2–4 Altera Corporation
Stratix Device Handbook, Volume 2 July 2005
TriMatrix Memory
storage. The parity bit, along with logic implemented in logic elements
(LEs), can implement parity checking for error detection to ensure data
integrity. Parity-size data words can also store user-specified control bits.
Byte Enable Support
In the M4K and M-RAM blocks, byte enables can mask the input data so
that only specific bytes of data are written. The unwritten bytes retain the
previous written value. The write enable signals (wren), in conjunction
with the byte enable signals (byteena), controls the RAM block’s write
operations. The default value for the byteena signals is high (enabled),
in which case writing is controlled only by the wren signals.
Asserting the clear port of the byte enable registers drives the byte enable
signals to their default high level.
M4K Blocks
M4K blocks support byte writes when the write port has a data width of
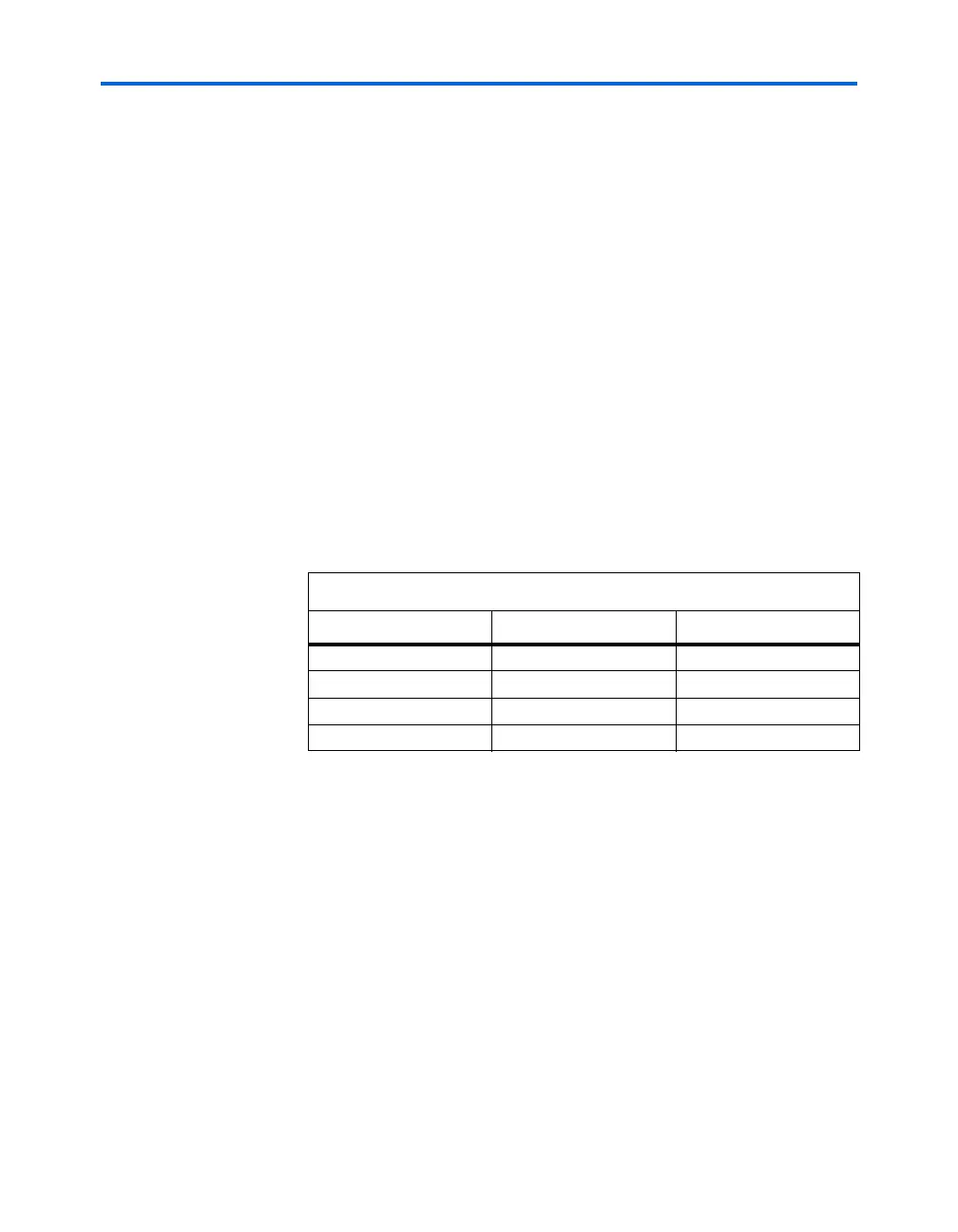
16, 18, 32, or 36 bits. Table 2–4 summarizes the byte selection.
Table 2–4. Byte Enable for M4K Blocks Notes (1), (2)
byteena datain × 18 datain × 36
[0] = 1 [8..0] [8..0]
[1] = 1 [17..9] [17..9]
[2] = 1 – [26..18]
[3] = 1 – [35..27]
Notes to Ta b le 2 – 4 :
(1) Any combination of byte enables is possible.
(2) Byte enables can be used in the same manner with 8-bit words, i.e., in × 16 and × 32
modes.
 Loading...
Loading...