where
FR = resolution of the frequency measurement (Hz)
S = scan interval of CRBasic program
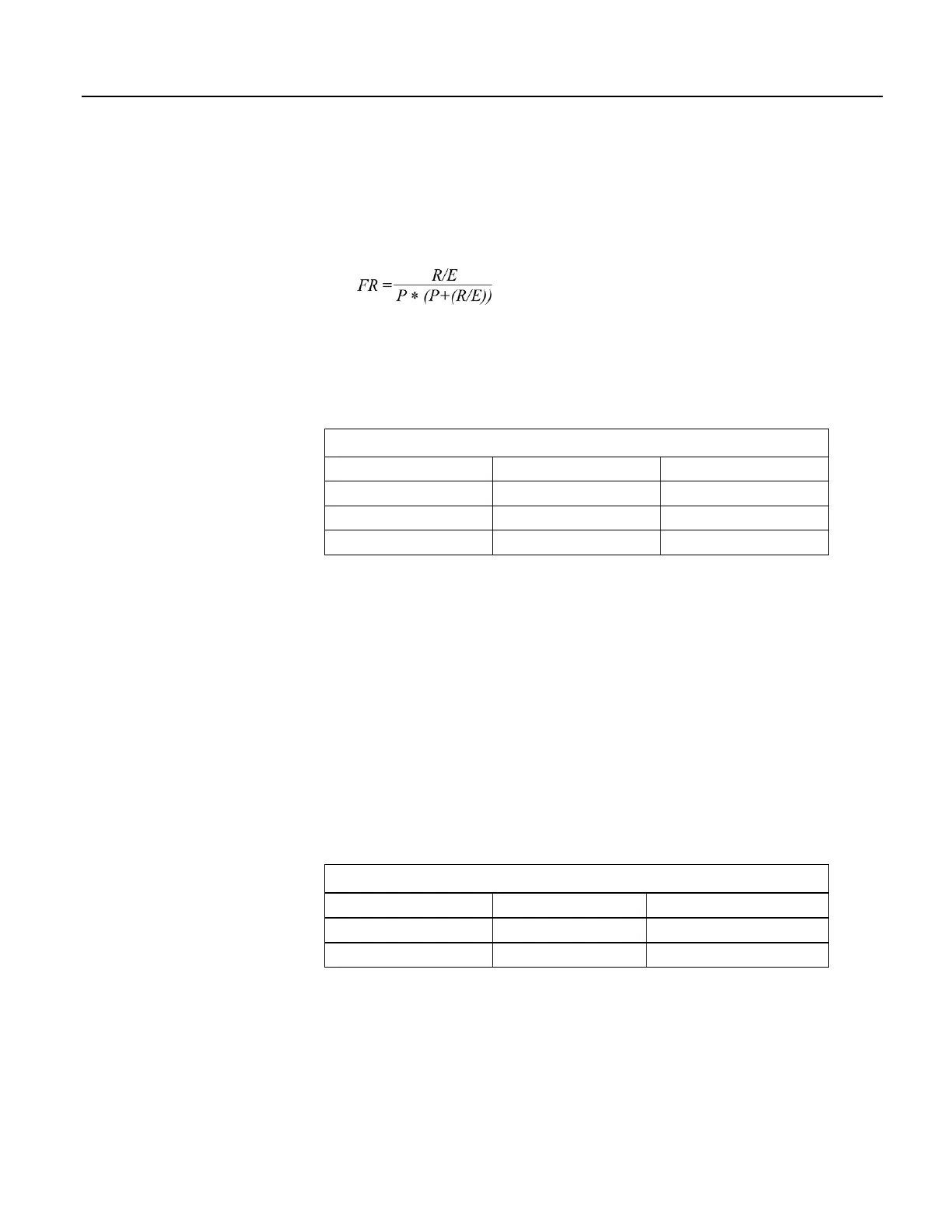
Resolution of a frequency measurement made with the TimerIO() instruction is
where
FR = frequency resolution of the measurement (Hz)
R = timing resolution of the TimerIO() measurement = 540 ns
P = period of input signal (seconds). For example, P = 1 / 1000 Hz = 0.001 s
E = Number of rising edges per scan or 1, whichever is greater.
Table 77. Example. E for a 10 Hz input signal
Scan Rising Edge / Scan E
5.0 50 50
0.5 5 5
0.05 0.5 1
TimerIO() instruction measures frequencies of ≤ 1 kHz with higher frequency
resolution over short (sub-second) intervals. In contrast, sub-second frequency
measurement with PulseCount() produce measurements of lower resolution.
Consider a 1 kHz input. Table Frequency Resolution Comparison
(p. 354) lists
frequency resolution to be expected for a 1 kHz signal measured by TimerIO()
and PulseCount() at 0.5 s and 5.0 s scan intervals.
Increasing a measurement interval from 1 s to 10 s, either by increasing the scan
interval (when using PulseCount()) or by averaging (when using PulseCount()
or TimerIO()), improves the resulting frequency resolution from 1 Hz to 0.1 Hz.
Averaging can be accomplished by the Average(), AvgRun(), and AvgSpa()
instructions. Also, PulseCount() has the option of entering a number greater than
1 in the POption parameter. Doing so enters an averaging interval in milliseconds
for a direct running-average computation. However, use caution when averaging.
Averaging of any measurement reduces the certainty that the result truly
represents a real aspect of the phenomenon being measured.
Table 78. Frequency Resolution Comparison
0.5 s Scan 5.0 s Scan
PulseCount(), POption=1 FR = 2 Hz FR = 0.2 Hz
TimerIO(), Function=2 FR = 0.0011 Hz FR = 0.00011 Hz
8.1.3.3.2 Frequency Measurement Q & A
Q: When more than one pulse is in a scan interval, what does TimerIO() return
when configured for a frequency measurement? Does it average the measured
periods and compute the frequency from that (f = 1/T)? For example,
Scan(50,mSec,10,0)
TimerIO(WindSpd(),11111111,00022000,60,Sec)
354

 Loading...
Loading...