JUNOS Internet Software Network Operations Guide: Hardware
454 ! Understanding the FEB
Understanding the FEB
Purpose Inspect the FEB to ensure that communication occurs with the Routing Engine.
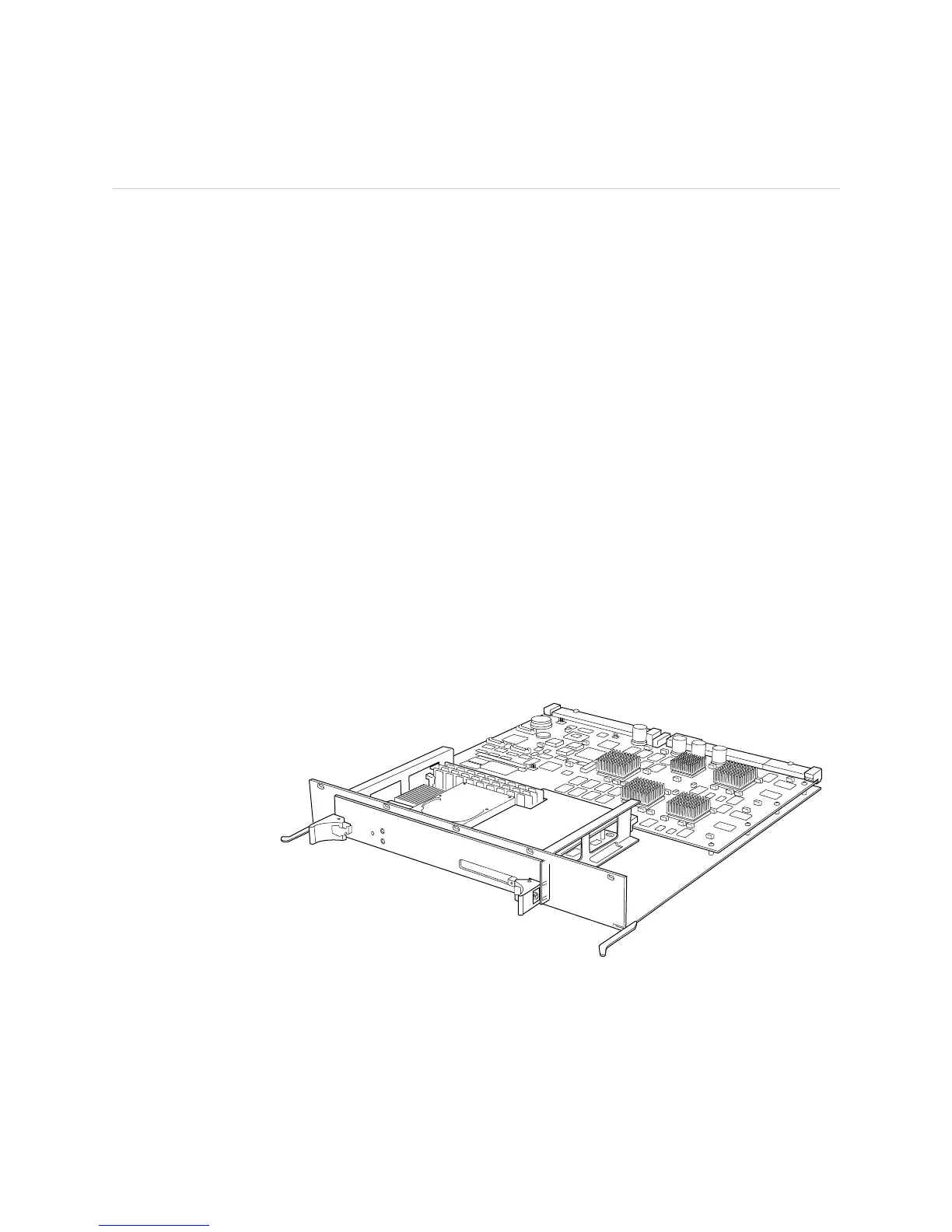
What Is an FEB The FEB is a control board for the M5 and M10 routers (see Figure 180). The FEB
communicates with the Routing Engine using a dedicated 100-Mbps link that
transfers routing table data from the Routing Engine to the forwarding table in the
Internet Processor II application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). The link is also
used to transfer routing link-state updates and other packets destined for the router
from the FEB to the Routing Engine. The FEB provides the following functions:
! Route lookups—The Internet Processor II ASIC on the FEB performs route
lookups using the forwarding table stored in synchronous SRAM (SSRAM).
! Shared memory management—One Distributed Buffer Manager ASIC on the
FEB uniformly allocates incoming data packets throughout the router’s shared
memory.
! Outgoing data packet transfer—A second Distributed Buffer Manager ASIC on
the FEB passes data packets to the destination Physical Interface Card (PIC)
when the data is ready to be transmitted.
! Exception and control packet transfer—The Internet Processor II ASIC passes
exception packets to the microprocessor on the FEB, which processes almost all
of them. The remaining packets are sent to the Routing Engine for further
processing. Any errors originating in the Packet Forwarding Engine and
detected by the FEB are sent to the Routing Engine using system log messages.
Figure 180: FEB Component
1307
 Loading...
Loading...