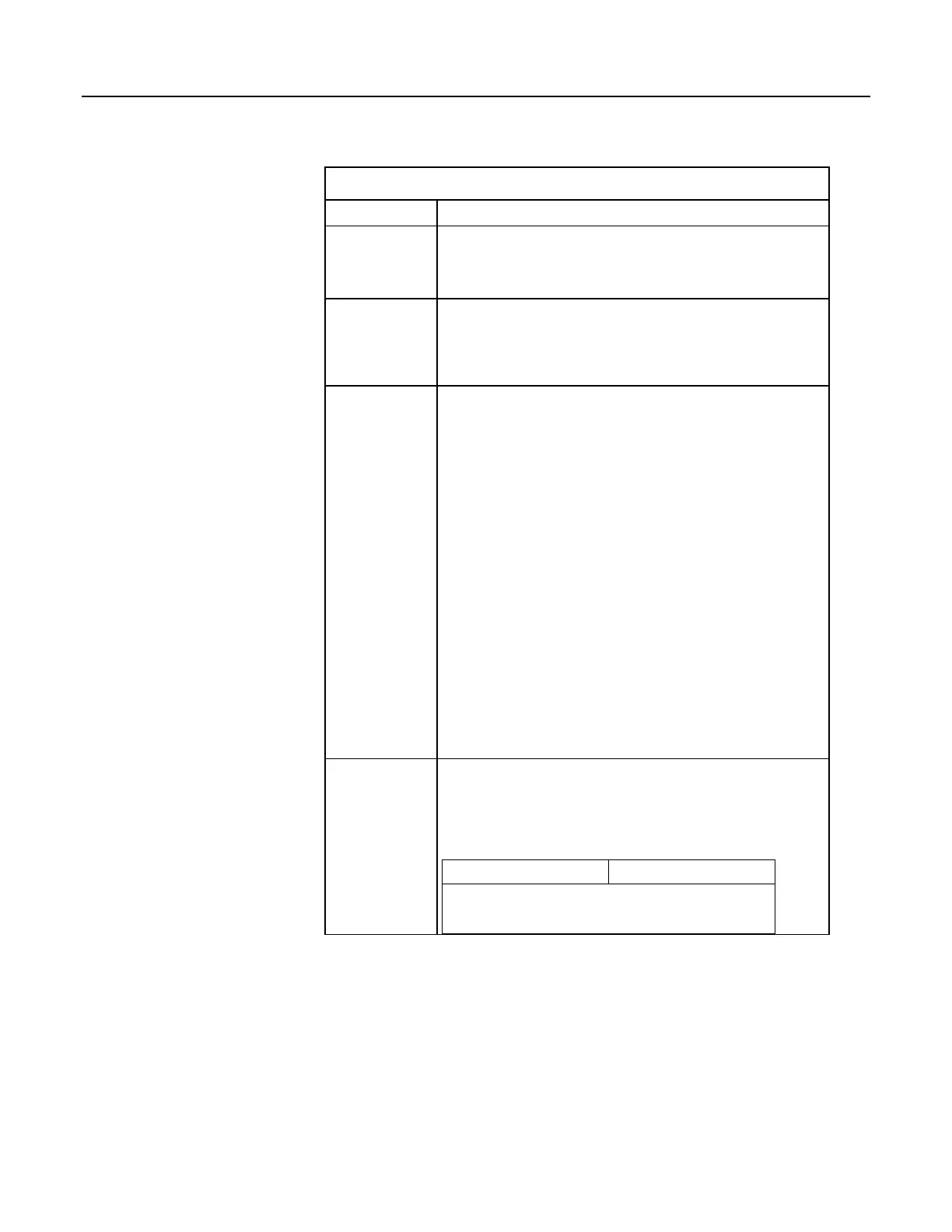
Table 46. String Operators
Operator Description
&
Concatenates strings. Forces numeric values to strings before
concatenation.
Example
1 & 2 & 3 & "a" & 5 & 6 & 7 = "123a567"
+
Adds numeric values until a string is encountered. When a string is
encountered, it is appended to the sum of the numeric values. Subsequent
numeric values are appended as strings.
Example:
1 + 2 + 3 + "a" + 5 + 6 + 7 = "6a567"
-
"Subtracts" NULL ("") from the end of ASCII characters for conversion to
an ASCII code (LONG data type).
Example:
"a" - "" = 97
ASCII codes of the first characters in each string are compared. If the
difference between the codes is zero, codes for the next characters are
compared. When unequal codes or NULL are encountered (NULL
terminates all strings), the difference between the last compared ASCII
codes is returned.
Examples:
Note — ASCII code for a = 97, b = 98, c = 99, d = 100, e = 101, and all
strings end with NULL.
Difference between NULL and NULL
"abc" - "abc" = 0
Difference between e and c
"abe" - "abc" = 2
Difference between c and b
"ace" - "abe" = 1
Difference between d and NULL
<, >, <>, <=, >=, =
ASCII codes of the first characters in each string are compared. If the
difference between the codes is zero, codes for the next characters are
compared. When unequal codes or NULL are encountered (NULL
terminates all strings), the requested comparison is made. If the comparison
is true, -1 or True is returned. If false, 0 or False is returned.
Examples:
Expression Result
7.9.19.2 String Concatenation
Concatenation is the building of strings from other strings ("abc123"), characters
("a" or chr()), numbers, or variables. The table String Concatenation Examples
(p.
284)
lists some expressions and expected results. CRBasic example Concatenation
of Numbers and Strings
(p. 284) demonstrates several concatenation examples.
When non-string values are concatenated with strings, once a string is
encountered, all subsequent operands will first be converted to a string before the
283

 Loading...
Loading...