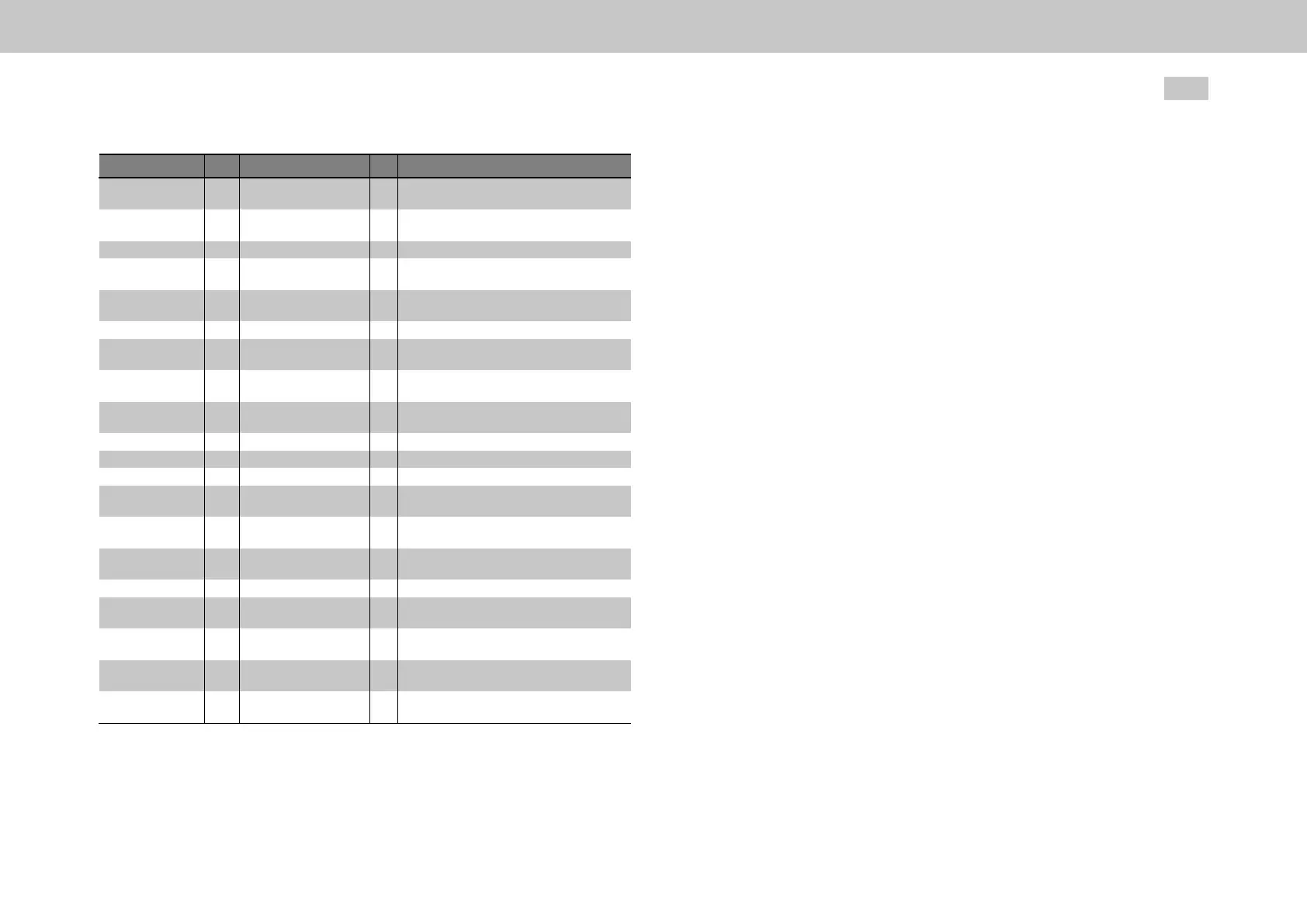
P No. Index Name Unit Description
792 2 d-Amplitudesinus A SCtestsignal:dcurrentamplitudeofsinusoidal
signal
792 3 q-Amplitudesinus A SCtestsignal:qcurrentamplitudeofsinusoidal
signal
792 4 PRBStime ms SCtestsignal:PRBSsignaltime
792 5 d-AmplitudePRBS A SCtestsignal:dcurrentamplitudeofPRBS
signal
792 6 q-AmplitudePRBS A SCtestsignal:qcurrentamplitudeofPRBS
signal
792 7 Fullsignalrange rpm SCtestsignal:Fulltestsignalamplituderange
792 8 Increasingsignalrange rpm SCtestsignal:Lineartransitionrangeupuntil
whichthetestsignalisreducedto0
792 9 d-currentoffset A SCtestsignal:dcurrentoffsetofsinusoidal
signal
794 ENC_CH4_Kalman_
ICOM
Sensorlesscontrol:Autocommutation
794 0 SettlingTime ms SCautocommutation:Risetime
794 1 ICOM_current A SCautocommutation:Currentoffset
794 2 ICOM_time ms SCautocommutation:Time(0=OFF)
794 3 ICOM_1st_L_ident mH SCautocommutation:Firstmeasured
inductance
794 4 ICOM_2nd_L_ident mH SCautocommutation:Secondmeasured
inductance
796 ENC_CH4_Kalman_isd_
add
Sensorlesscontrol:Additiveload-dependentd
current
796 0 Amplitude A SCload-dependentdcurrent:Amplitude
796 1 Fullsignalrange A SCload-dependentdcurrent:qcurrentatwhich
themaximumdcurrentisinjected
796 2 Increasingsignalrange A SCload-dependentdcurrent:Transitionrange
upuntilwhichthedcurrentisreducedto0
796 3 PT1_Tfil ms SCload-dependentdcurrent:Filtertimeford
current(PT1)
797 0 ENC_CH4_Kalman_
Compare
Sensorlesscontrol:Referenceencoder
selection
Table 6.29: “Sensorless synchronous motor control” parameters (continue)
MOOG
ID
No.: CB40859-001 Date: 02/2018
MSD Servo Drive- Device Help
90
6 Encoder
6.8.1.1Autocommutation
When using sensorless control, auto commutation is required in order to ensure
that the motor will not align itself towards a direction in an uncontrolled manner.
There are two options for commutating the motor when using sensorless operation:
6.8.1.1.1Mode1(defaultmethodfornon-brakedmotors)
This mode uses the “Current injection (IENCC)” default auto commutation from
P390[0] - CON_ICOM.
If the encoder selection set with P520[0] - ENC_MCon, P521[0] - ENC_SCon and
P522[0] - ENC_PCon has been set to channel 4, the commutation angle will be set
to 0 at the end of the alignment phase, as the motor will be in the d axis at this point.
6.8.1.1.2Mode2
In this auto commutation mode, a positive measuring current and a negative
measuring current are injected into the motor in order to take inductance
measurements. The measured inductances can then be used to determine whether
the motor is in an unstable rest position. The identified values will be entered in
P794[3] - ICOM_1st_L_ident and P794[4] - ICOM_2nd_L_ident. It is necessary to
ensure that the two values are sufficiently different from each other. If the difference
is too small, you can increase the amplitude. However, please note that excessively
large amplitudes can result in the motor being demagnetized if auto commutation is
used frequently. In case of doubt, ask the motor manufacturer what the maximum
permissible current is.
P792[1] - Frequency and P792[2] - d-Amplitude sinus will be used as the
measuring frequency and measuring amplitude. In addition, P794[0] - SettlingTime,
P794[1] - ICOM_current and P794[2] - ICOM_time need to be configured.

 Loading...
Loading...