Chapter 1: Cyclone IV Transceivers Architecture 1–31
Transceiver Clocking Architecture
February 2015 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV Device Handbook,
Volume 2
1 In any configuration, a receiver channel cannot source CDR clocks from other PLLs
beyond the two multipurpose PLLs directly adjacent to transceiver block where the
channel resides.
The Cyclone IV GX transceivers support non-bonded (×1) and bonded (×2 and ×4)
channel configurations. The two configurations differ in regards to clocking and
phase compensation FIFO control. Bonded configuration provides a relatively lower
channel-to-channel skew between the bonded channels than in non-bonded
configuration. Table 1–8 lists the supported conditions in non-bonded and bonded
channel configurations.
Non-Bonded Channel Configuration
In non-bonded channel configuration, the high- and low-speed clocks for each
channel are sourced independently. The phase compensation FIFOs in each channel
has its own pointers and control logic. When implementing multi-channel serial
interface in non-bonded channel configuration, the clock skew and unequal latency
results in larger channel-to-channel skew.
1 Altera recommends using bonded channel configuration (×2 or ×4) when
implementing multi-channel serial interface for a lower channel-to-channel skew.
In a transceiver block, the high- and low-speed clocks for each channel are distributed
primarily from one of the two multipurpose PLLs directly adjacent to the block.
Transceiver channels for devices in F484 and larger packages support additional
clocking flexibility. In these packages, some channels support high-speed and low-
speed clock distribution from PLLs beyond the two multipurpose PLLs directly
adjacent to the block.
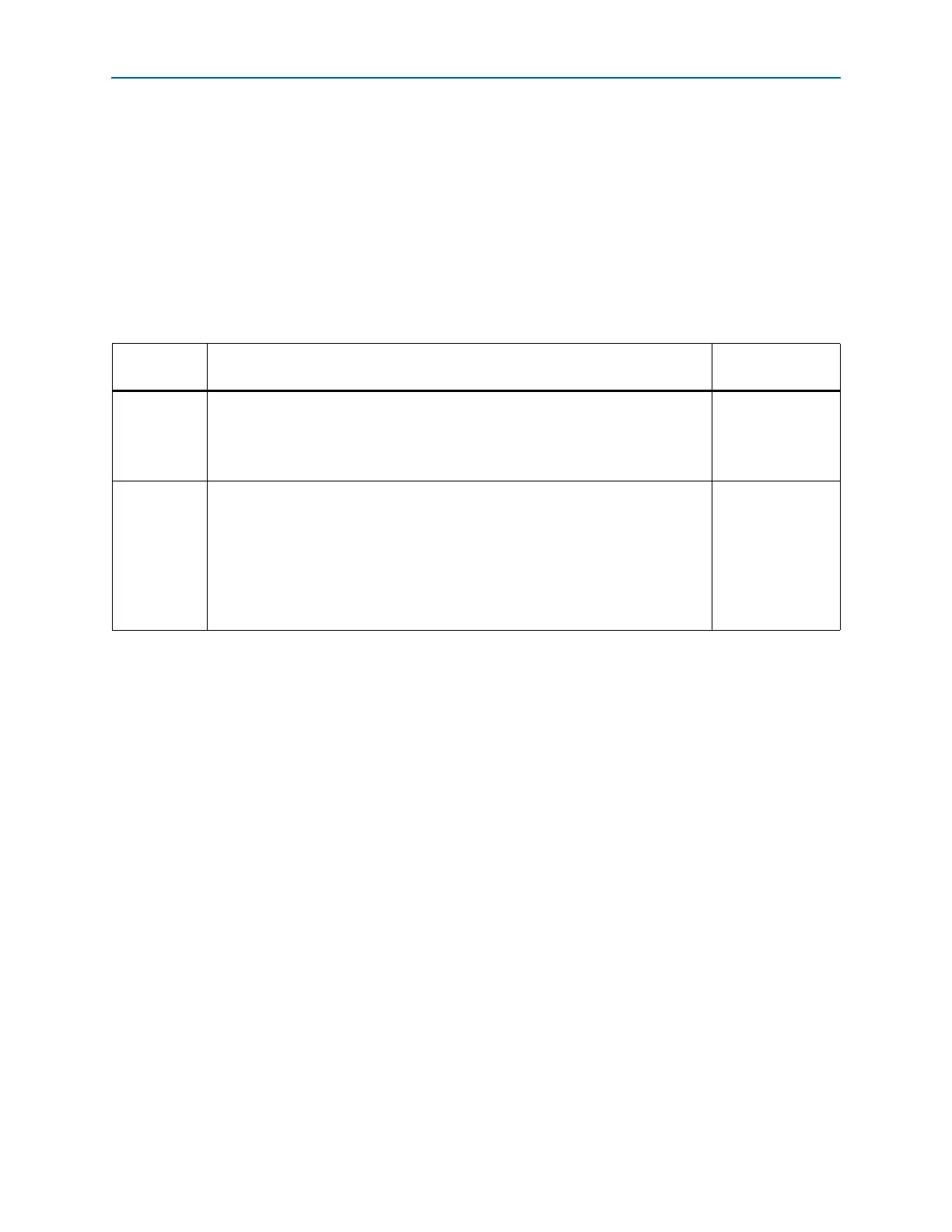
Table 1–8. Supported Conditions in Non-Bonded and Bonded Channel Configurations
Channel
Configuration
Description
Supported Channel
Operation Mode
Non-bonded
(×1)
■ Low-speed clock in each channel is sourced independently
■ Phase compensation FIFO in each channel has its own pointers and control logic
■ Transmitter Only
■ Receiver Only
■ Transmitter and
Receiver
Bonded (×2
and ×4)
■ Low-speed clock in each bonded channel is sourced from a common bonded
clock path for lower channel-to-channel skew
■ Phase compensation FIFOs in bonded channels share common pointers and
control logic for equal latency through the FIFOs in all bonded channels
■ ×2 bonded configuration is supported with channel 0 and channel 1 in a
transceiver block
■ ×4 bonded configuration is supported with all four channels in a transceiver block
■ Transmitter Only
■ Transmitter and
Receiver
 Loading...
Loading...