Serial Peripheral Interface (S12SPIV5)
MC9S12G Family Reference Manual Rev.1.27
NXP Semiconductors 701
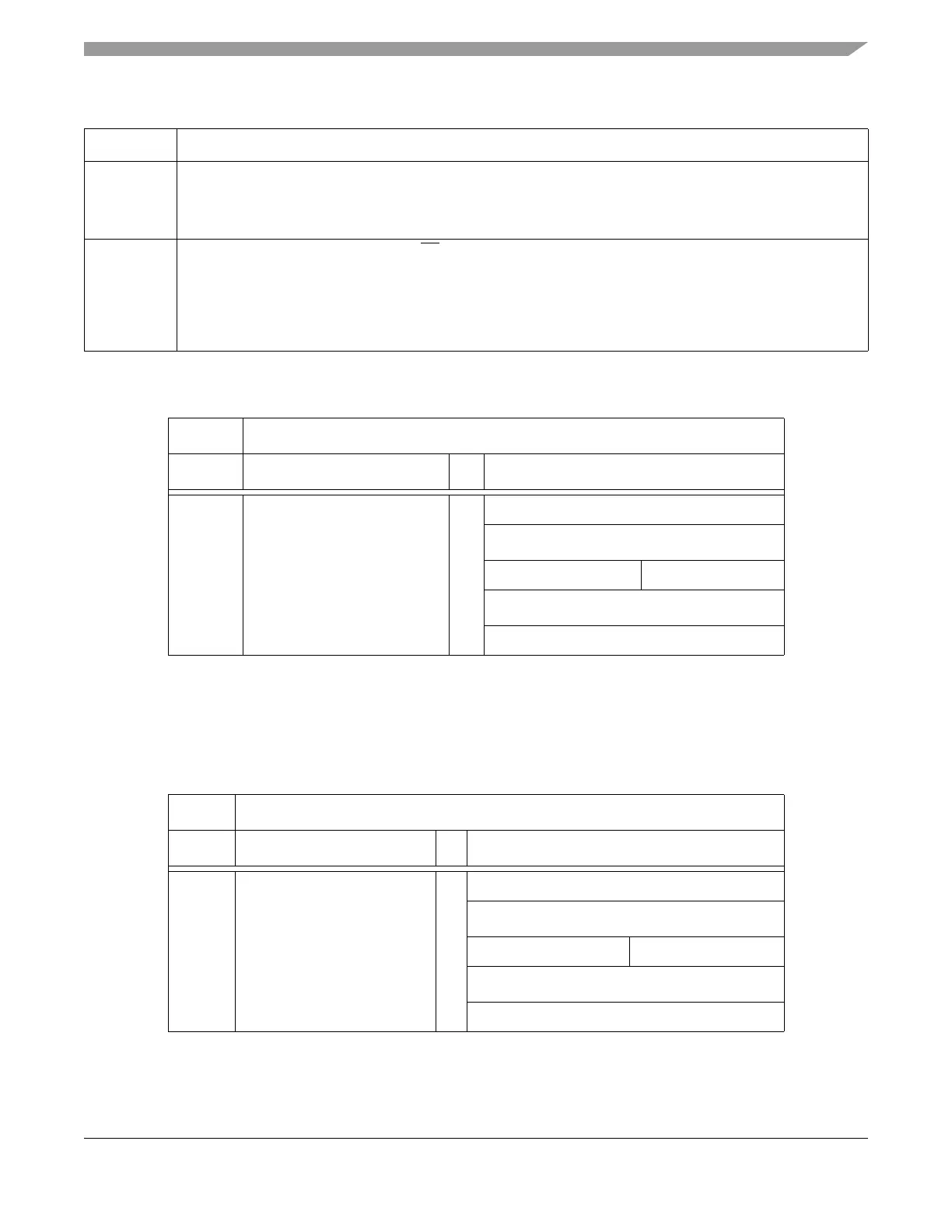
Table 21-8. SPIF Interrupt Flag Clearing Sequence
Table 21-9. SPTEF Interrupt Flag Clearing Sequence
5
SPTEF
SPI Transmit Empty Interrupt Flag — If set, this bit indicates that the transmit data register is empty. For
information about clearing this bit and placing data into the transmit data register, please refer to Table 21-9.
0 SPI data register not empty.
1 SPI data register empty.
4
MODF
Mode Fault Flag — This bit is set if the SS
input becomes low while the SPI is configured as a master and mode
fault detection is enabled, MODFEN bit of SPICR2 register is set. Refer to MODFEN bit description in
Section 21.3.2.2, “SPI Control Register 2 (SPICR2)”. The flag is cleared automatically by a read of the SPI status
register (with MODF set) followed by a write to the SPI control register 1.
0 Mode fault has not occurred.
1 Mode fault has occurred.
XFRW Bit SPIF Interrupt Flag Clearing Sequence
0 Read SPISR with SPIF == 1
then
Read SPIDRL
1 Read SPISR with SPIF == 1
then
Byte Read SPIDRL
1
1
Data in SPIDRH is lost in this case.
or
Byte Read SPIDRH
2
2
SPIDRH can be read repeatedly without any effect on SPIF. SPIF Flag is cleared only by the read
of SPIDRL after reading SPISR with SPIF == 1.
Byte Read SPIDRL
or
Word Read (SPIDRH:SPIDRL)
XFRW Bit SPTEF Interrupt Flag Clearing Sequence
0 Read SPISR with SPTEF == 1
then
Write to SPIDRL
1
1
Any write to SPIDRH or SPIDRL with SPTEF == 0 is effectively ignored.
1 Read SPISR with SPTEF == 1
then
Byte Write to SPIDRL
12
2
Data in SPIDRH is undefined in this case.
or
Byte Write to SPIDRH
13
Byte Write to SPIDRL
1
or
Word Write to (SPIDRH:SPIDRL)
1
Table 21-7. SPISR Field Descriptions
Field Description
 Loading...
Loading...