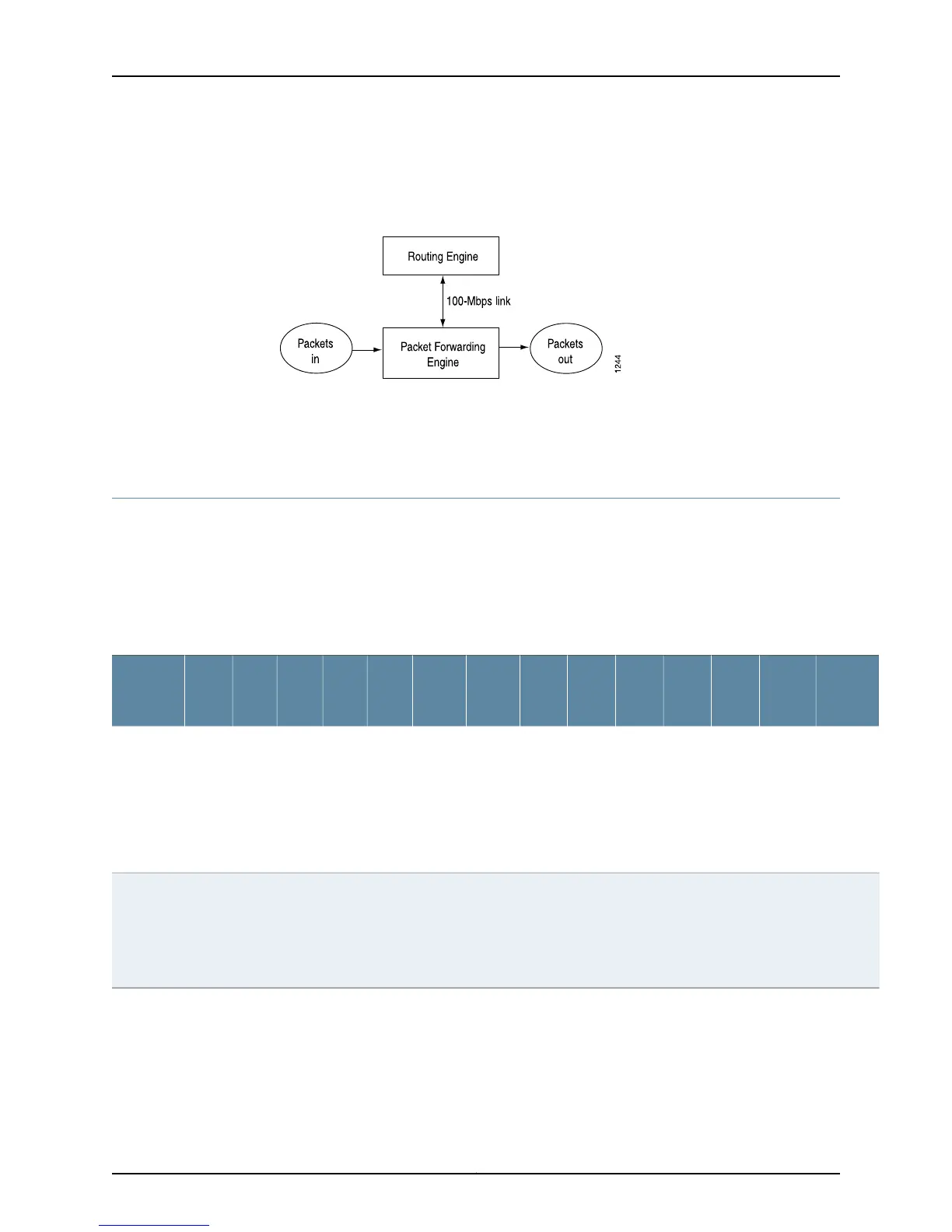
to run Internet-scale backbone networks at high speeds. Figure 22 on page 120 illustrates
the relationship between the Packet Forwarding Engine and the Routing Engine.
Figure 22: Router Architecture
Related
Documentation
Basic Router Component Monitoring Method on page 51•
• Router Chassis Overview on page 142
Packet Forwarding Engine
The Packet Forwarding Engine provides Layer 2 and Layer 3 packet switching, route
lookups, packet forwarding, and route lookup functions. Table 36 on page 120 lists the
Packet Forwarding Engine forwarding rate and aggregate throughput for each routing
platform.
Table 36: Packet Forwarding Engine Forwarding Rate and Aggregate Throughput Characteristics
per Routing Platform
TX
Matrix
Plus
TX
MatrixT1600T640T320M320M160M120M40eM40M20M10iM7i
M5/
M10Specifications
7.68
billion
pps
3
billion
pps
1.92
billion
pps
77038538516090404040161640Packet
forwarding
rate in
million
packets
per
second
(Mpps)
6.4
Tbps
2.5
Tbps
1.6
Tbps
64032032016012051.24025.612.88.46.4Aggregate
throughput
in gigabits
per
second
(Gbps)
For M Series routers, the Packet Forwarding Engine is implemented in ASICs that are
located on the System Control Board (SCB): a Forwarding Engine Board (FEB) (M5/M10
router), System and Switch Board (SSB) (M20 router), SCB (M40 router), or Switching
and Forwarding Module (SFM) (M40e and M160 routers). It uses a centralized route
lookup engine and shared memory. For T Series routers, the Packet Forwarding Engine
Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks, Inc.120
M Series and T Series Routers Monitoring and Troubleshooting Guide

 Loading...
Loading...