Understanding Redundant SFMs ! 579
Chapter 44: Monitoring Redundant SFMs
Understanding Redundant SFMs
Purpose Inspect redundant SFMs to ensure that all traffic leaving the Flexible PIC
Concentrators (FPCs) is handled properly.
What Are Redundant
SFMs
SFMs are control boards that handle traffic transiting the router. The SFMs provide
route lookup, filtering, and switching. (See Figure 229.)
Up to four interconnected SFMs can be installed in the M160 router, providing a
total of 160 million packets per second (Mpps) of forwarding. Up to two SFMs can
be installed in the M40e router. Each SFM can process 40 Mpps.
The SFM is a two-board system containing the Switch Plane Processor (SPP) card
and the Switch Plane Router (SPR) card. When the serial stream of bits leaves the
FPC, it is directed to one of the SFMs. The Distributed Buffer Manager ASIC on the
SFM distributes the data cells throughout memory banks that are shared over all
FPCs. The Internet Processor II ASIC on the SFM performs route lookups and makes
forwarding decisions. The Internet Processor II ASIC notifies a second Distributed
Buffer Manager ASIC SFM, which forwards the notifications to the outbound
interface. Each SFM effectively handles from one-half to one-quarter of the traffic
on each FPC.
The SFMs are hot-removable and hot-insertable. Inserting or removing an SFM
causes a brief interruption in forwarding performance (about 500 ms) as the Packet
Forwarding Engine reconfigures the distribution of packets across the remaining
SFMs.
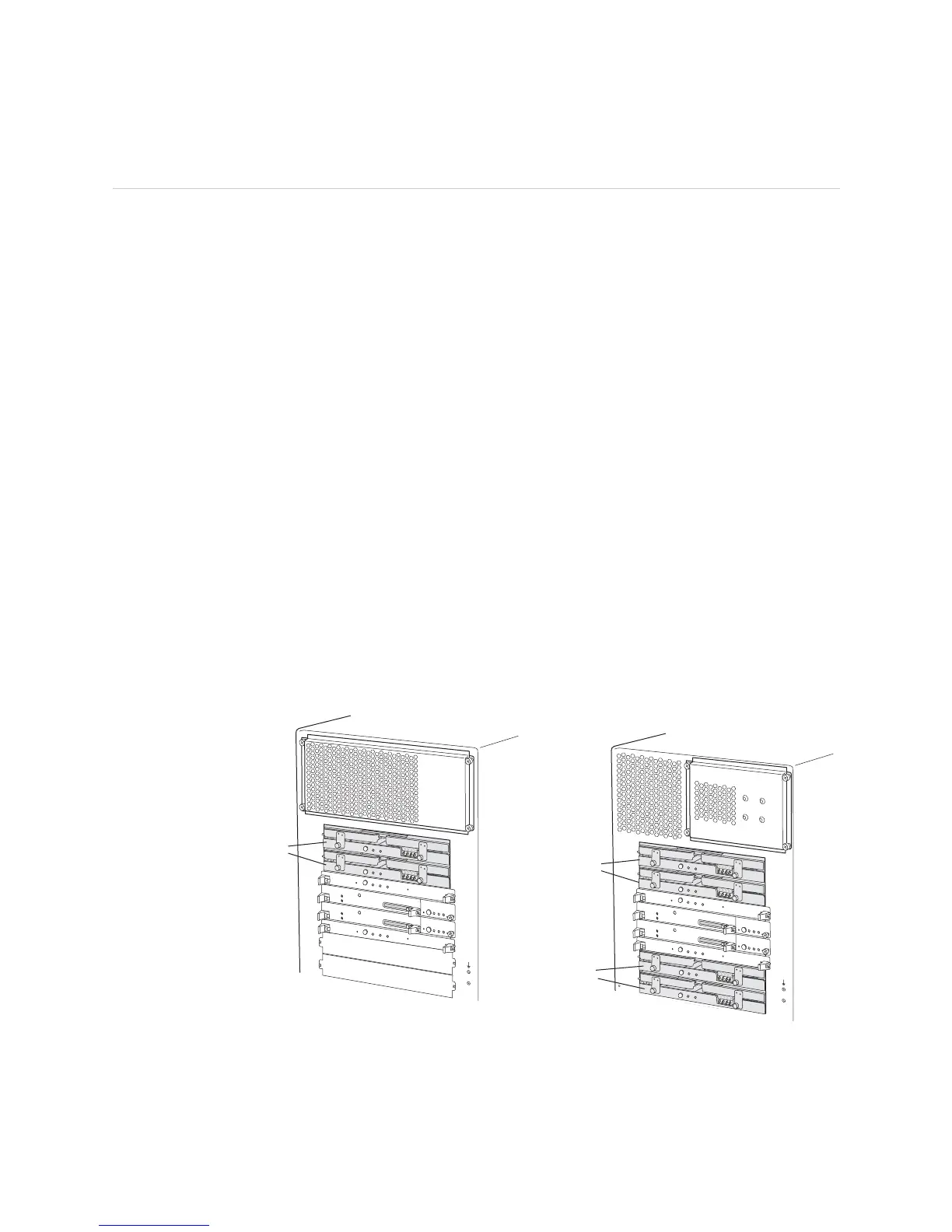
Figure 229: M40e and M160 Router SFM Location
PCG 0
SFM 0
SFM 1
M
CS 0
RE 0
RE 1
MCS
1
PCG
1
SFMs
D
o
n
o
t in
sta
ll a
n
S
F
M
in
th
i
s
s
lo
t
D
o
n
o
t in
sta
ll a
n
S
F
M
in
th
i
s slot
1776
P
C
G
0
S
F
M
0
S
F
M
1
MC
S 0
R
E 0
R
E 1
MCS 1
S
F
M
2
S
F
M
3
P
C
G
1
SFMs
SFMs
M40e router rear M160 router rear

 Loading...
Loading...