Chapter 1: Cyclone IV Transceivers Architecture 1–9
Transmitter Channel Datapath
February 2015 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV Device Handbook,
Volume 2
■ Bit reversal—reverses the transmit bit order from LSB-to-MSB (default) to
MSB-to-LSB at the input to the serializer. For example, input data to serializer
D[7..0]
is rewired to
D[0..7]
for 8-bit data width, and
D[9..0]
is rewired to
D[0..9]
for 10-bit data width. Figure 1–10 shows the transmitter bit reversal
feature.
■ Input bit-flip—reverses the bit order at a byte level at the input of the transmitter
phase compensation FIFO. For example, if the 16-bit parallel transmitter data at
the
tx_datain
port is '10111100 10101101' (16'hBCAD), selecting this option
reverses the input data to the transmitter phase compensation FIFO to '00111101
10110101' (16'h3DB5).
■ Bit-slip control—delays the data transmission by a number of specified bits to the
serializer with the
tx_bitslipboundaryselect
port. For usage details, refer to the
“Transmit Bit-Slip Control” on page 1–76.
Serializer
The serializer converts the low-speed parallel 8-bit or 10-bit data from the transmitter
PCS to high-speed serial data for the transmitter output buffer. The serializer operates
with a high-speed clock at half of the serial data rate. The serializer transmission
sequence is LSB to MSB.
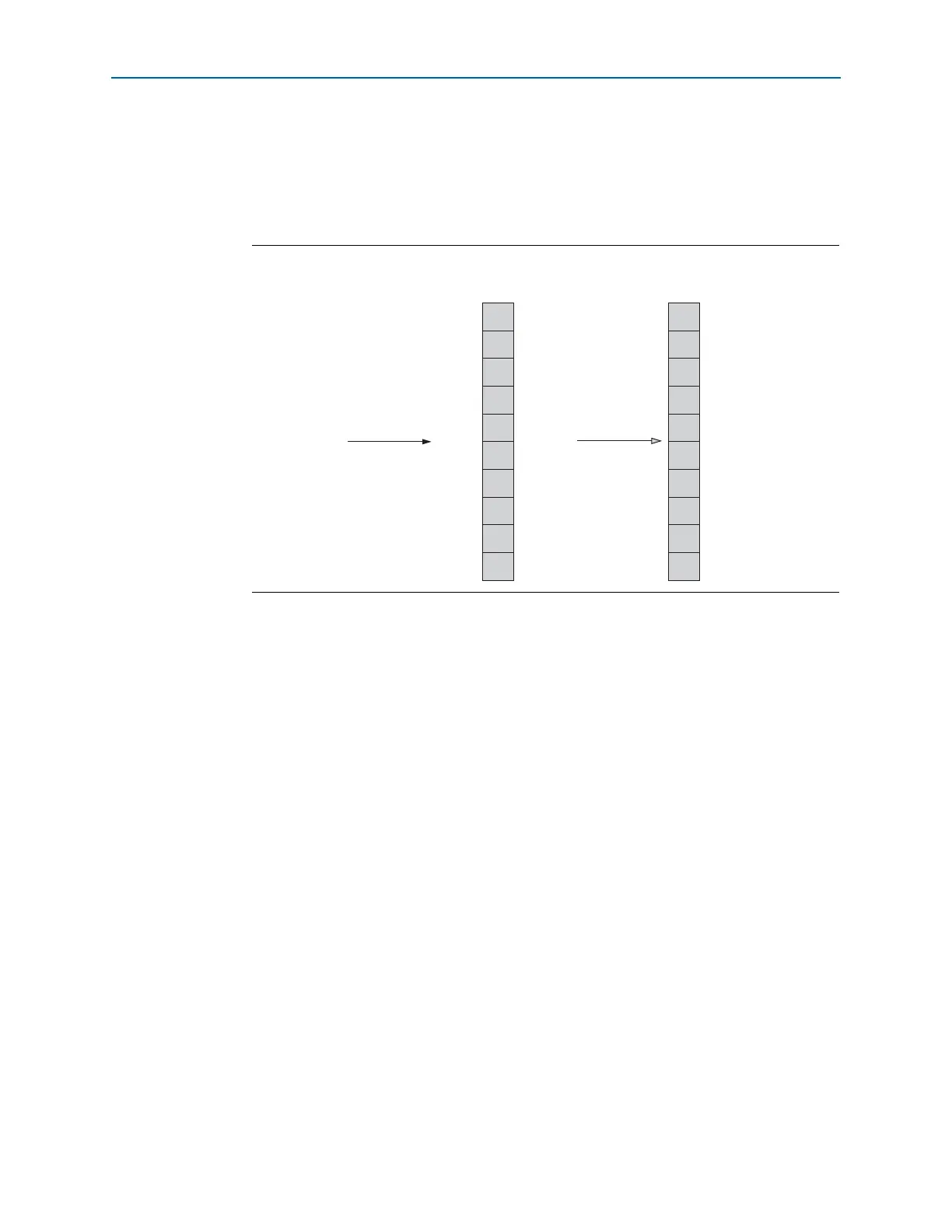
Figure 1–10. Transmitter Bit Reversal Operation in Basic Single-Width Mode
Output from transmitter PCS
Converted data output to the
transmitter serializer
TX bit reversal option enabled in
the ALTGX MegaWizard
D[9]
D[8]
D[7]
D[6]
D[5]
D[4]
D[3]
D[2]
D[1]
D[0]
D[0]
D[1]
D[2]
D[3]
D[4]
D[5]
D[6]
D[7]
D[8]
D[9]
 Loading...
Loading...