RL78/G15 CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
R01UH0959EJ0110 Rev.1.10 Page 86 of 765
Mar 7, 2023
3.5.6 Register indirect addressing
[Function]
Register indirect addressing specifies the target addresses using the contents of the register pair specified with the
instruction word as an operand address.
[Operand format]
Identifier Description
—
[DE], [HL]
(only the space from F0000H to FFFFFH is specifiable)
—
ES:[DE], ES:[HL]
(higher 4-bit addresses are specified by the ES register)
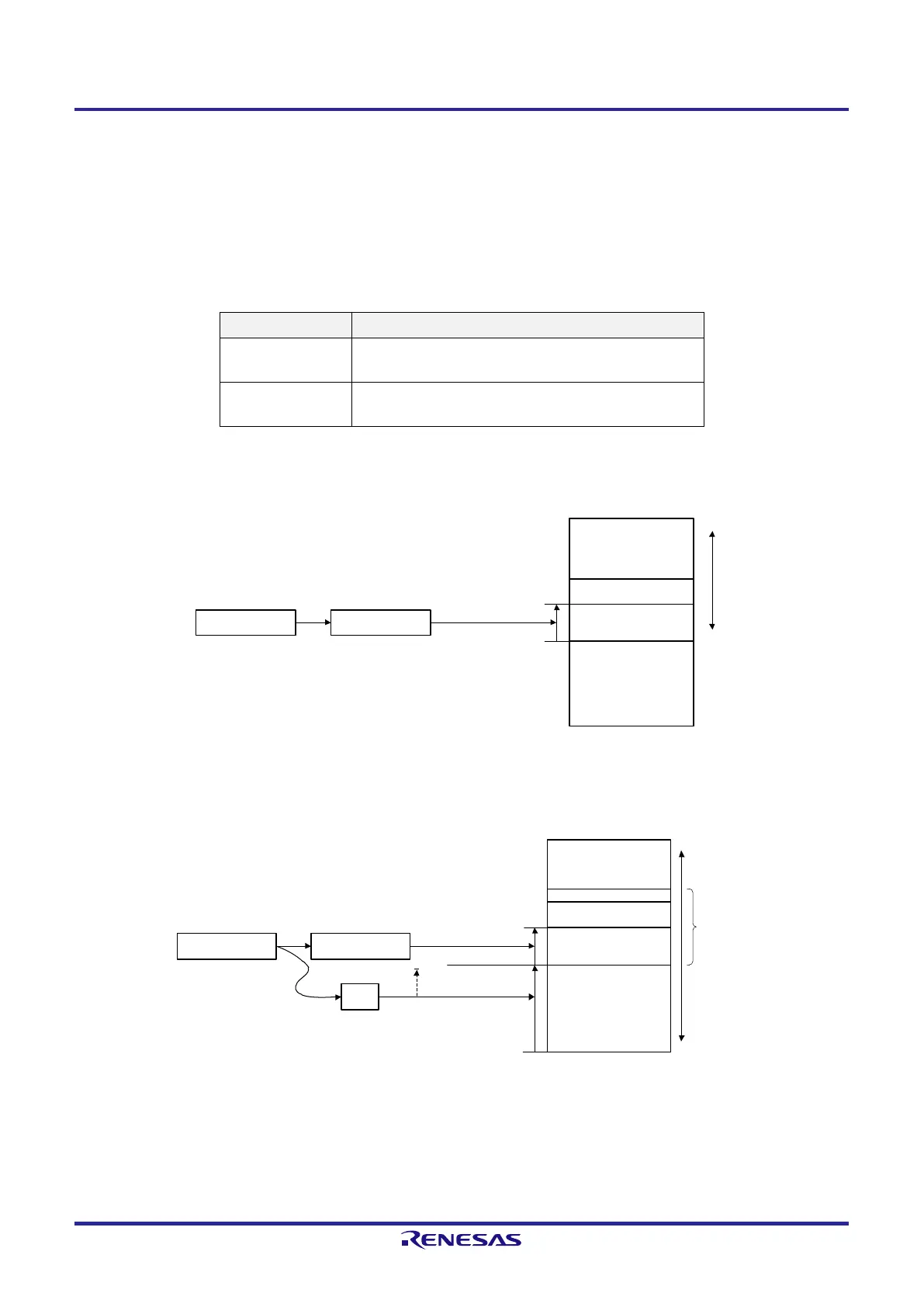
Figure 3-21. Example of [DE], [HL]
Specifies the address
in memory
Instruction code
OP-code rp (HL/DE)
Target memory
FFFFFH
Memory
F0000H
<1>
• Either pair of registers <1> specifies the target location as
an address in the 64-Kbyte area from F0000H to FFFFFH.
[DE],
<1>
[HL]
<1>
<1>
Figure 3-22. Example of ES:[DE], ES:[HL]
Target memory
FFFFFH
Memory
00000H
• The ES register <1> specifies a 64-Kbyte area within the
overall 1-Mbyte space as the four higher-order bits, X, of the
address range.
• Either pair of registers <2> and the ES register <1> specify
the target location in the area from X0000H to XFFFFH.
ES:
<1>
[DE],
<2>
Area from
X0000H to
XFFFFH
ES
X0000H
Specifies a 64-Kbyte
area
ES:
<1>
[HL]
<2>
Specifies the address in
memory
Instruction code
OP-code
rp (HL/DE)
<2>
<2>
<1>
<1>

 Loading...
Loading...