Altera Corporation 7–59
September 2004 Stratix Device Handbook, Volume 2
Implementing High Performance DSP Functions in Stratix & Stratix GX Devices
Arithmetic
Functions
Arithmetic functions, such as trigonometric functions, including sine,
cosine, magnitude and phase calculation, are important DSP elements.
This section discusses the implementation of a simple vector magnitude
function in a Stratix device.
Background
Complex numbers can be expressed in two parts: real and imaginary.
where:
a is the real part
b is the imaginary part
j
2
= –1
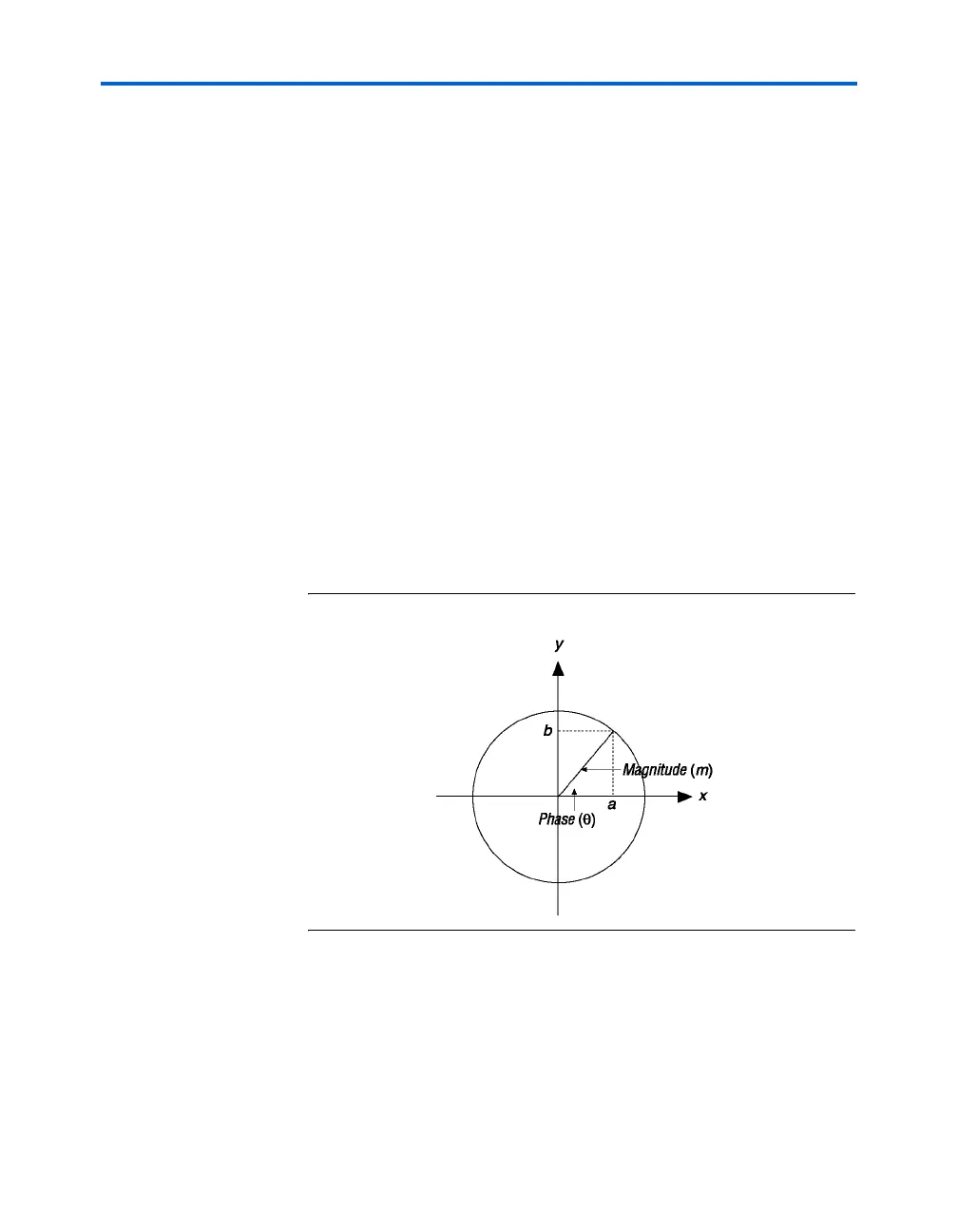
In a two-dimensional plane, a vector (a,b) with reference to the origin
(0,0) can also be represented as a complex number. In essence, the x-axis
represents the real part, and the y-axis represents the imaginary part (see
Figure 7–37).
Figure 7–37. Magnitude of Vector (a,b)
Complex numbers can be converted to phase and amplitude or
magnitude representation, using a Cartesian-to-polar coordinate
conversion. For a vector (a,b), the phase and magnitude representation is
the following:
zajb+=
 Loading...
Loading...