Operation Manual - Network Protocol
Quidway S3500 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 5 DHCP Configuration
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
5-1
Chapter 5 DHCP Configuration
Note:
This chapter only applies to S3552G, S3552P, S3528G, S3528P, S3552F, S3526E,
S3526E FM, S3526E FS and S3526C in S3500 series switches.
5.1 DHCP Overview
5.1.1 DHCP Fundamentals
This is a world where networks are ever-growing with configurations getting complex,
computers (such as laptop computers and wireless networks) are often moved, and the
available IP addresses are far from adequate for the ever-increasing number of
computers. In such a background dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) was
introduced. DHCP operates in Client/Server model, where the DHCP client dynamically
requests the DHCP server for configuration information and the DHCP server returns
the configuration information (an IP address for example) based on the adopted policy.
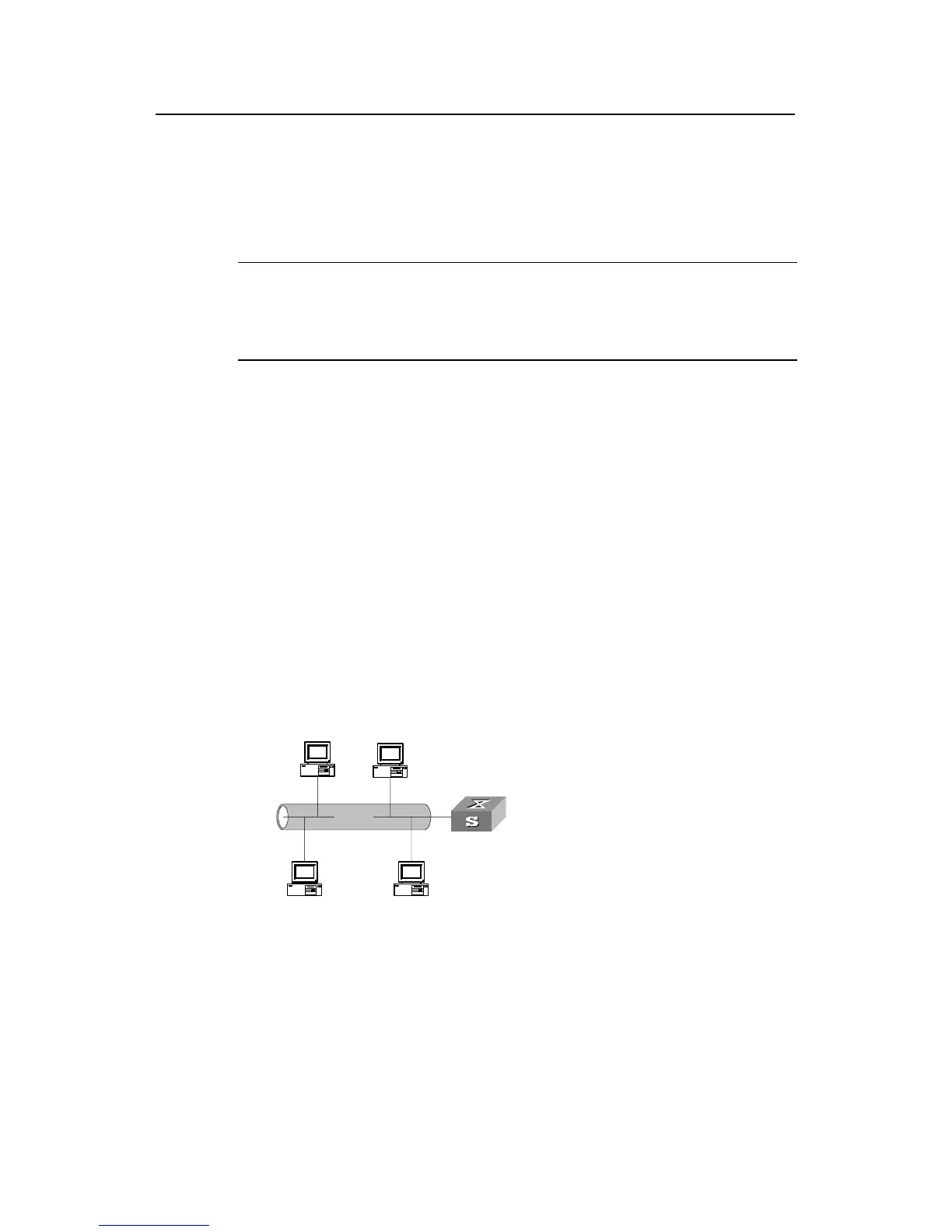
A typical DHCP application network usually comprises a DHCP server and multiple
clients such as PCs and laptop computers (see the following figure):
LAN
DHCP Server
DHCP Client DHCP Client
DHCP Client DHCP Client
Figure 5-1 Typical networking application of DHCP Server
I. Allocating IP addresses using DHCP
1) IP address allocation policy
The time duration for a client to occupy an IP address depends on the type of the client.
A server tends to use a fixed IP address for a long time, some hosts perhaps need to

 Loading...
Loading...











