Five variables are declared, each 36 characters long:
StringVar(1)
StringVar(2)
StringVar(3)
StringVar(4)
StringVar(5)
7.8.4.3.4 Declaring Flag Variables
A flag is a variable, usually declared As Boolean (p. 508), that indicates True or
False, on or off, go or not go, etc. Program execution can be branched based on
the value in a flag. Sometime flags are simply used to inform an observer that an
event is occurring or has occurred. While any variable of any data type can be
used as a flag, using Boolean variables, especially variables named "Flag", usually
works best in practice. CRBasic example Flag Declaration and Use
(p. 135)
demonstrates changing words in a string based on a flag.
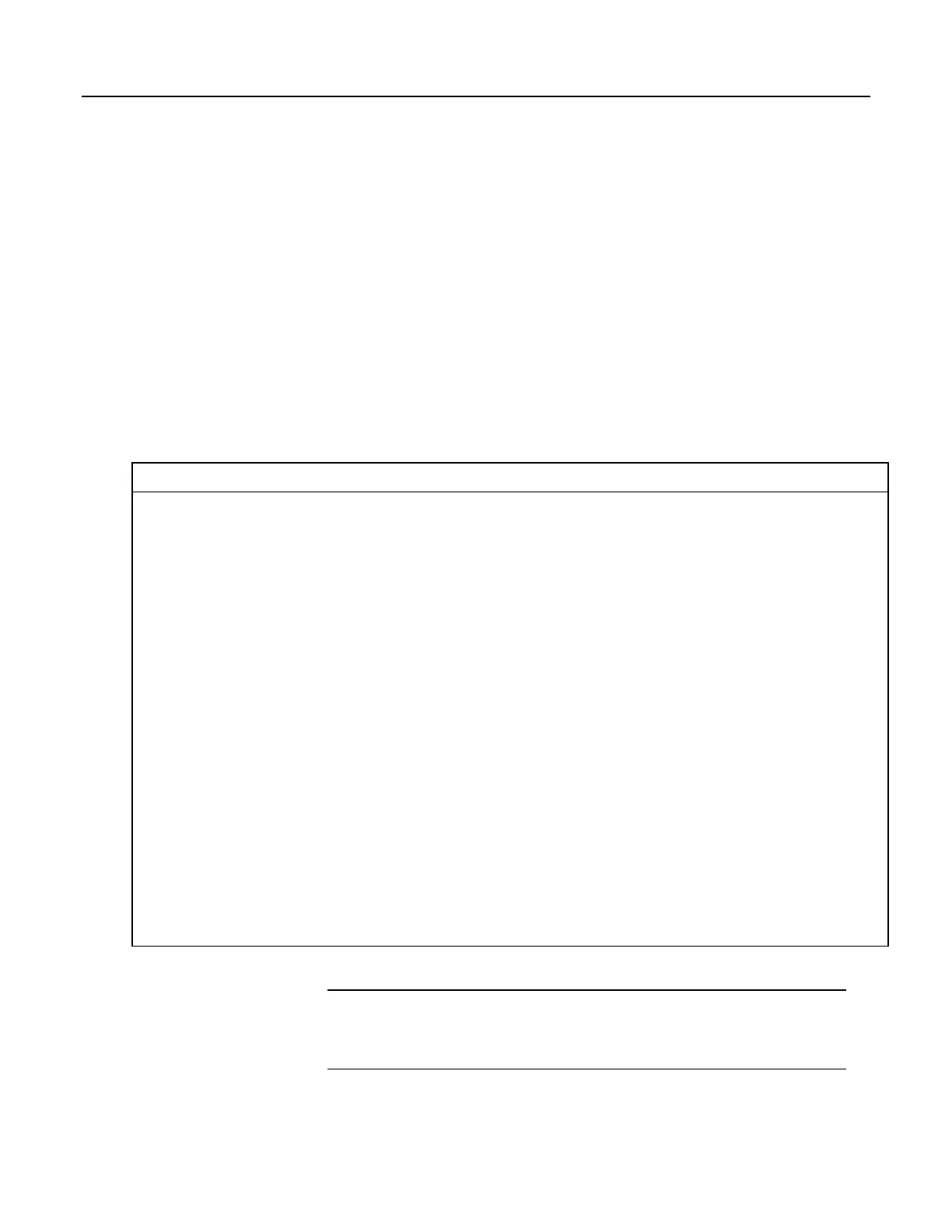
CRBasic Example 5. Flag Declaration and Use
'This program example demonstrates the declaration and use of flags as Boolean variables,
'and the use of strings to report flag status. To run the demonstration, send this program
'to the CR1000, then toggle variables Flag(1) and Flag(2) to true or false to see how the
'program logic sets the words "High" or "Low" in variables FlagReport(1) and FlagReport(2).
'To set a flag to true when using LoggerNet Connect Numeric Monitor, simply click on the
'forest green dot adjacent to the word "false." If using a keyboard, a choice of "True" or
'"False" is made available.
Public Flag(2) As Boolean
Public FlagReport(2) As String
BeginProg
Scan(1,Sec,0,0)
If Flag(1) = True Then
FlagReport(1) = "High"
Else
FlagReport(1) = "Low"
EndIf
If Flag(2) = True Then
FlagReport(2) = "High"
Else
FlagReport(2) = "Low"
EndIf
NextScan
7.8.4.4 Declaring Arrays
Related Topics:
• Declaring Arrays (p. 135)
• Arrays of Multipliers and Offsets
• VarOutOfBounds
(p. 488)
Multiple variables of the same root name can be declared. The resulting series of
like-named variables is called an array. An array is created by placing a suffix of
135

 Loading...
Loading...