87Service Manual – CS7010™ 22 - Steering System
Steering Motor
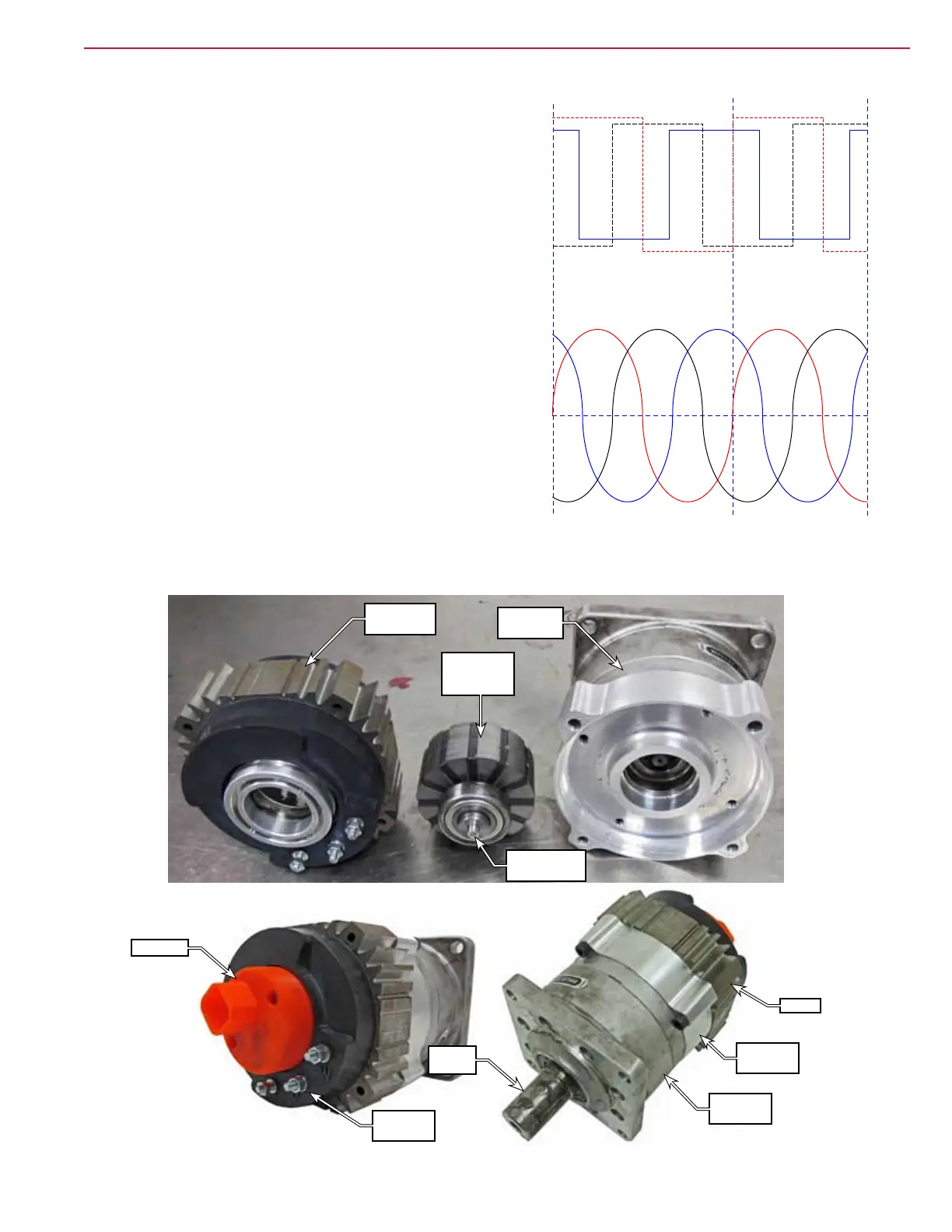
The steering motor is a 3-phase AC, permanent magnet,
remotely commutated motor with internal resolver
commutation feedback. The rst part of this description is
fairly common, and is electrically the same as brushless
DC motors used elsewhere. The difference with this motor
is that it is intended to operate from a simulated 3-phase
sinusoidal input.
The motor itself could be driven by either square wave DC,
or sinusoidal AC, but the sinusoidal waveform permits
higher torque and holding power than the square wave.
With a square wave input, the magnetic eld in the motor
winding is at full magnitude both before and after the
optimal timing for maximum torque. An analogy is the
pedals of a bicycle, and this would represent pushing down
on a pedal before the pedal has reached the top of its stroke.
You waste some power opposing the desired rotation.
With a sinusoidal waveform, the peak magnetic eld
coincides with the optimal torque timing. This results in a
higher torque for the same amount of power.
The drawback to the sinusoidal input is that it requires more complexity to control in order to achieve the
correct timing. The motor provides this greater detail in position feedback by using a “Resolver” instead of
an “encoder”. A resolver is the analog version of an encoder, which is digital.
Stator
(Windings)
Planetary
Gearset
Permanent
Magnet
Rotor
Commutator
Magnet
Resolver
Winding
Terminals
Planetary
Gearset
Output
Shaft
Shaft
Coupling
Motor
AØ
CØ
BØ
3Ø Sinusoid
3Ø Square Wave
 Loading...
Loading...