Operation Manual - Multicast
Quidway S3500 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 IP Multicast Overview
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-4
Class D address Meaning
224.0.0.12 DHCP server/Relay agent
224.0.0.13 All PIM routers
224.0.0.14 RSVP encapsulation
224.0.0.15 All CBT routers
224.0.0.16 Designated SBM
224.0.0.17 All SBMS
224.0.0.18 VRRP
…… ……
1.2.2 Ethernet Multicast MAC Addresses
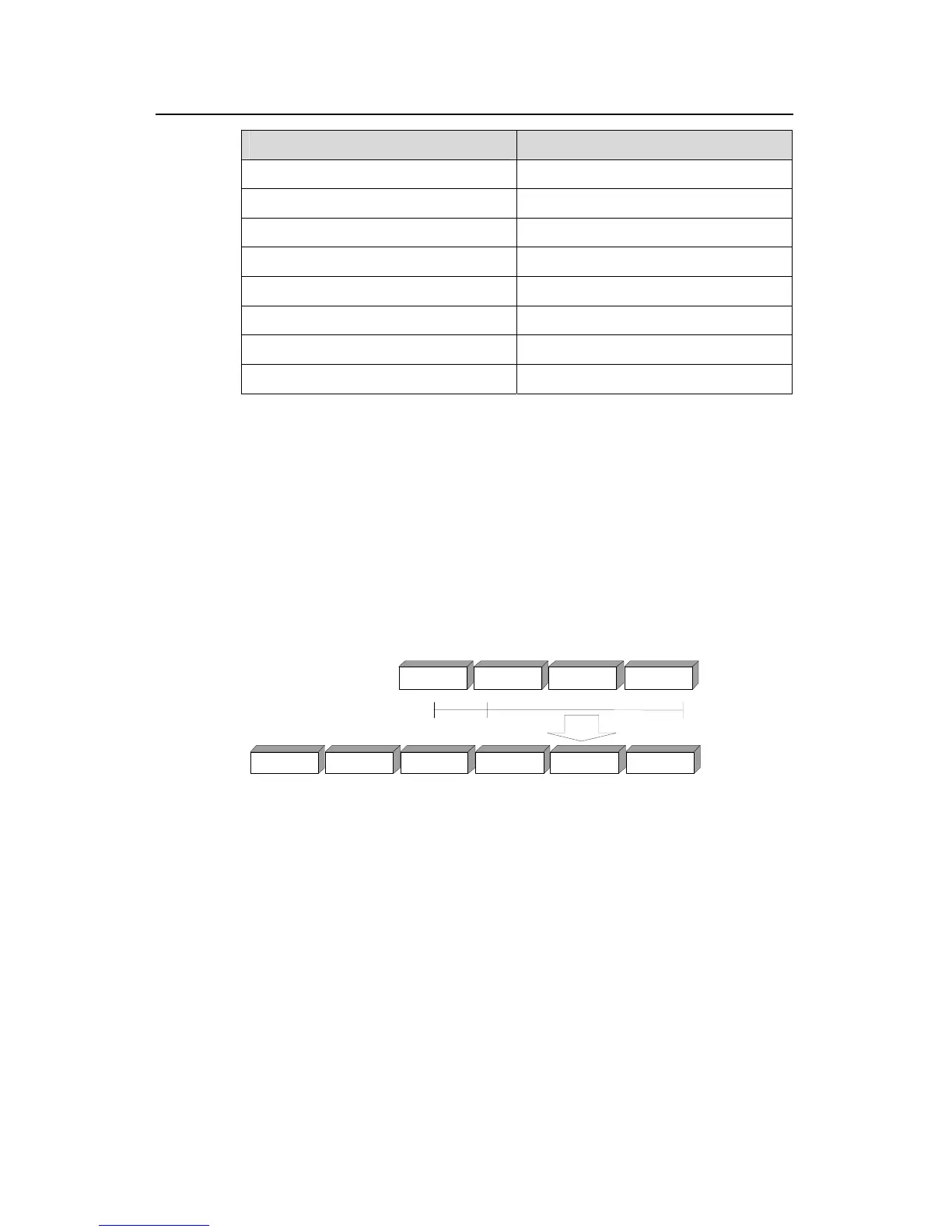
When unicast IP packets are transmitted on the Ethernet, the destination MAC address
is the MAC address of the receiver. However, when multicast packets are transmitted,
the destination is no longer a specific receiver but a group with unspecific members.
Therefore, the multicast MAC address should be used. Multicast MAC addresses are
correspondent to multicast IP addresses. IANA (Internet Assigned Number Authority)
stipulates that higher 24 bits of the multicast MAC address are 0x01005e and the lower
23 bits of the MAC address is the lower 23 bits of the multicast IP address.
111 0
XXXX
32 bits IP address
48 bits MAC address
5 bits not mapped
Lower 23 bits directly mapped
XXXX
XXX X
XXXX
XXXX
XXXX
X X X X
XXXX
XXXX
XXXX
XXXX
XXXX
XXXX
XXXX
X X X X
XXXX
X X XX
XXXX
X X X X
Figure 1-2 Mapping between the multicast IP address and the Ethernet MAC address
Because only 23 bits of the last 28 bits in the IP multicast address are mapped into the
MAC address, 32 IP multicast addresses are mapped into the same MAC address.
1.3 IP Multicast Protocols
Multicast involves the multicast group management protocol and multicast routing
protocol. At present, the multicast group management protocol uses the IGMP that is
used as IP multicast basic signaling protocol. It is run between hosts and routers,
enabling routers to know whether there are members of the multicast group on the
network segment. The multicast routing protocol is run between multicast routers,
creating and maintaining multicast routes and implementing correct and high-efficient
multicast packet forwarding. At present, multicast routing protocols mainly include

 Loading...
Loading...











