8–78 Chapter 8: Configuration and Remote System Upgrades in Cyclone IV Devices
Remote System Upgrade
Cyclone IV Device Handbook, May 2013 Altera Corporation
Volume 1
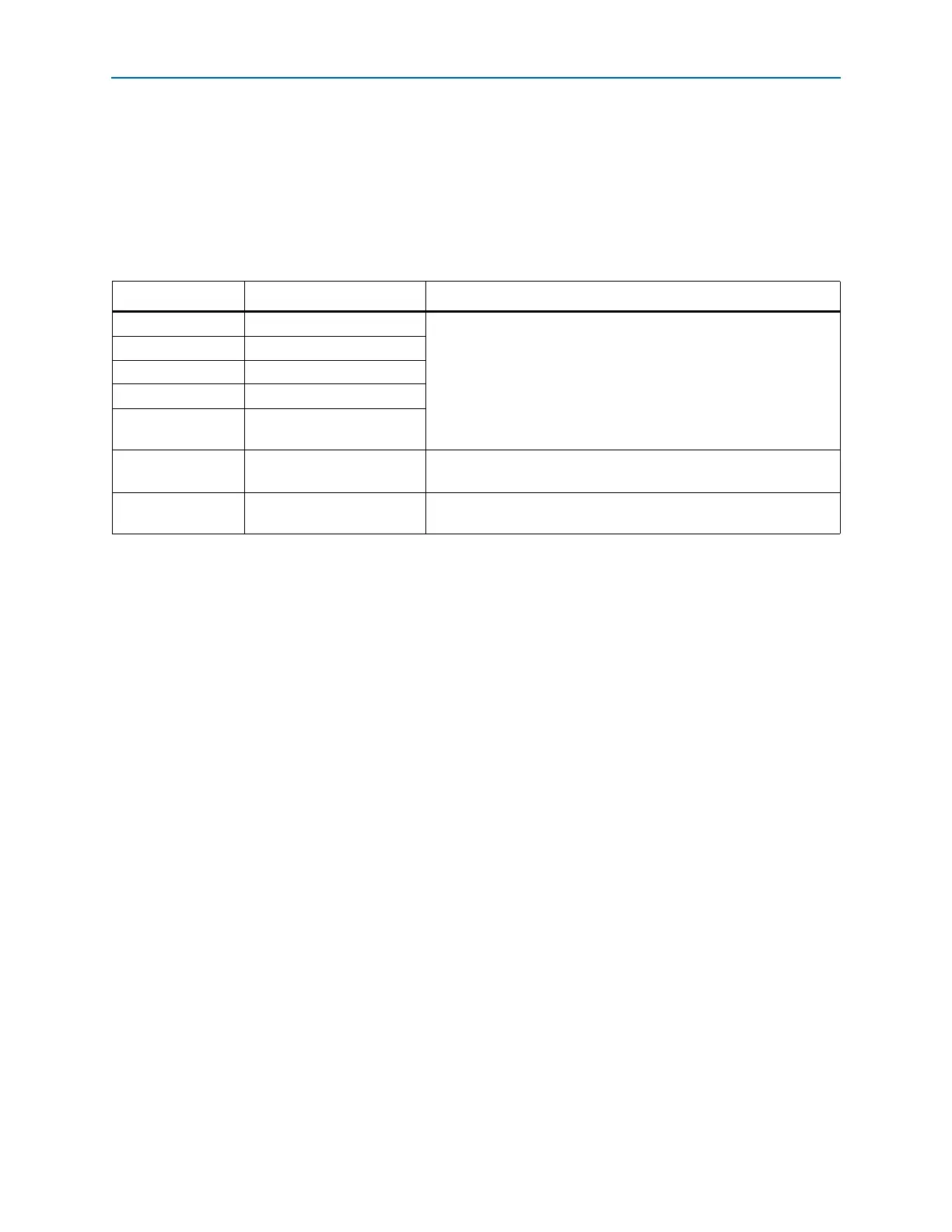
Tab le 8 –2 5 lists the contents of previous state register 1 and previous state register 2 in
the status register. The status register bit in Table 8–25 shows the bit positions in a
3-bit register. The previous state register 1 and previous state register 2 have the same
bit definitions. The previous state register 1 reflects the current application
configuration and the previous state register 2 reflects the previous application
configuration.
If a capture is inappropriately done while capturing a previous state before the system
has entered remote update application configuration for the first time, a value outputs
from the shift register to indicate that the capture is incorrectly called.
Remote System Upgrade State Machine
The remote system upgrade control and update registers have identical bit
definitions, but serve different roles (Table 8–22 on page 8–75). While both registers
can only be updated when the device is loaded with a factory configuration image,
the update register writes are controlled by the user logic, and the control register
writes are controlled by the remote system upgrade state machine.
In factory configurations, the user logic should send the option bits (
Cd_early
and
Osc_int
), the configuration address, and watchdog timer settings for the next
application configuration bit to the update register. When the logic array
configuration reset (
RU_nCONFIG
) goes high, the remote system upgrade state machine
updates the control register with the contents of the update register and starts system
reconfiguration from the new application page.
1 To ensure the successful reconfiguration between the pages, assert the
RU_nCONFIG
signal for a minimum of 250 ns. This is equivalent to strobing the
reconfig
input of
the ALTREMOTE_UPDATE megafunction high for a minimum of 250 ns.
If there is an error or reconfiguration trigger condition, the remote system upgrade
state machine directs the system to load a factory or application configuration (based
on mode and error condition) by setting the control register accordingly.
Tab le 8 –2 6 lists the contents of the control register after such an event occurs for all
possible error or trigger conditions.
Table 8–25. Remote System Upgrade Previous State Register 1 and Previous State Register 2 Contents in Status
Register
Status Register Bit Definition Description
30 nCONFIG
source
One-hot, active-high field that describes the reconfiguration source
that caused the Cyclone IV device to leave the previous application
configuration. If there is a tie, the higher bit order indicates
precedence. For example, if
nCONFIG
and remote system upgrade
nCONFIG
reach the reconfiguration state machine at the same time,
the
nCONFIG
precedes the remote system upgrade
nCONFIG
.
29
CRC error source
28 nSTATUS
source
27
User watchdog timer source
26
Remote system upgrade
nCONFIG
source
25:24
Master state machine
current state
The state of the master state machine during reconfiguration causes
the Cyclone IV device to leave the previous application configuration.
23:0
Boot address
The address used by the configuration scheme to load the previous
application configuration.
 Loading...
Loading...