10-10
ABSOLUTE POSITION SYSTEM
- SV Series User’s Manual -
10-5 Acquisition of Absolute Position
When KV-ML16V is Connected
When KV-ML16V is connected, the absolute position of servo motor can be read from the buffer memory or data
memory (only in simple mode) automatically.
For details, see KV-ML16V/MC40V/MC20V/MX1 User's Manual, Chapter 6 "Axis Control Common Function/Common Setting"
Chapter 14 "Auxiliary Function".
When KV-MC40V/MC20V is Connected
When KV-MC40V/MC20V is used, the absolute offset of servo motor is read into the buffer through KV-MX1.
For details, see KV-ML16V/MC40V/MC20V/MX1 User's Manual, Chapter 6 "Axis Control Common Function/Common Setting"
Chapter 14 "Auxiliary Function".
When other Company's Controller is Connected
MECHATROLINK-II type
Absolute position of MECHATROLINK-II type is acquired via MECHATROLINK-II communication command. See PC
manual, send SENS_ON command.
When sending SENS_ON command, like the pulse/analog input type, A+/A- terminals will also output
pulses. For details, see "Conditions when other company's positioning unit is connected". This allows
servo motor not to be affected by pulses generated by SENS_ON command.
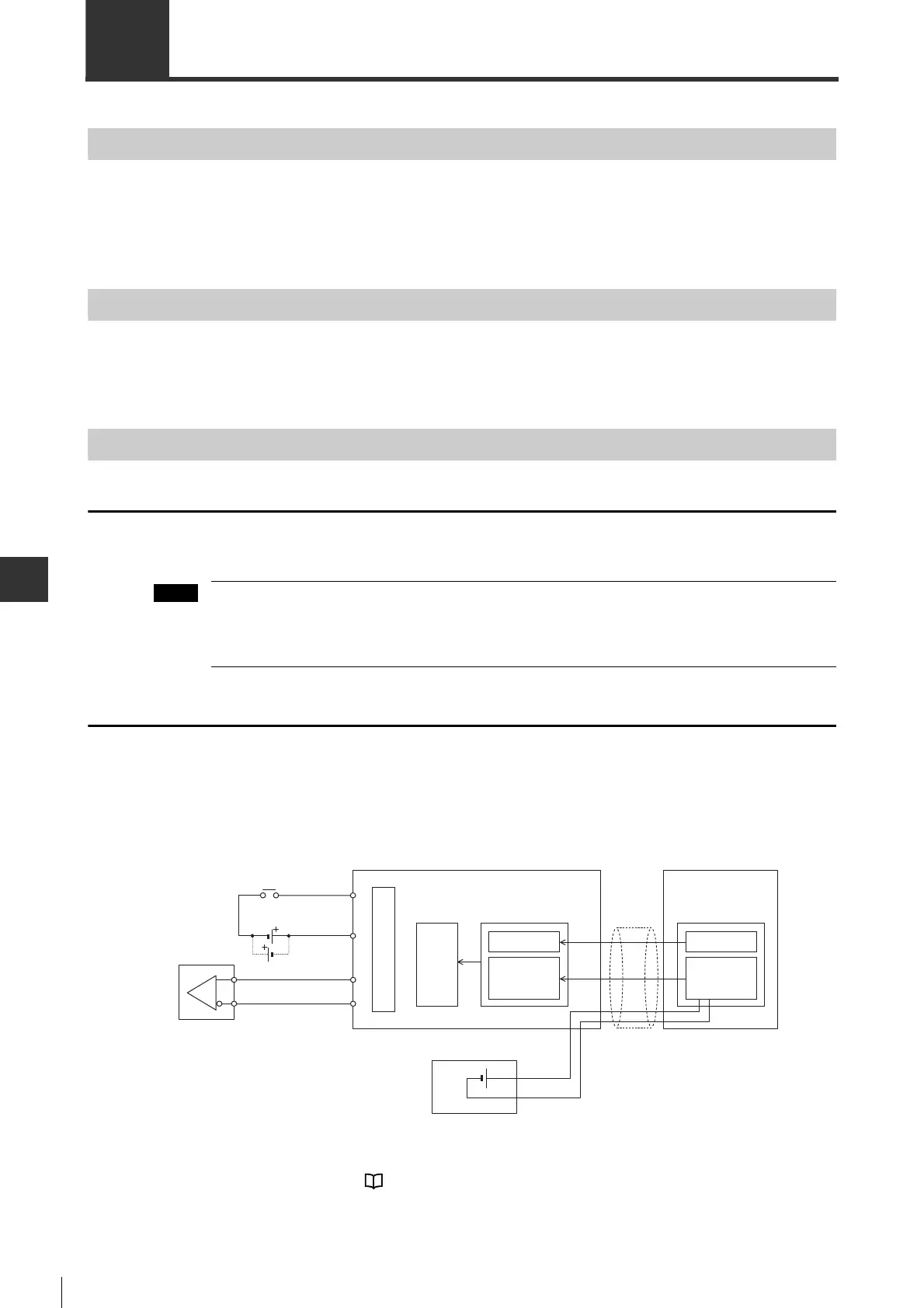
Pulse/analog input type
The "SEN (absolute position data request)" is used by the
pulse/analog input type to automatically switch from encoder
pulse output to absolute position acquisition input which then sends absolute position data to higher-level equipment.
● Internal block diagram
*1 For wiring of SEN signal, see "4-5 Wiring I/O Signals", Page 4-24.
Servo amplifier
Current position
(Absolute position)
Servo motor*
Within 1 revolution
position
Lithium battery
with battery case
Rotary
accumulation
counter
Encoder
Encoder cable
*Absolute encoder
COM+
Serial data
External serial
interface
A+/B+
A
-
/B
-
SEN
*1
Internal circuit
Rotary
accumulation
counter
Within 1 revolution
position
 Loading...
Loading...