240 Configuring Device Information
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Configuring the Spanning Tree Protocol
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides tree topography for any arrangement of bridges. STP also
provides one path between end stations on a network, eliminating loops.
Loops occur when alternate paths exist between hosts. Loops in an extended network can cause
bridges to forward traffic indefinitely, resulting in increased traffic and reducing network efficiency.
The devices support the following Spanning Tree protocols:
•
Classic STP
— Provides a single path between end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops.
For more information on configuring Classic STP, see "Defining STP Global Settings".
•
Rapid STP
— Detects and uses of network topologies that provide faster spanning tree
convergence, without creating forwarding loops. For more information on configuring Rapid
STP, see "Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree".
To open the
Spanning Tree
page, click
Switch
→
Spanning Tree
in the tree view.
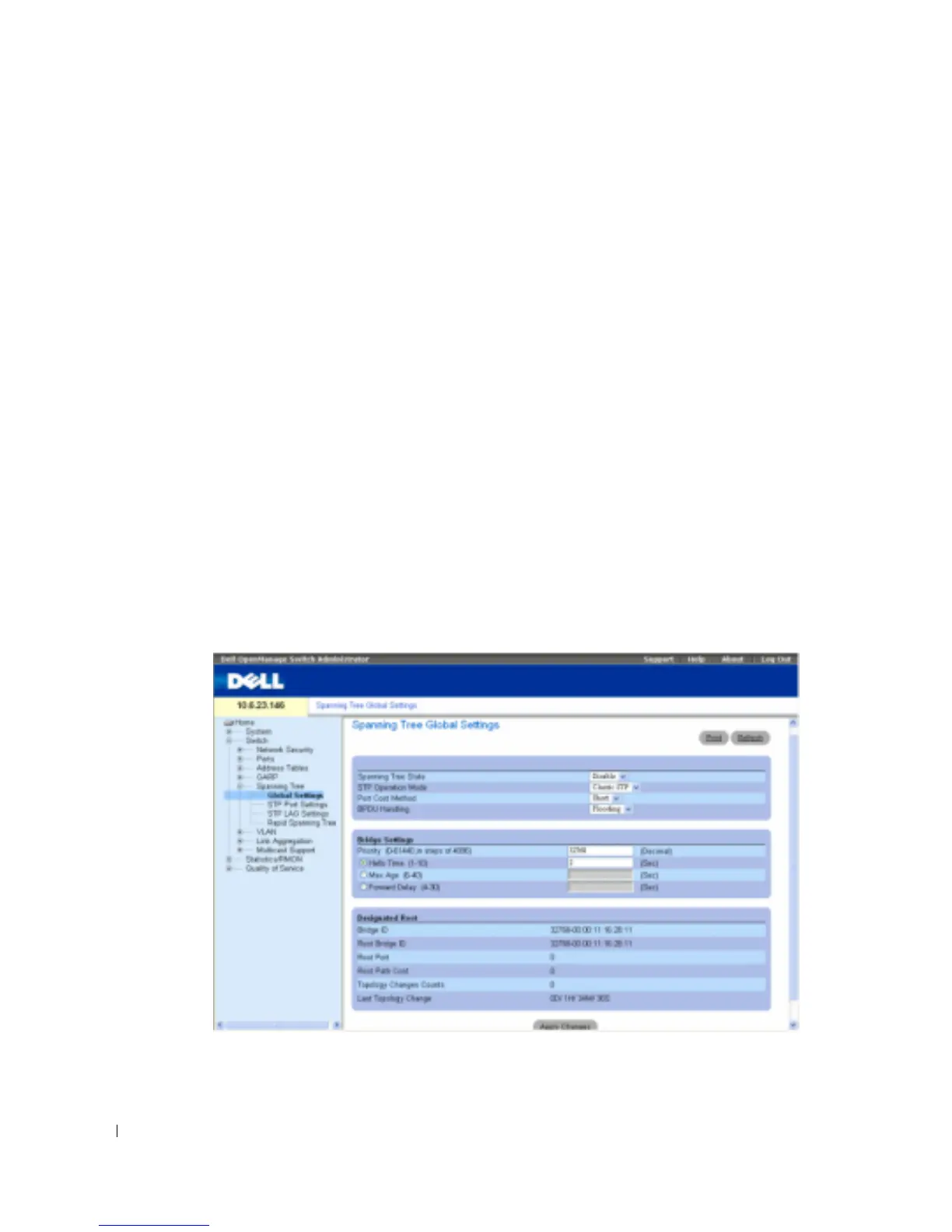
Defining STP Global Settings
The
STP Global Settings
page contains parameters for enabling and configuring STP operation on
the device. To open the
STP Global Settings
page, click
Switch
→
Spanning Tree
→
Global Settings
in the tree view.
Figure 7-98. STP Global Settings
Spanning Tree State
— Enables or disables Spanning Tree on the device. The possible field values
are:

 Loading...
Loading...











