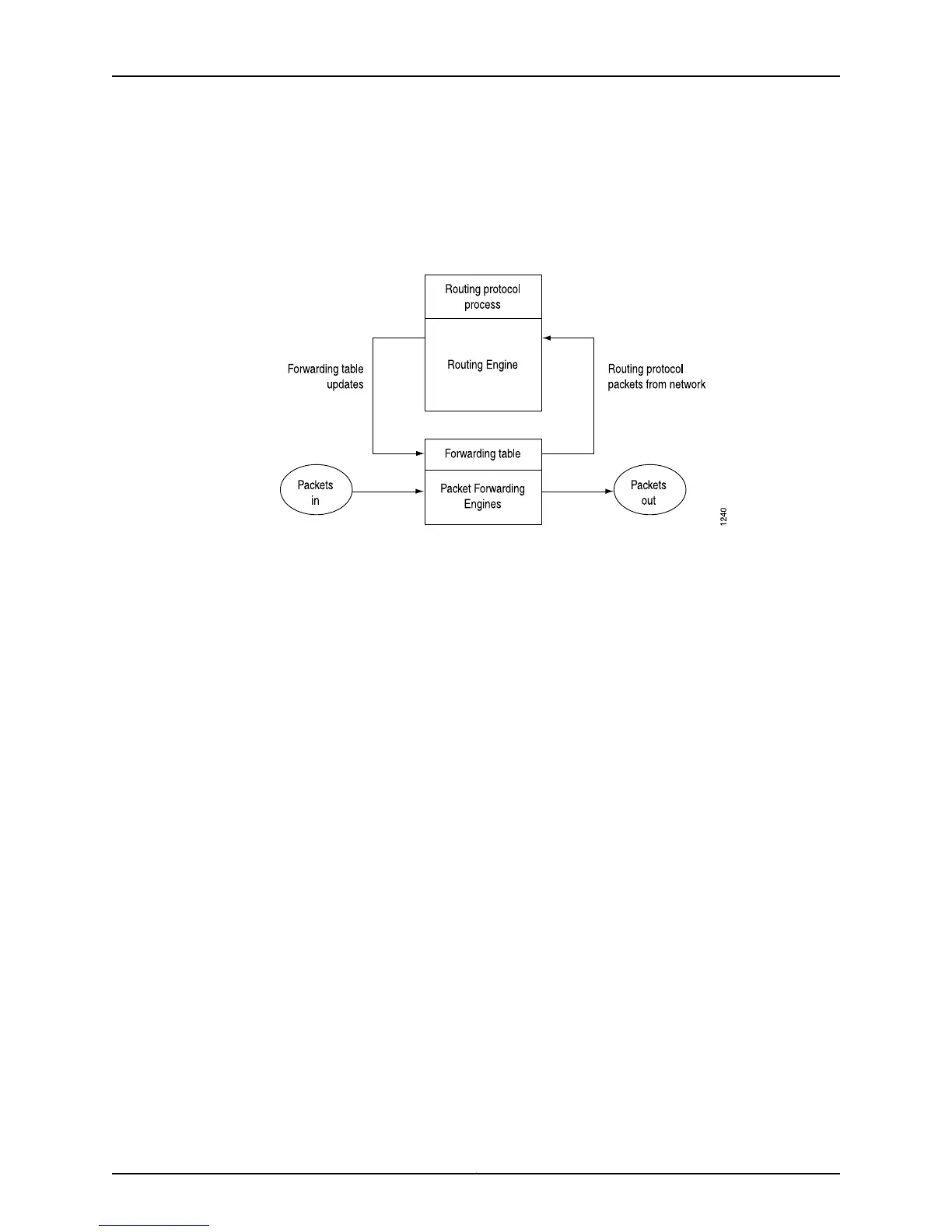
called the forwarding table, which is copied into the Packet Forwarding Engines. The
design of the T-series Internet Processor allows the forwarding table in the Packet
Forwarding Engines to be updated without interrupting the router’s forwarding.
Figure 35: Control Packet Handling for Routing and Forwarding Table
Update
On the M320 and T320 routers and the T640 router, the host subsystem provides the
routing and system management functions. The host subsystem consists of the Routing
Engine and the Control Board. For more information about the Control Boards and host
subsystem, see “Checklist for Monitoring the Control Board” on page 381 and “Checklist
for Monitoring the Host Subsystem” on page 367.
On the M40e and M160 routers, the host module provides the routing and system
management functions. The host module consists of the Routing Engine and the
Miscellaneous Control Subsystem (MCS). For more information about the host module,
see “Checklist for Monitoring the Host Subsystem” on page 367. For more information
about the MCS, see “Checklist for Monitoring the MCS” on page 455 .
On the M10i router, the Routing Engine works with its companion High-Availability Chassis
Manager (HCM) to provide control and monitoring functions for router components. For
more information about the HCM, see “Checklist for Monitoring the HCM” on page 531.
Related
Documentation
• Routing Engine Overview on page 168
139Copyright © 2012, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 4: Monitoring Key Router Components

 Loading...
Loading...