JUNOS Internet Software Network Operations Guide: Hardware
92 ! Understanding Key Router Components
Understanding Key Router Components
Purpose Inspect the Routing Engine and the Packet Forwarding Engine to ensure that the
router is handling general routing operations and is forwarding packets properly.
What Are the Key
Router Components
The router consists of two major architectural components:
! Packet Forwarding Engine—This high-performance, application-specific
integrated circuit (ASIC)-based component provides Layer 2 and Layer 3 packet
switching, route lookups, and packet forwarding.
! Routing Engine—Provides Layer 3 routing services and network management.
The Packet Forwarding Engine and the Routing Engine perform their primary tasks
independently, although they constantly communicate through a 100-Mbps internal
link. This arrangement provides streamlined forwarding and routing control and the
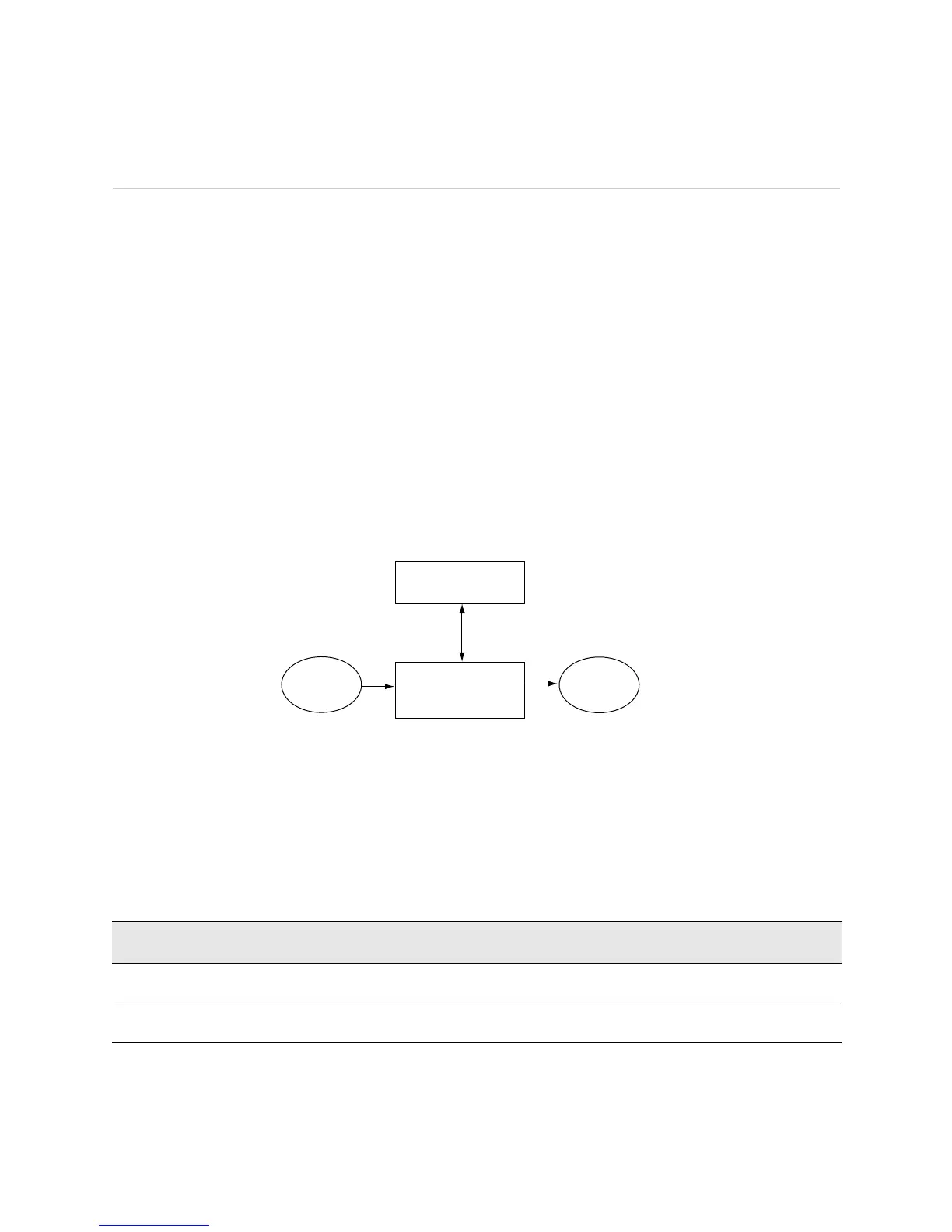
capability to run Internet-scale backbone networks at high speeds. Figure 12
illustrates the relationship between the Packet Forwarding Engine and the Routing
Engine.
Figure 12: Router Architecture
Packet Forwarding Engine
The Packet Forwarding Engine provides Layer 2 and Layer 3 packet switching, route
lookups, packet forwarding, and route lookup functions. Table 28 lists the Packet
Forwarding Engine forwarding rate and aggregate throughput for each routing
platform.
Table 28: Packet Forwarding Engine Forwarding Rate and Aggregate Throughput Characteristics Per Routing
Platform
Packet Forwarding
Engine
Routing Engine
1244
Packets
in
Packets
out
100-Mbps link
Specifications
M5/
M10
M7i M10i M20 M40 M40e M160 M320 T320 T640
Packet forwarding rate in million
packets per second (Mpps)
40 16 16 40 40 40 160 385 385 770
Aggregate throughput in gigabits per
second (Gbps)
6.4 8.4 12.8 25.6 40 51.2 160 320 320 640

 Loading...
Loading...