32 KByte Flash Module (S12FTMRG32K1V1)
MC9S12G Family Reference Manual Rev.1.27
818 NXP Semiconductors
The FPROT register, described in Section 25.3.2.9, can be set to protect regions in the Flash memory from
accidental program or erase. Three separate memory regions, one growing upward from global address
0x3_8000 in the Flash memory (called the lower region), one growing downward from global address
0x3_FFFF in the Flash memory (called the higher region), and the remaining addresses in the Flash
memory, can be activated for protection. The Flash memory addresses covered by these protectable
regions are shown in the P-Flash memory map. The higher address region is mainly targeted to hold the
boot loader code since it covers the vector space. Default protection settings as well as security information
that allows the MCU to restrict access to the Flash module are stored in the Flash configuration field as
described in Table 25-4.
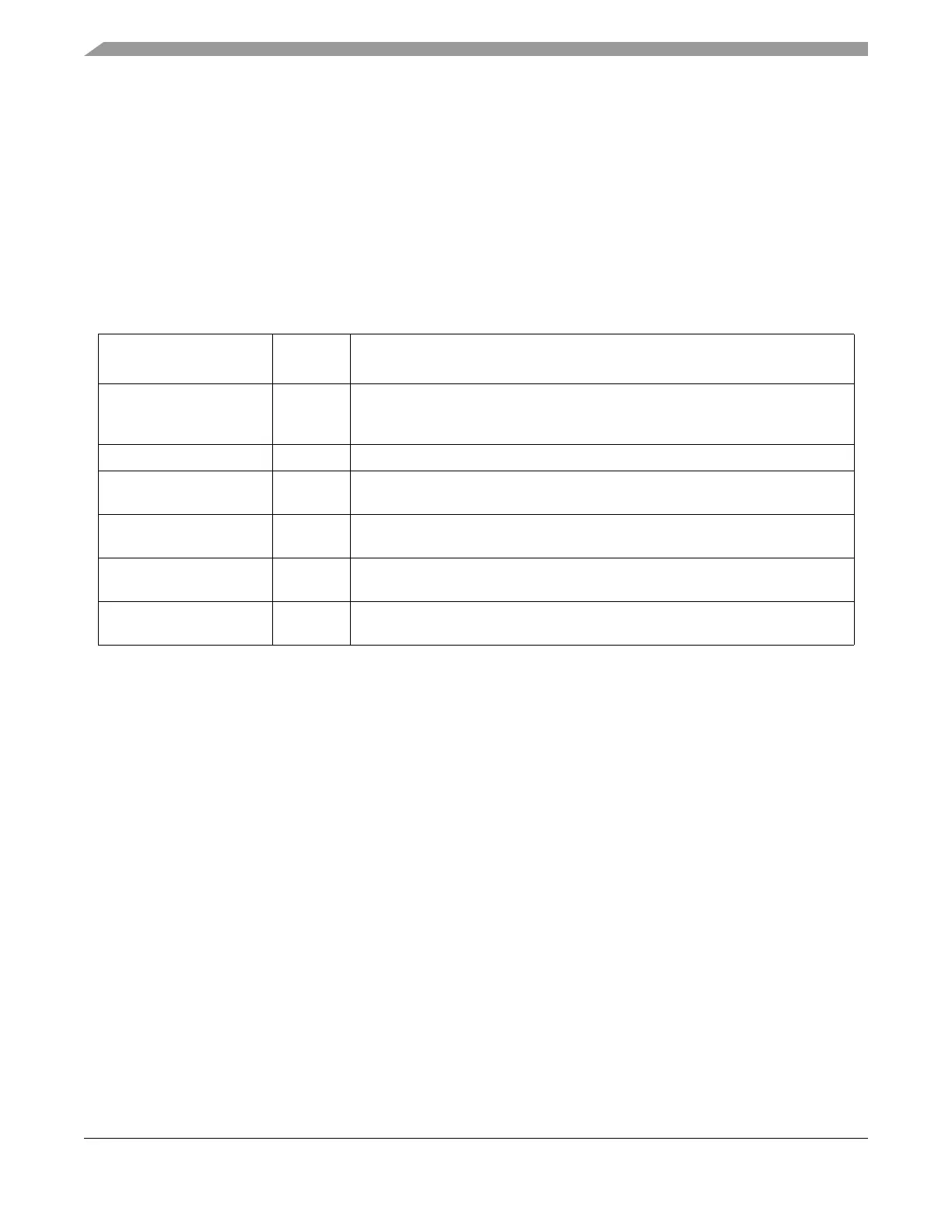
Table 25-4. Flash Configuration Field
Global Address
Size
(Bytes)
Description
0x3_FF00-0x3_FF07 8
Backdoor Comparison Key
Refer to Section 25.4.6.11, “Verify Backdoor Access Key Command,” and
Section 25.5.1, “Unsecuring the MCU using Backdoor Key Access”
0x3_FF08-0x3_FF0B
1
1
0x3FF08-0x3_FF0F form a Flash phrase and must be programmed in a single command write sequence. Each byte in
the 0x3_FF08 - 0x3_FF0B reserved field should be programmed to 0xFF.
4 Reserved
0x3_FF0C
1
1
P-Flash Protection byte
.
Refer to Section 25.3.2.9, “P-Flash Protection Register (FPROT)”
0x3_FF0D
1
1
EEPROM Protection byte
.
Refer to Section 25.3.2.10, “EEPROM Protection Register (EEPROT)”
0x3_FF0E
1
1
Flash Nonvolatile byte
Refer to Section 25.3.2.16, “Flash Option Register (FOPT)”
0x3_FF0F
1
1
Flash Security byte
Refer to Section 25.3.2.2, “Flash Security Register (FSEC)”
 Loading...
Loading...