S12 Clock, Reset and Power Management Unit (S12CPMU)
MC9S12G Family Reference Manual Rev.1.27
390 NXP Semiconductors
The phase detector inside the PLL compares the feedback clock (FBCLK = VCOCLK/(SYNDIV+1)) with
the reference clock (REFCLK = (IRC1M or OSCCLK)/(REFDIV+1)). Correction pulses are generated
based on the phase difference between the two signals. The loop filter alters the DC voltage on the internal
filter capacitor, based on the width and direction of the correction pulse, which leads to a higher or lower
VCO frequency.
The user must select the range of the REFCLK frequency (REFFRQ[1:0] bits) and the range of the
VCOCLK frequency (VCOFRQ[1:0] bits) to ensure that the correct PLL loop bandwidth is set.
The lock detector compares the frequencies of the FBCLK and the REFCLK. Therefore the speed of the
lock detector is directly proportional to the reference clock frequency. The circuit determines the lock
condition based on this comparison.
If PLL LOCK interrupt requests are enabled, the software can wait for an interrupt request and for instance
check the LOCK bit. If interrupt requests are disabled, software can poll the LOCK bit continuously
(during PLL start-up) or at periodic intervals. In either case, only when the LOCK bit is set, the VCOCLK
will have stabilized to the programmed frequency.
• The LOCK bit is a read-only indicator of the locked state of the PLL.
• The LOCK bit is set when the VCO frequency is within the tolerance
Lock
and is cleared when
the VCO frequency is out of the tolerance
unl
.
• Interrupt requests can occur if enabled (LOCKIE = 1) when the lock condition changes, toggling
the LOCK bit.
10.4.2 Startup from Reset
An example of startup of clock system from Reset is given in Figure 10-30.
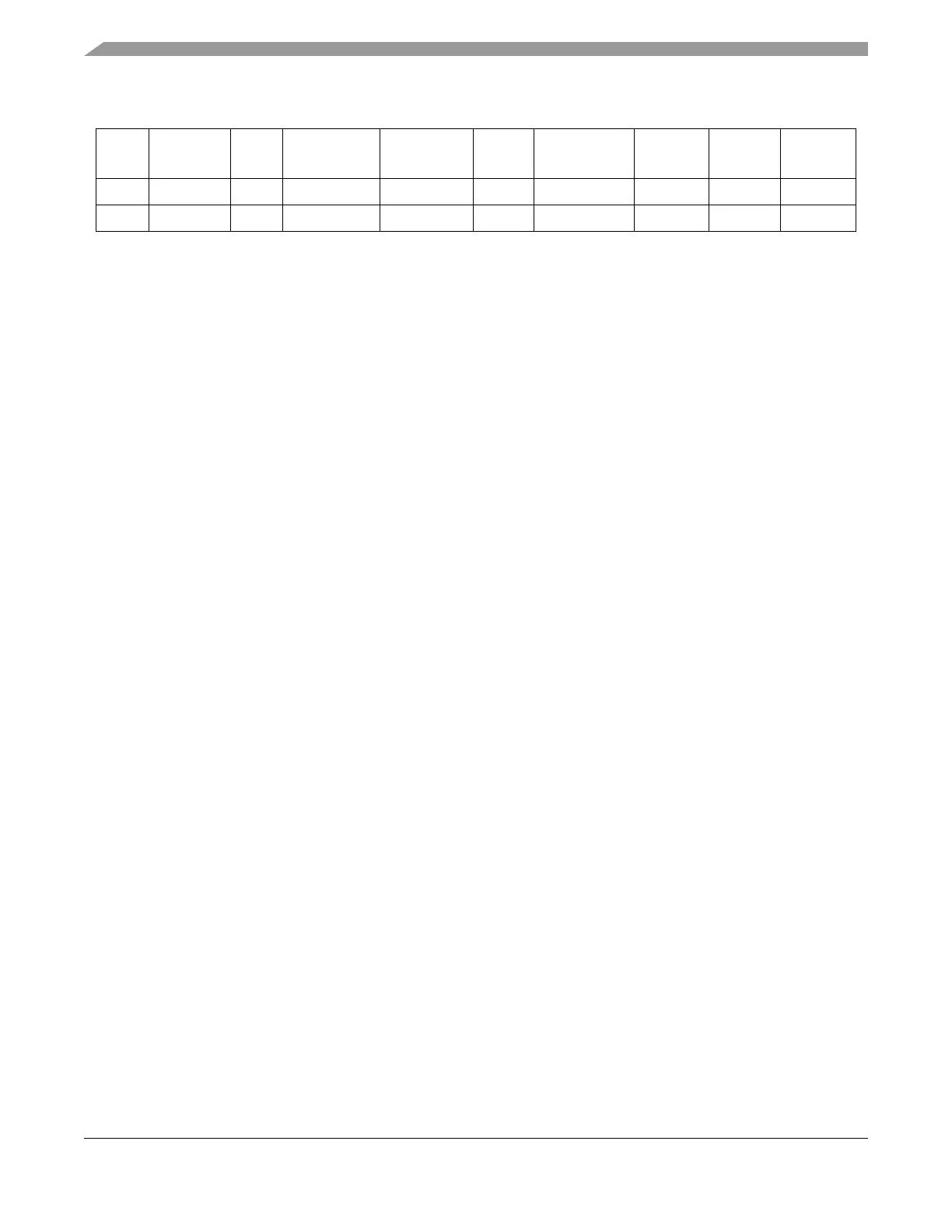
off $00 1MHz 00 $18 50MHz 01 $00 50MHz 25MHz
4MHz $00 4MHz 01 $05 48MHz 00 $00 48MHz 24MHz
Table 10-25. Examples of PLL Divider Settings
f
osc
REFDIV[3:
0]
f
REF
REFFRQ[1:0] SYNDIV[5:0] f
VCO
VCOFRQ[1:0]
POSTDIV
[4:0]
f
PLL
f
bus
 Loading...
Loading...