Basics
30
1.2 Addresses
In the List of Global Variables, enter the physical address in the field “Address” for each global variable used in
the PLC program.
The operand and the address number are part of the address. In FPWIN Pro you can use either FP and/or IEC
addresses. The following abbreviations are used:
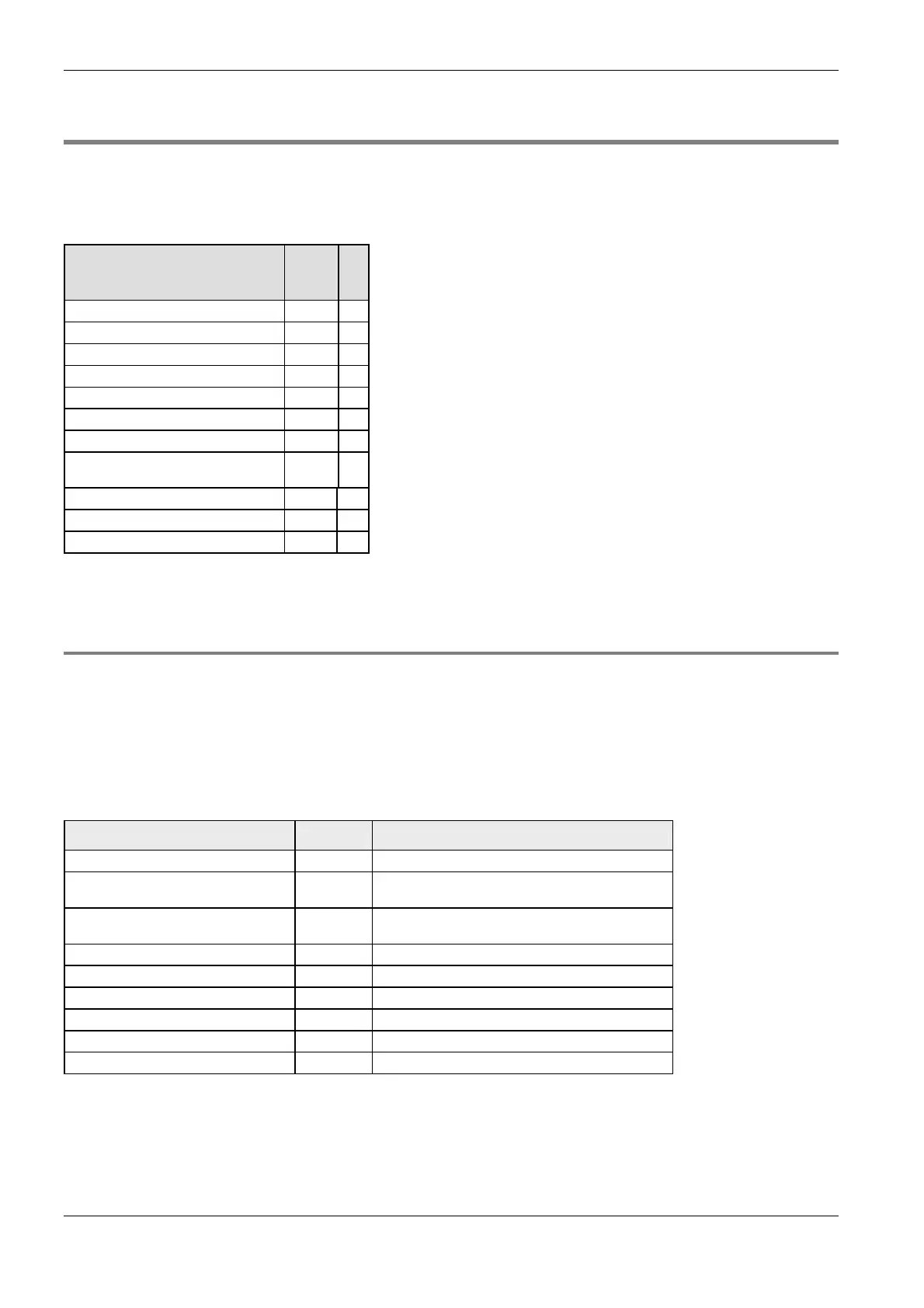
Meaning
FP
IE
C
Input X I
Output Y Q
Memory (internal memory area) R M0
Timer relay T M1
Counter relay C M2
Set value SV M3
Elapsed value EV M4
Data register DT/DD
T
M5
Link relay L M6
Link register LD M7
File register FL M8
You find the register numbers (e.g. DT9000/DT90000) in your hardware description. The next two sections
show how FP and IEC addresses are composed.
1.2.1 FP Addresses
An address represents the hardware address of an in-/output, register, or counter.
For example, the hardware address of the 1st input and the 4th output of a PLC is:
X0 (X = input, 0 = first relay)
Y3 (Y = output, 3 = fourth relay)
Use the following address abbreviations for the memory areas. You find the register numbers in your hardware
description.
Memory Area Abbr. FP Example
Memory (internal memory area) R R9000: self diagnostic error
Timer relay T T200: timer relay no. 200
(settings in system register 5+6)
Counter relay C C100: counter relay no. 100
(settings in system register 5+6)
Set value SV SV200 (set value for counter relay 200)
Elapsed value EV EV100 (elapsed value for timer relay 100)
Data register DT DT9001/DT90001 (signals power failure)
Link relay L L1270
Link register LD LD255
File register FL FL8188

 Loading...
Loading...











