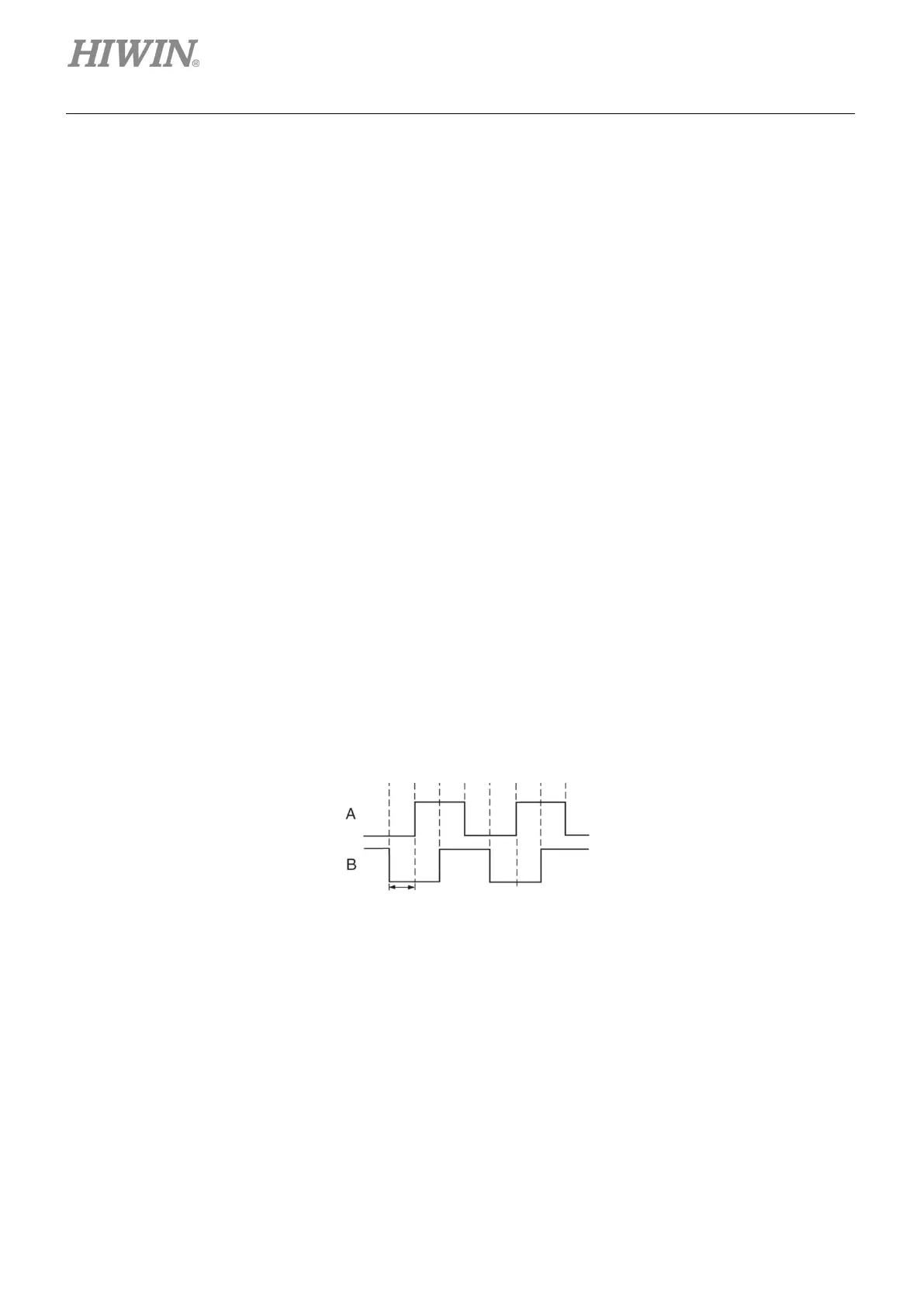
The digital or so-called incremental encoder normally outputs the differential signal of TTL RS422.
The main feature of this signal is two digital pulses with the 90°-phase difference. The definition of
resolution for this signal is given in figure 3.2.1.
Figure3.2.1
(2) Analog type
The analog encoder has two-phase signals: sin and cos. The hardware normally takes the
differential signal of 1 Vpp. The main feature of this signal is two sinusoidal signals with the
90°-phase difference. Its specification is normally represented by the grating period. For example,
the grating period of common linear analog scale is 40 um.
 Loading...
Loading...