Virtex-6 FPGA GTX Transceivers User Guide www.xilinx.com 241
UG366 (v2.5) January 17, 2011
RX Clock Correction
Clock correction should be used whenever there is a frequency difference between XCLK
and RXUSRCLK. It can be avoided by using the same frequency source for TX and RX, or
by using the recovered clock to drive RXUSRCLK. The RX Elastic Buffer section has more
details about the steps required if clock correction is not used.
Ports and Attributes
Table 4-46 defines the RX clock correction ports.
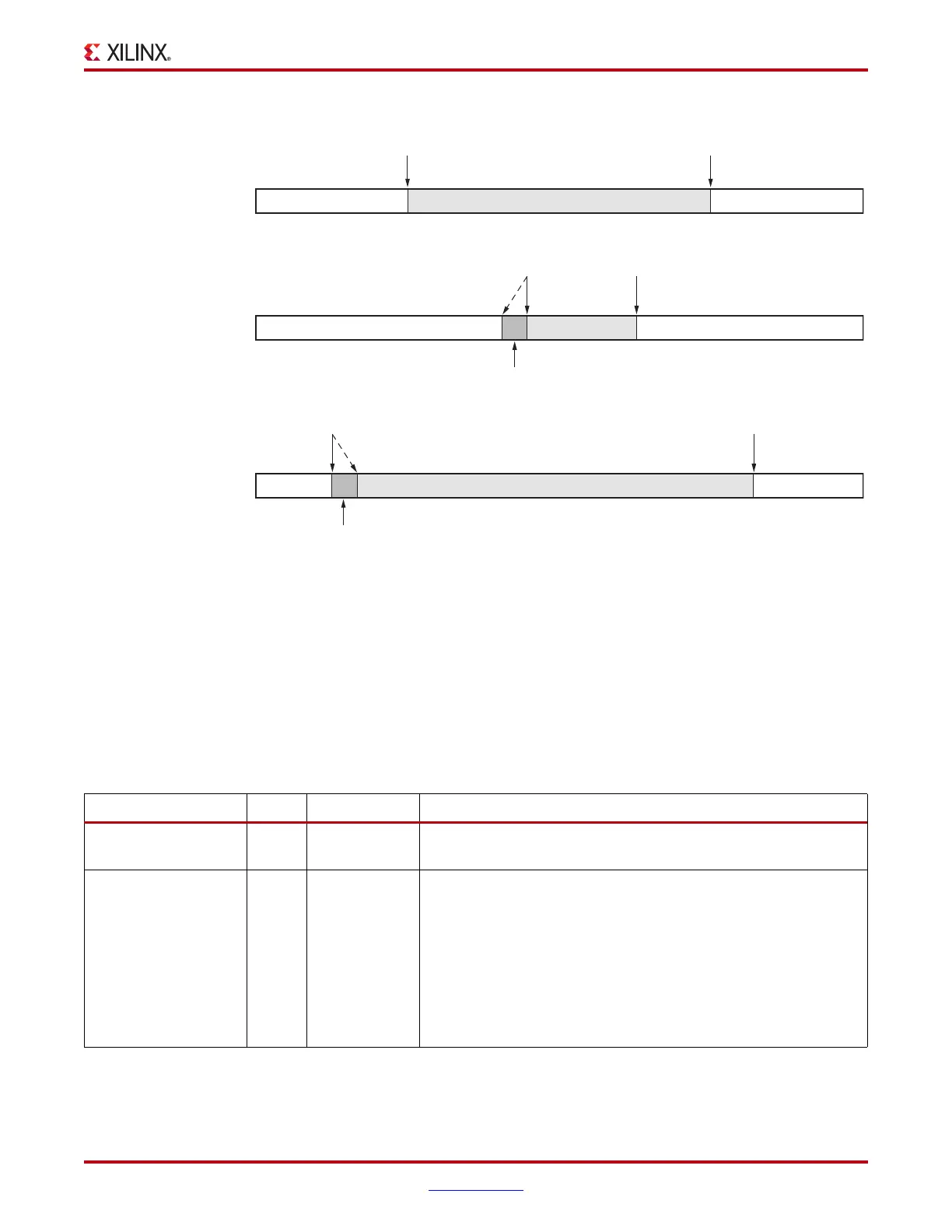
X-Ref Target - Figure 4-35
Figure 4-35: Clock Correction
Write
XCLK
“Nominal” Condition: Buffer Half Full
Buffer Less Than Half Full (Emptying)
Buffer More Than Half Full (Filling Up)
Read
RXUSRCLK
WriteRead
Repeatable Sequence
Write
UG366_c4_32_051509
Repeatable Sequence
Read
Table 4-46: RX Clock Correction Ports
Port Dir Clock Domain Description
RXBUFRESET In Async Resets the RX elastic buffer logic and re-initializes the RX elastic
buffer.
RXBUFSTATUS[2:0] Out RXUSRCLK2 Indicates the status of the RX elastic buffer as follows:
000: Nominal condition
001: Number of bytes in the buffer are less than
CLK_COR_MIN_LAT
010: Number of bytes in the buffer are greater than
CLK_COR_MAX_LAT
101: RX elastic buffer underflow
(1)
110: RX elastic buffer overflow
(1)

 Loading...
Loading...