Configuring Device Information 249
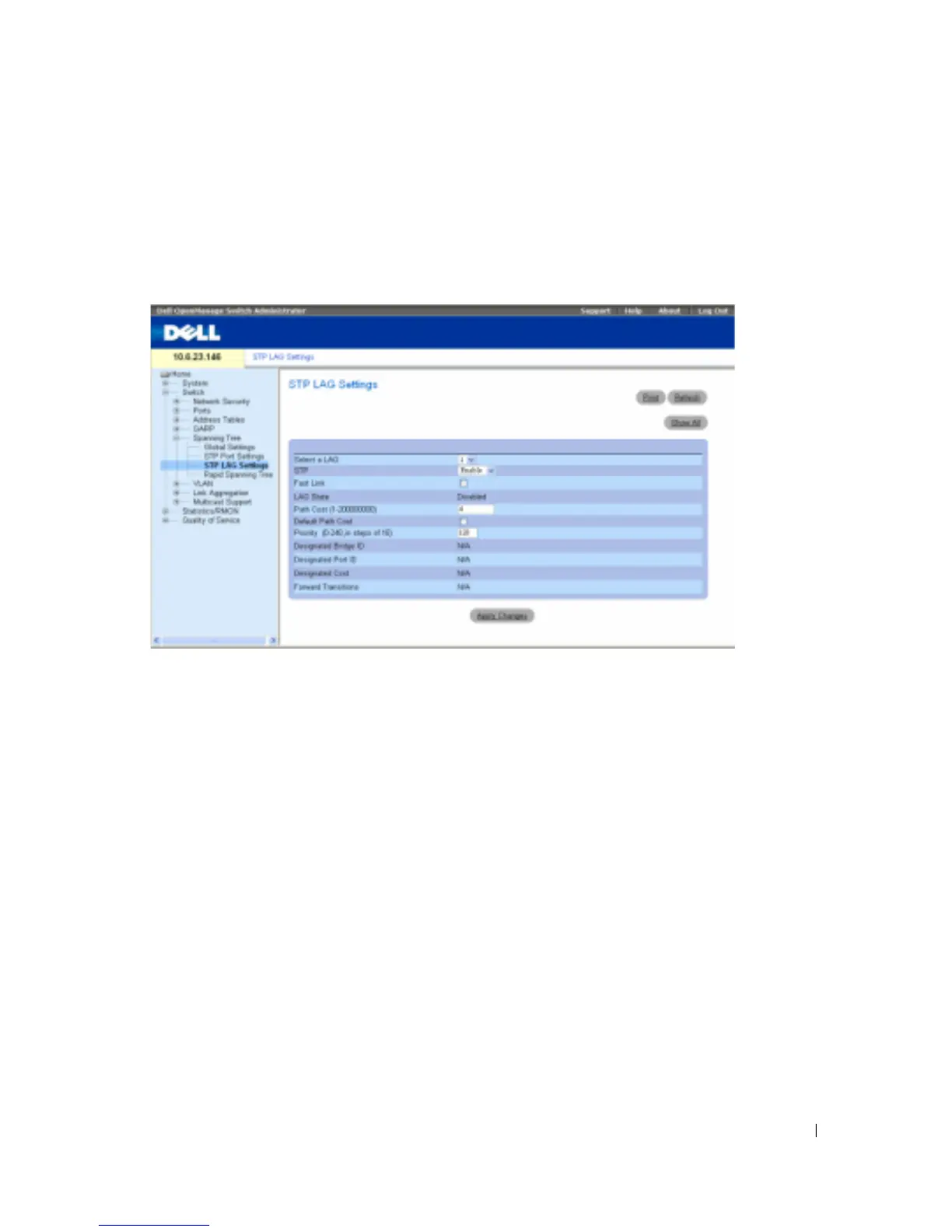
Defining STP LAG Settings
The
STP LAG Settings
page contains fields for assigning STP aggregating port parameters. To
open the
STP LAG Settings
page, click
Switch
→
Spanning Tree
→
LAG Settings
in the tree view.
Figure 7-100. STP LAG Settings
Select a LAG
— The user-defined LAG. For more information, see "Defining LAG Membership".
STP
— Enables or disables STP on the LAG.
Fast Link
— Enables Fast Link mode for the LAG. If Fast Link mode is enabled for a LAG, the
LAG State
is automatically placed in the
Forwarding
state
when the LAG is up. Fast Link mode
optimizes the time it takes for the STP protocol to converge. STP convergence can take 30-60
seconds in large networks.
LAG State
— Current STP state of a LAG. If enabled, the LAG state determines what forwarding
action is taken on traffic. If the bridge discovers a malfunctioning LAG, the LAG is placed in the
Broken
state. Possible LAG states are:
Disabled
— The LAG link is currently down.
Blocking
— The LAG is blocked and cannot be used to forward traffic or learn MAC
addresses.
Listening
— The LAG is in the listening mode and cannot forward traffic or learn MAC
addresses.
Learning
— The LAG is in the learning mode and cannot forward traffic, but it can learn new
MAC addresses.

 Loading...
Loading...











