8.3.6.2Cubicinterpolation
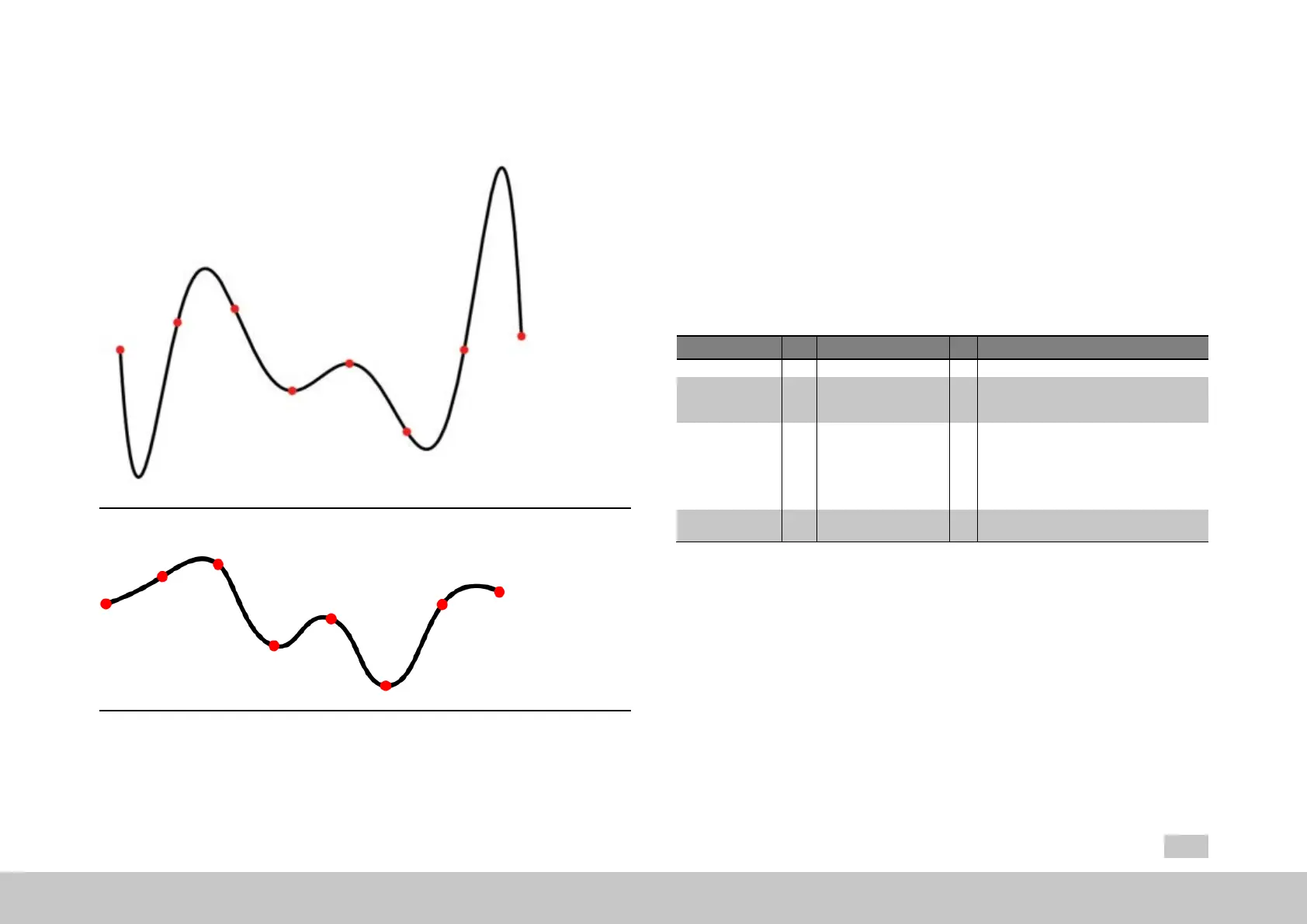
Fig. 8.35: Interpolation polynomial, 7th degree
Fig. 8.36: Cubic spline interpolation
MOOG
ID
No.: CB40859-001 Date: 02/2018
MSD Servo Drive- Device Help
186
8 Motion profile
As polynomials become more and more unstable as the order of magnitude
increases – that is to say, fluctuate widely between the interpolation points – in
practice polynomials of an order greater than 5 are rarely applied. Instead, large
data sets are interpolated in chunks.
In the case of linear interpolation, that would be a frequency polygon; in the case of
2nd or 3rd order polynomials the usual term used is spline interpolation. In the case
of sectionally defined interpolants, the question of consistency and differentiation at
the interpolation points is of major importance.
8.3.6.3MSDServoDriveinterpolationtypes
P No. Index Name / Setting Unit Description
370 0 CON_IP InterpolationtypeinIPmode
NoIp(0) Nointerpolation:
Thevalueswillbetransferred1:1tothesetpoint
processingin1mscycles.
Lin(1) Linearinterpolation:
Inthelinearinterpolationmethodthe
accelerationbetweentwopointsisgenerally
zero.Pre-controloftheaccelerationvaluesis
thusnotpossibleandspeedjumpsarealways
caused.
SplineExtFF(2) Interpolationwithexternalfeed-forwardcontrol:
MustbeexplicitlyrequestedfromMoog
Table 8.18: Interpolation types MSD Servo Drive

 Loading...
Loading...