144 www.xilinx.com Virtex-6 FPGA GTX Transceivers User Guide
UG366 (v2.5) January 17, 2011
Chapter 3: Transmitter
K Characters
The 8B/10B table includes special characters (K characters) that are often used for control
functions. To transmit TXDATA as a K character instead of regular data, the TXCHARISK
port must be driven High. If TXDATA is not a valid K character, the encoder drives
TXKERR High.
Running Disparity
8B/10B uses running disparity to balance the number of ones and zeros transmitted.
Whenever a character is transmitted, the encoder recalculates the running disparity. The
current TX running disparity can be read from the TXCHARDISP port. This running
disparity is calculated several cycles after the TXDATA is clocked into the FPGA TX
interface, so it cannot be used to decide the next value to send, as required in some
protocols.
Normally, running disparity is used to determine whether a positive or negative 10-bit
code is transmitted next. The encoder allows the next disparity value to be controlled
directly as well, to accommodate protocols that use disparity to send control information.
For example, an Idle character sent with reversed disparity might be used to trigger clock
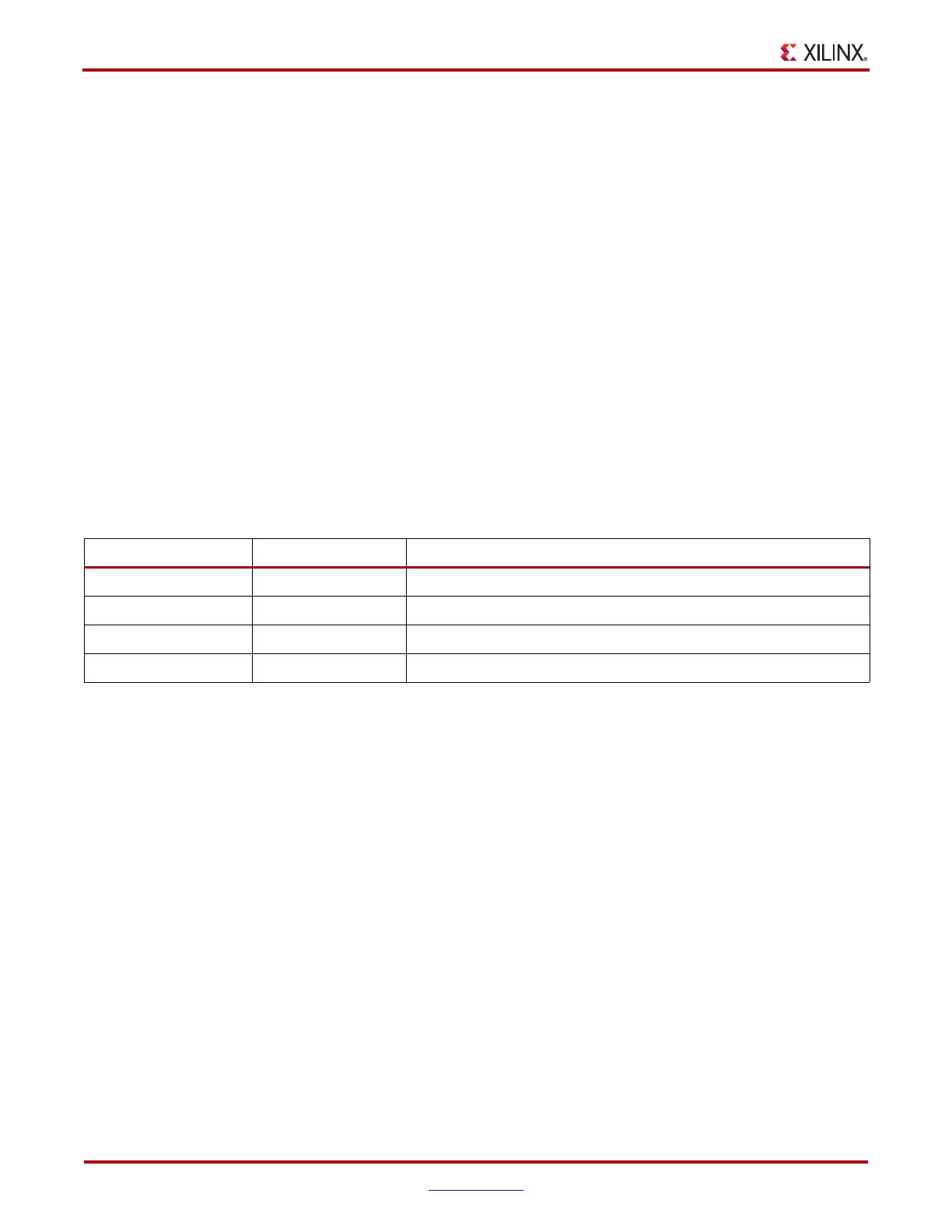
correction. Table 3-11 shows how the TXCHARDISPMODE and TXCHARDISPVAL ports
are used to control outgoing disparity values.
Ports and Attributes
Table 3-12 defines the TX encoder ports.
Table 3-11: TXCHARDISPMODE and TXCHARDISPVAL vs. Outgoing Disparity
TXCHARDISPMODE TXCHARDISPVAL Outgoing Disparity
0 0 Calculated normally by the 8B/10B encoder
0 1 Inverts normal running disparity when encoding TXDATA
1 0 Forces running disparity negative when encoding TXDATA
1 1 Forces running disparity positive when encoding TXDATA

 Loading...
Loading...