The Polymer Sample Counter decrements only for wells that contain sample, but the
P
olymer Injection Counter decrements for each injection, regardless of whether all
wells contain sample. The sample limit and the corresponding injection limit may not
coincide. The rst limit that is reached depends on whether you perform partial or full
injections.
Example: Instrument c
onfiguration: 24-capillary, 960 sample polymer pouch
Partial injection
example (not all
wells contain
sample)
1 injection with 24 samples +
49 injections with 1 sample =
73 samples, 50 injections
The 50 injection count limit is
reached before the 960 sample
count limit.
Full injection
example (all wells
contain sample)
40 injections with 24 samples =
960 samples, 40 injections
The 960 sample count limit is
reached before the 50 injection
count limit.
1.
Inspect the instrument interior.
2.
Wipe any spills.
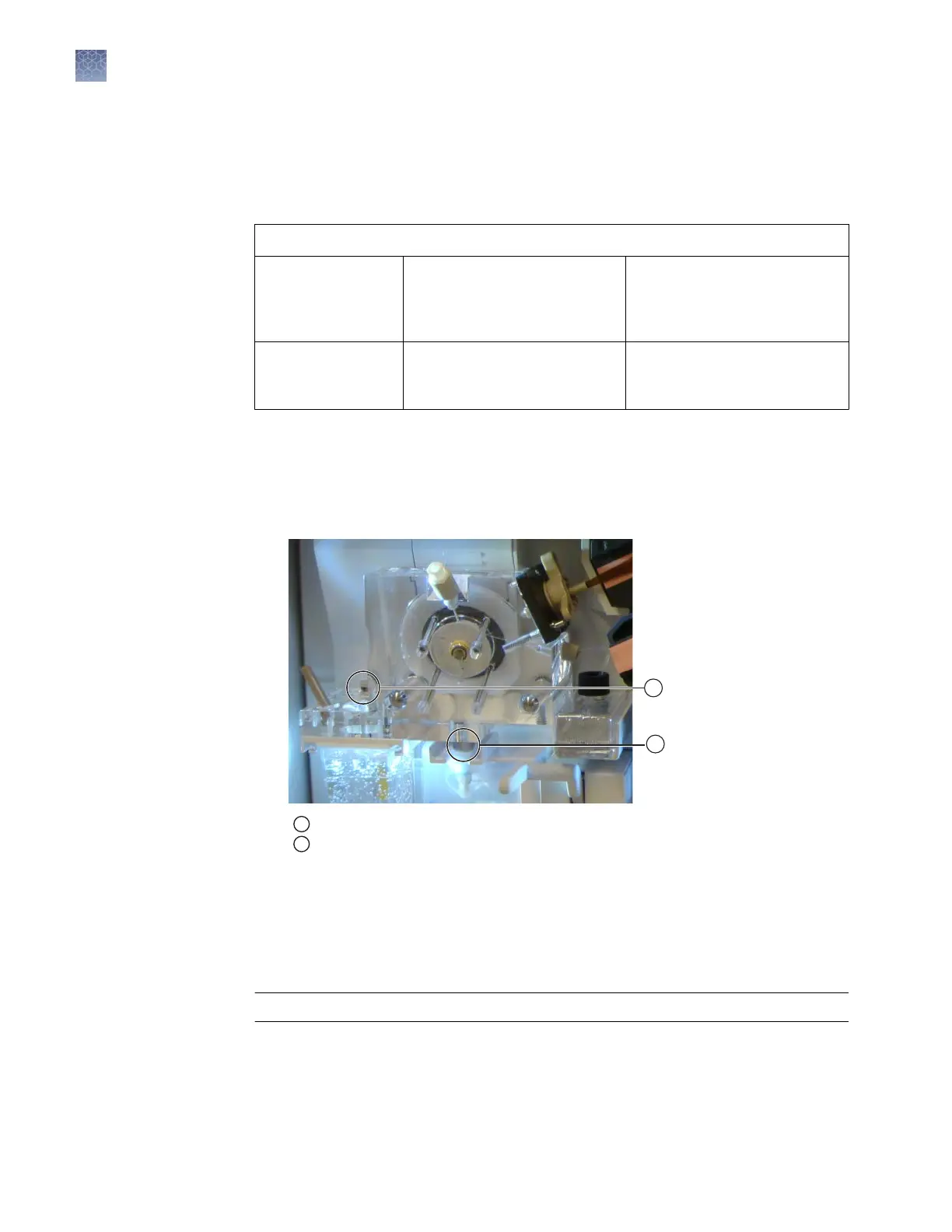
3.
Check for leaks around the buer-pin valve, check valve, and array locking lever.
1
Buffer-pin valve
2
CV (check valve) fitting
4.
Remov
e dried residue and ensure that the array locking lever is pushed securely
in place.
Check the ll levels on buers. Verify that the buer level is at the top of the ll line
and check that the seal is intact. The meniscus must line up at or above the ll line.
Ensure that the septa on the CBC are properly seated.
IMPORTANT! Replace the buer if the buer lev
el is too low.
How the polymer
sample and
injection counters
calculate usage
Check for leaks
and spills
Check buffer fill
l
evels
Chapter 2 St
art the system
Check system status in the Dashboard
2
34
3500/3500xL Genetic Analyzer User Guide—Data Collection Software v3.1

 Loading...
Loading...