Operation Manual - QoS/ACL
Quidway S3500 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 QoS Configuration
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
2-26
You may configure queue scheduling using the queue-scheduler command and its
negative form described in the following table.
Perform the following configuration in Ethernet interface view.
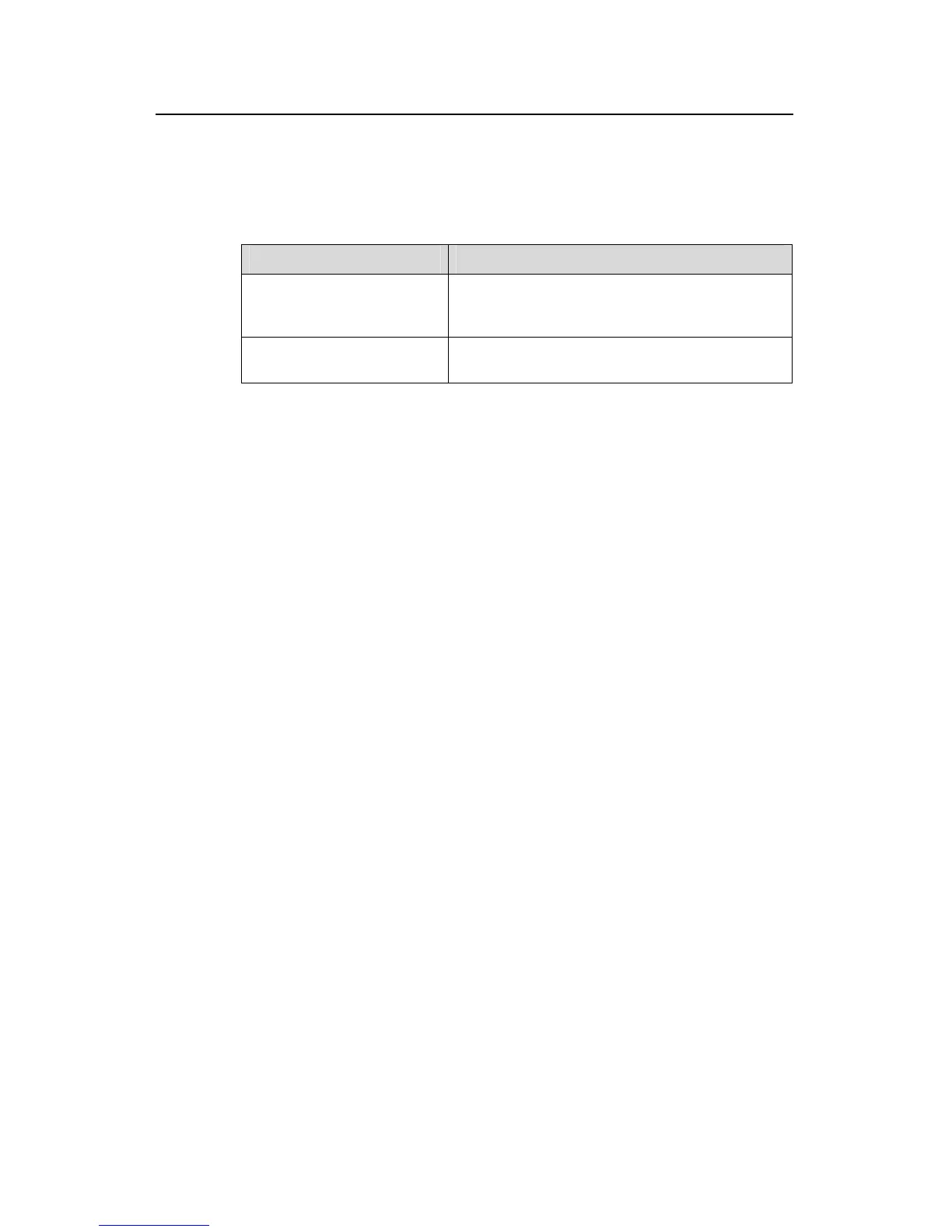
Table 2-37 Configuring the queue scheduling algorithm
Operation Command
Configure queue scheduling
algorithm.
queue-scheduler wrr { group1 { queue-id
queue-weight } &<1-8> | group2 { queue-id
queue-weight } &<1-8> }*
Restore the default queue
scheduling algorithm setting.
undo queue-scheduler [ queue-id ] &<1-8>
By default, SP scheduling applies. As for the queues on which WRR scheduling does
not apply, SP scheduling applies.
For more information about the queue-scheduler command and its negative form,
refer to Command Manual.
2.4.7 Configuring Congestion Avoidance
When congestion occurs on a switch, the switch will try to alleviate it by releasing
queue resources as soon as possible and putting packets into the queues other than
those suffering high latency.
Upon the receipt of a packet, the switch assigns a conform-level value to it. This is also
known as coloring packets. Conform-level can be set to 0, 1, or 2, meaning red, yellow,
or green. When congestion occurs, red packets are the first ones being dropped and
green packets are the last ones.
You may configure congestion avoidance parameters and drop thresholds for each
queue and conform-level.
Two drop algorithms are supported:
1) Tail drop: sets different drop thresholds for different queues. Thus, after the
number of red (yellow or green) packets exceeds the specified upper threshold,
the arriving red (yellow or green) packets will be dropped.
2) WRED drop: takes into consideration the conform-level of packets in each queue
when dropping them. Thus, before the number of packets in a (red, yellow, or
green) queue exceeds the specified upper threshold, the system starts dropping
packets once the number of packets in the queue exceeds the lower threshold.
The number of packets dropped at a moment is dynamically decided taking into
account the factors of specified maximum drop probability and the number of
packets waiting for transmission in the queue. If the number of the packets
exceeds the upper threshold, however, the system will drops all the arriving
packets.

 Loading...
Loading...











