7.8.1 Program Structure
Essential elements of a CRBasic program are listed in the table CRBasic Program
Structure
(p. 123) and demonstrated in CRBasic example Program Structure (p. 123).
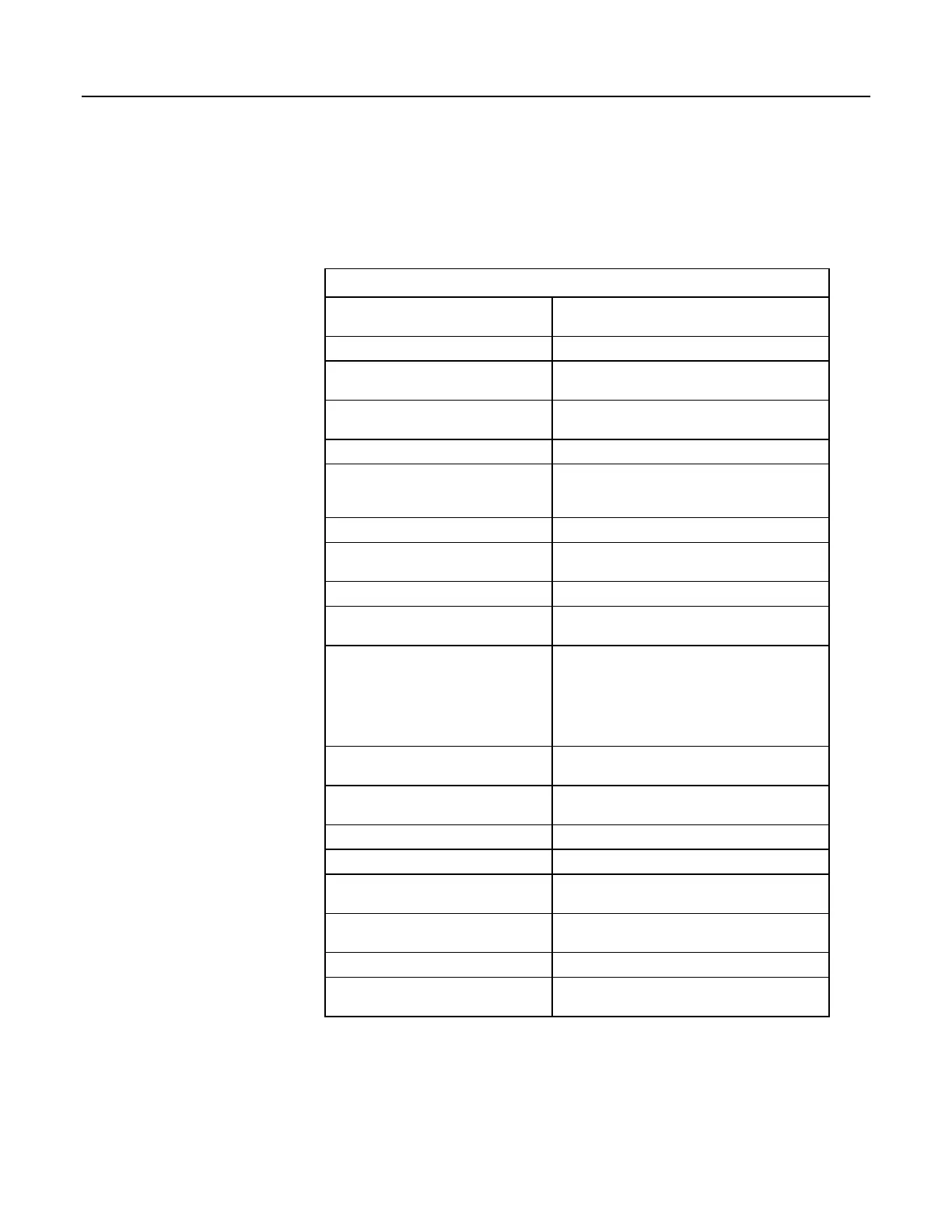
Table 8. CRBasic Program Structure
Declarations
Define CR1000 memory usage. Declare constants,
variables, aliases, units, and data tables.
Declare constants List fixed constants.
Declare Public variables
List / dimension variables viewable during program
execution.
Declare Dim variables
List / dimension variables not viewable during
program execution.
Define Aliases Assign aliases to variables.
Define Units
Assign engineering units to variable (optional).
Units are strictly for documentation. The CR1000
makes no use of Units nor checks Unit accuracy.
Define data tables. Define stored data tables.
Process / store trigger
Set triggers when data should be stored. Triggers
may be a fixed interval, a condition, or both.
Table size Set the size of a data table.
Other on-line storage devices
Send data to a Campbell Scientific mass storage
device or memory card if available.
Processing of data
List data to be stored in the data table, e.g. samples,
averages, maxima, minima, etc.
Processes or calculations repeated during program
execution can be packaged in a subroutine and
called when needed rather than repeating the code
each time.
Begin program
Begin program defines the beginning of statements
defining CR1000 actions.
Set scan interval
The scan sets the interval for a series of
measurements.
Measurements Enter measurements to make.
Processing Enter any additional processing.
Call data table(s)
Declared data tables must be called to process and
store data.
Initiate controls
Check measurements and initiate controls if
necessary.
NextScan
Loop back to set scan and wait for the next scan.
End program
End program defines the ending of statements
defining CR1000 actions.
123

 Loading...
Loading...