Section 5. System Overview
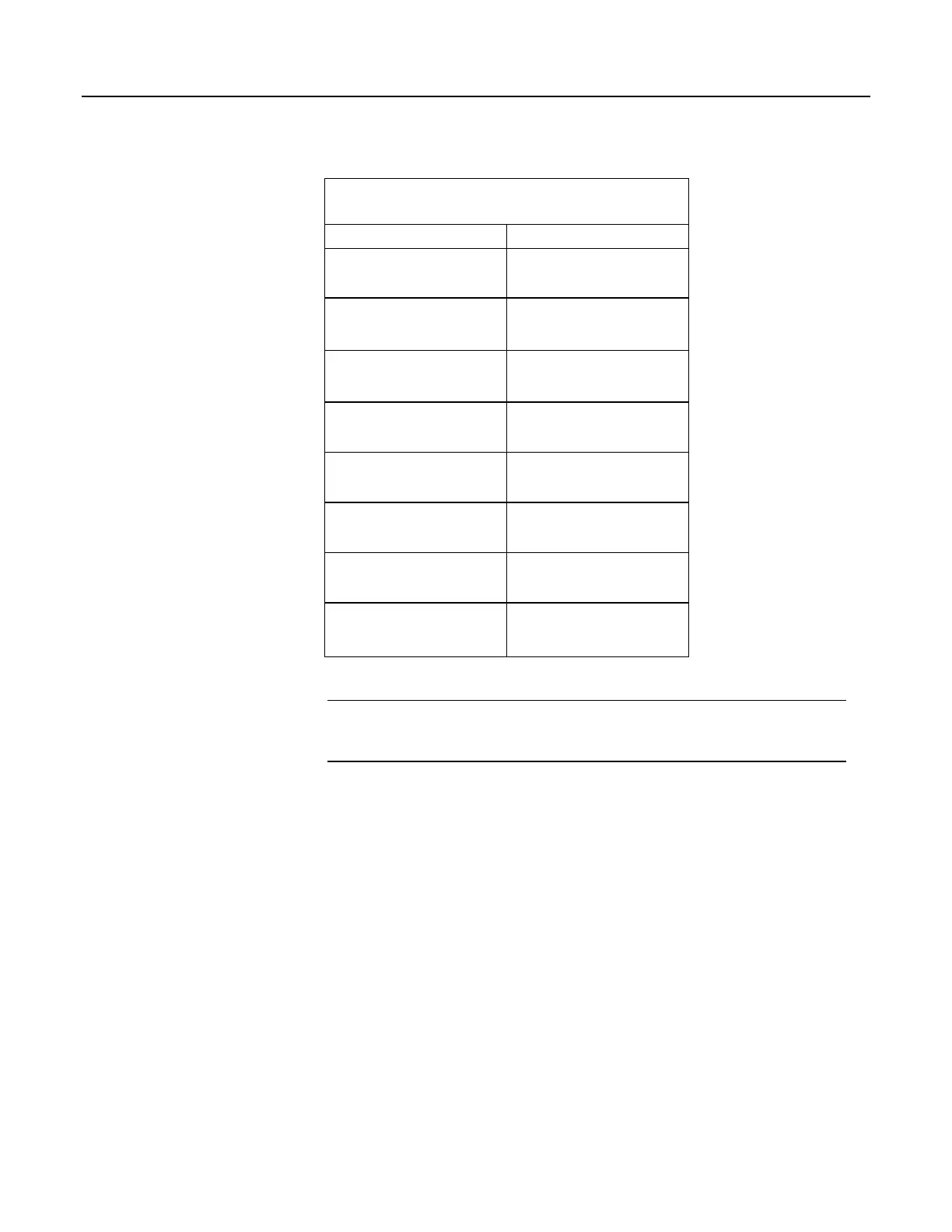
Table 2. Differential and Single-Ended Input
Terminals
DIFF Terminals SE Terminals
1H 1
1L 2
2H 3
2L 4
3H 5
3L 6
4H 7
4L 8
5H 9
5L 10
6H 11
6L 12
7H 13
7L 14
8H 15
8L 16
5.1.2.1.1 Single-Ended Measurements — Overview
Related Topics:
• Single-Ended Measurements — Overview (p. 65)
• Single-Ended Measurements — Details
(p. 307)
A single-ended measurement measures the difference in voltage between the
terminal configured for single-ended input and the reference ground. The
measurement sequence is illustrated in figure Simplified Voltage Measurement
Sequence
(p. 306). While differential measurements are usually preferred, a single-
ended measurement is often adequate in applications wherein some types of noise
are not a problem and care is taken to avoid problems caused by ground currents.
Examples of applications wherein a single-ended measurement may be preferred
include:
• Not enough differential terminals available. Differential measurements use
twice as many H/L] terminals as do single-ended measurements.
• Rapid sampling is required. Single-ended measurement time is about half
that of differential measurement time.
• Sensor is not designed for differential measurements. Many Campbell
Scientific sensors are not designed for differential measurement, but the draw
backs of a single-ended measurement are usually mitigated by large
programmed excitation and/or sensor output voltages.
65

 Loading...
Loading...