JUNOS Internet Software Network Operations Guide: Hardware
316 ! Understanding the SCG
Understanding the SCG
Purpose You monitor the SCGs to ensure that they provide a clock signal for the SONET/SDH
interfaces on the router and that they select a clock signal from any FPC, or from
the external clock inputs.
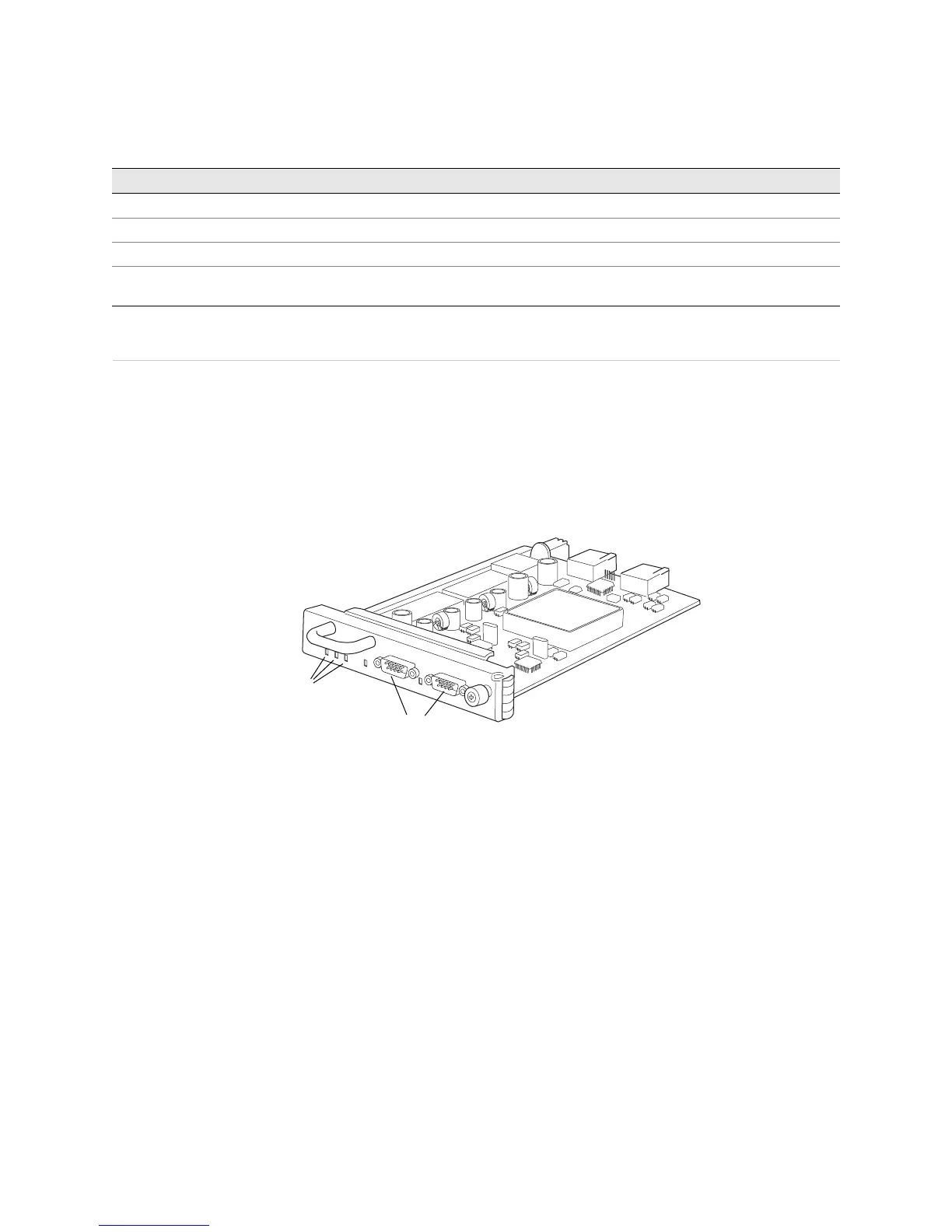
What Is an SCG The SCGs provide a 19.44-MHz Stratum 3 clock signal for the SONET/SDH
interfaces on the router. The SCGs can also select a clock signal from any FPC, or
from the external clock inputs (see Figure 131).
Figure 131: SCG Component
Two SCGs are installed in the T320 router and the T640 routing node. The SCGs
install into the upper rear of the chassis in the slots labeled
SCG0 and SCG1.
If both SCGs are installed and functioning normally,
SCG0 is master and SCG1 is
backup. Removing the backup SCG does not affect the functioning of the router or
routing node. Taking the master SCG offline might result in a brief loss of SONET
clock lock while the backup SCG becomes master.
The SCGs are hot-pluggable.
Figure 132 on page 317 shows the location of the SCGs on the T320 router and
T640 routing node.
Getting SCG Hardware Information on page 323
1. Display the SCG Hardware Information on page 323 show chassis hardware
2. Locate the SCG Serial Number ID Label on page 324 Look on the top of the SCG, close to the midplane connector.
Returning the SCG on page 324 See “Return the Failed Component” on page 86, or follow the
procedure in the appropriate router hardware guide.
Monitor SCG Tasks Command or Action
2021
External clock
inputs
LEDs
 Loading...
Loading...