Pediatrics Calculations
LOGIQ 7 Basic User Manual 13-5
Direction 2392206-100 Rev. 1
B-Mode Measurements (continued)
Hip Dysplasia
Measurement
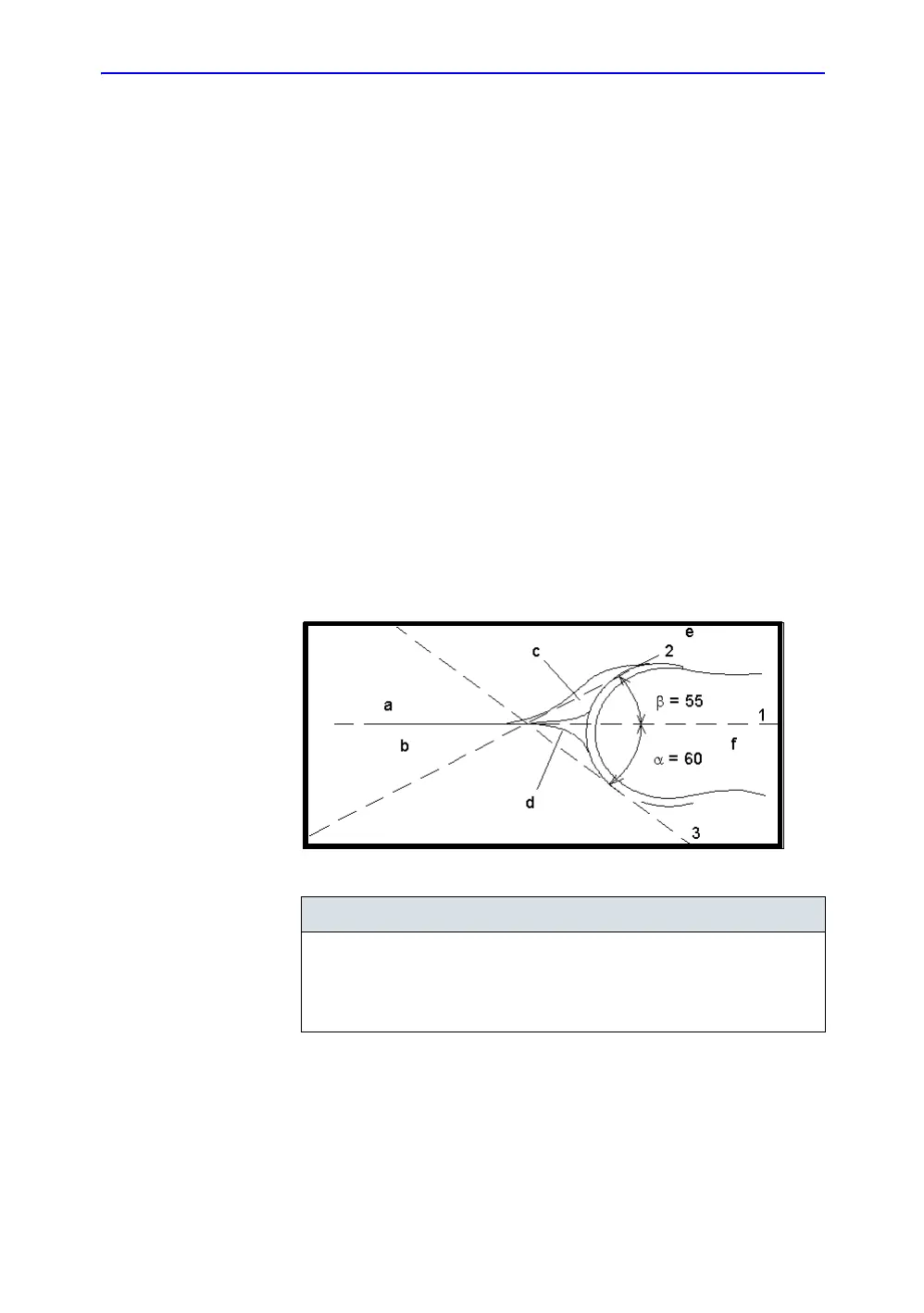
The HIP calculation assists in assessing the development of the
infant hip. In this calculation, three straight lines are
superimposed on the image and aligned with the anatomical
features. The two angles are computed, displayed, and can be
used by the physician in making a diagnosis.
The three lines are:
1
1. The baseline connects the osseous acetabulum convexity to
the point where the joint capsule and the perichondrium
unite with the iliac bone.
2. The inclination line connects the osseous convexity to
labrum acetabulare.
3. The Acetabulum roof line connects the lower edge of the
osilium to the osseous convexity.
The α (Alpha) angle is the supplement of the angle between 1
and 3. It characterizes the osseous convexity. The β (Beta)
angle is the angle between lines 1 and 2. It characterizes the
bone supplementing additional roofing by the cartilaginous
convexity.
Figure 13-2. Hip Dysplasia
1
Source: R GRAF, journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 4: 735-
740(1984)
Anatomical Landmarks
a. Ilium d. Bony Roof
b. Iliac Bone e. Cartilaginous acetabular roof
c. Labrum f. Femoral Head

 Loading...
Loading...