+ operation is performed. When working with strings, exclusive use of the &
operator ensures that no string value will be converted to an integer.
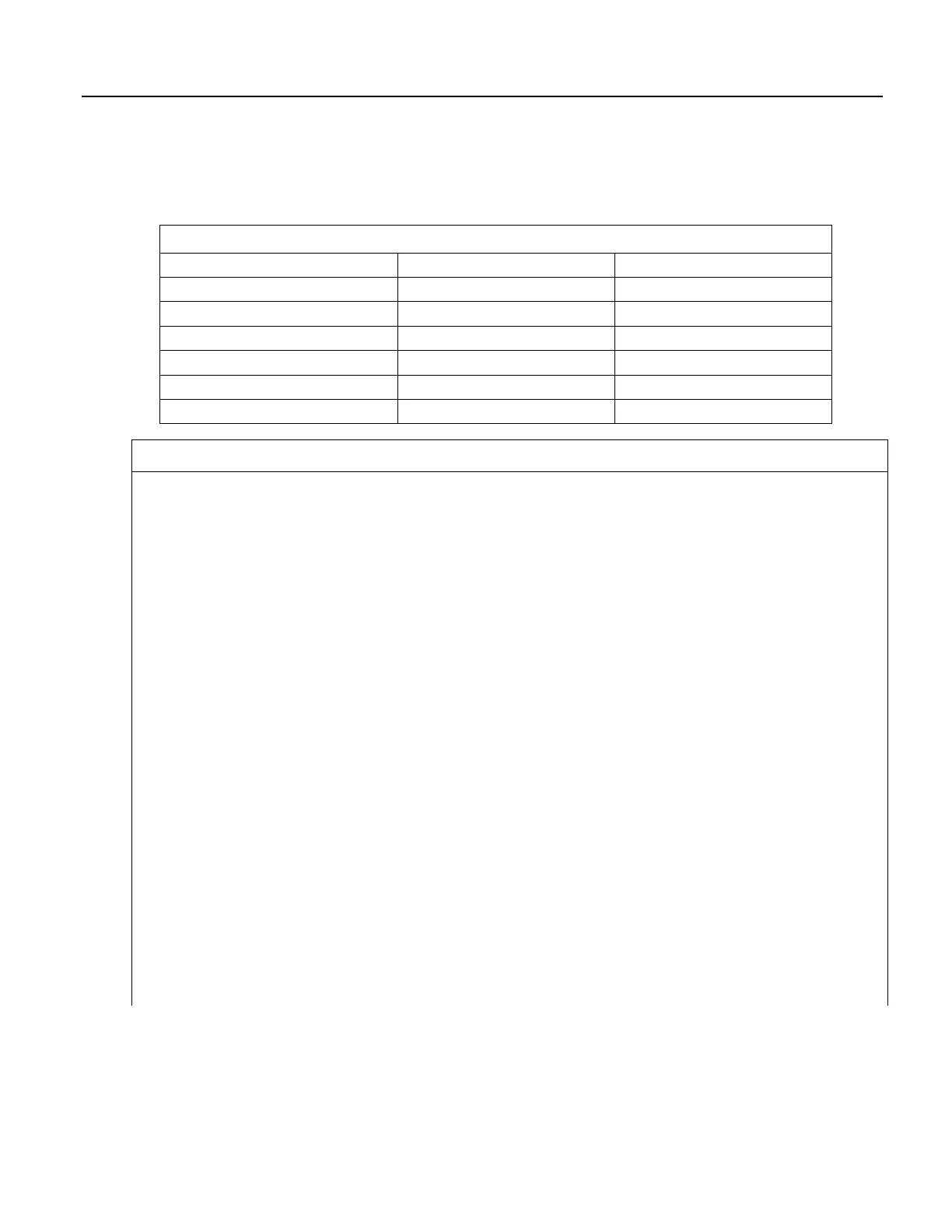
Table 47. String Concatenation Examples
Expression Comments Result
Str(1) = 5.4 + 3 + " Volts"
Add floats, concatenate strings
"8.4 Volts"
Str(2) = 5.4 & 3 & " Volts"
Concatenate floats and strings
"5.43 Volts"
Lng(1) = "123"
Convert string to long
123
Lng(2) = 1+2+"3"
Add floats to string / convert to long
33
Lng(3) = "1"+2+3
Concatenate string and floats
123
Lng(4) = 1&2&"3"
Concatenate floats and string
123
CRBasic Example 59. Concatenation of Numbers and Strings
'This program example demonstrates the concatenation of numbers and strings to variables
'declared As Float and As String.
'
'Declare Variables
Public Num(12) As Float
Public Str(2) As String
Dim I
BeginProg
Scan(1,Sec,0,0)
I = 0 'Set I to zero
'Data type of the following destination variables is Float
'because Num() array is declared As Float.
I += 1 'Increment I by 1 to clock through sequential elements of the Num() array
'As shown in the following expression, if all parameter are numbers, the result
'of using '+' is a sum of the numbers:
Num(I) = 2 + 3 + 4 '= 9
'Following are examples of using '+' and '*' when one or more parameters are strings.
'Parameters are processed in the standard order of operations. In the order of
'operation, once a string or an '&' is processed, all following parameters will
'be processed (concatenated) as strings:
I += 1
Num(I) = "1" + 2 + 3 + 4 '= 1234
I += 1
Num(I) = 1 + "2" + 3 + 4 '= 1234
I += 1
Num(I) = 1 + 2 + "3" + 4 '= 334
I += 1
Num(I) = 1 + 2 + 3 + "4" '= 64
284

 Loading...
Loading...