Understanding Redundant Routing Engines ! 499
Chapter 37: Monitoring Redundant Routing Engines
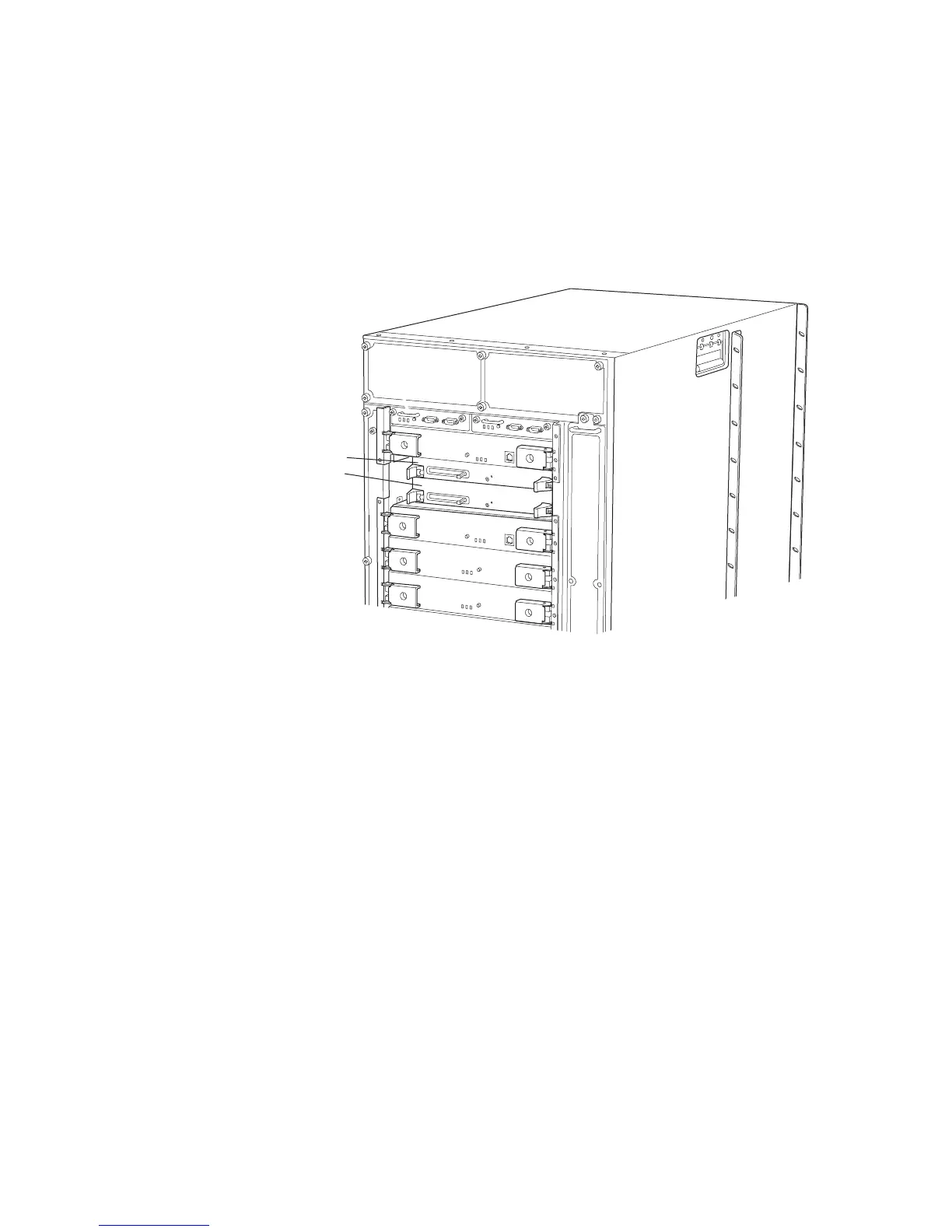
Figure 198 shows the T640 routing node redundant Routing Engines that are
components of the host subsystem.
Figure 198: T640 Routing Node Routing Engines
The host subsystem consists of a Routing Engine and a Control Board. You can
install two host subsystems in the T320 router and T640 routing node. For more
information about monitoring redundant Control Boards, see “Monitoring
Redundant Control Boards” on page 559.
Both the Routing Engine and the Control Board must be installed for the host
subsystem to function. When two host subsystems are installed in the router, both
are powered on, but only one is the master; the second host subsystem is the
backup and performs no functions. By default, the master host subsystem has
components installed in slots
RE0 and CB0; the backup host module has
components installed in slots
RE1 and CB1. If one Routing Engine physically fails,
the other one assumes the routing functions. If a software failure occurs, the other
backup Routing Engine assumes routing functions if some preliminary
configuration has been done. For more information, see“Host Redundancy
Overview” on page 463.
The T320 router and T640 routing node craft interface LEDs indicate the Routing
Engine operating status and mastership. (See “Check the T320 Router Routing
Engine LEDs” on page 144 and “Check the T640 Routing Node Routing Engine
LEDs” on page 145.)
g003292
Routing
Engines
T640 router rear
 Loading...
Loading...