Understanding Redundant MCSs ! 569
Chapter 43: Monitoring Redundant MCSs
Understanding Redundant MCSs
Purpose Inspect redundant MCSs to ensure that functions are interrupted, such as
component alarm messages; component power-up and power-down; Routing
Engine, MCS, and PCG mastership control; SONET clock generation and
monitoring; and system clock monitoring.
What Are Redundant
MCSs
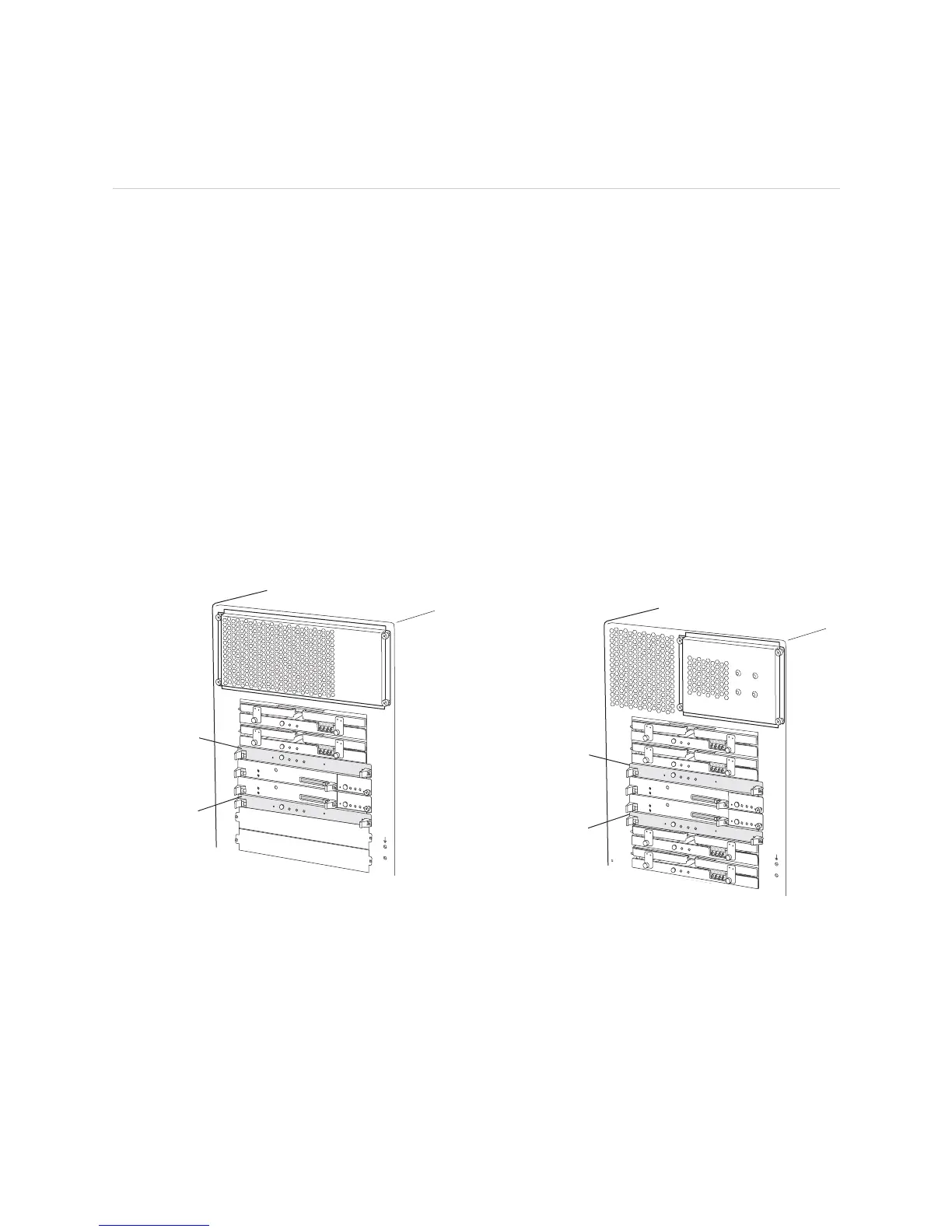
Redundant MCSs are two MCSs installed in the M40e or M160 router.
The MCS is a component of the host module. Each MCS requires a Routing Engine
to be installed in an adjacent slot.
MCS0 installs above slot RE0, and MCS1 installs
below slot
RE1. Even if an MCS is physically installed in the chassis, it does not
function if there is no Routing Engine present in the adjacent slot.
If two MCSs are installed,
MCS0 acts as the master MCS and MCS1 acts as a backup.
If the master MCS fails or is removed, the backup restarts and becomes the master
MCS.
The MCSs install into the midplane from the back of the chassis (see Figure 228).
Figure 228: M40e and M160 Router Redundant MCSs
See Also
! Monitoring the Host Module on page 341
! Monitoring the MCS on page 359
! Monitoring Redundant Routing Engines on page 491
PCG 0
SFM 0
SFM 1
M
CS 0
RE 0
RE 1
MCS
1
PCG 1
MCS 0
MCS 1
D
o
n
o
t
in
s
ta
ll
a
n
SFM
in
th
is
slo
t
D
o no
t
in
s
ta
ll
an SF
M
in th
is
slo
t
M40e router rear
MCS 0
MCS 1
1843
P
C
G
0
S
F
M
0
S
F
M 1
MC
S 0
R
E 0
R
E 1
MCS 1
S
F
M 2
S
F
M 3
P
C
G
1
M160 router rear

 Loading...
Loading...