7.5 1.0 2.0
2.5 0.33 0.67
Note — see Specifications (p. 97) for a complete tabulation of measurement resolution
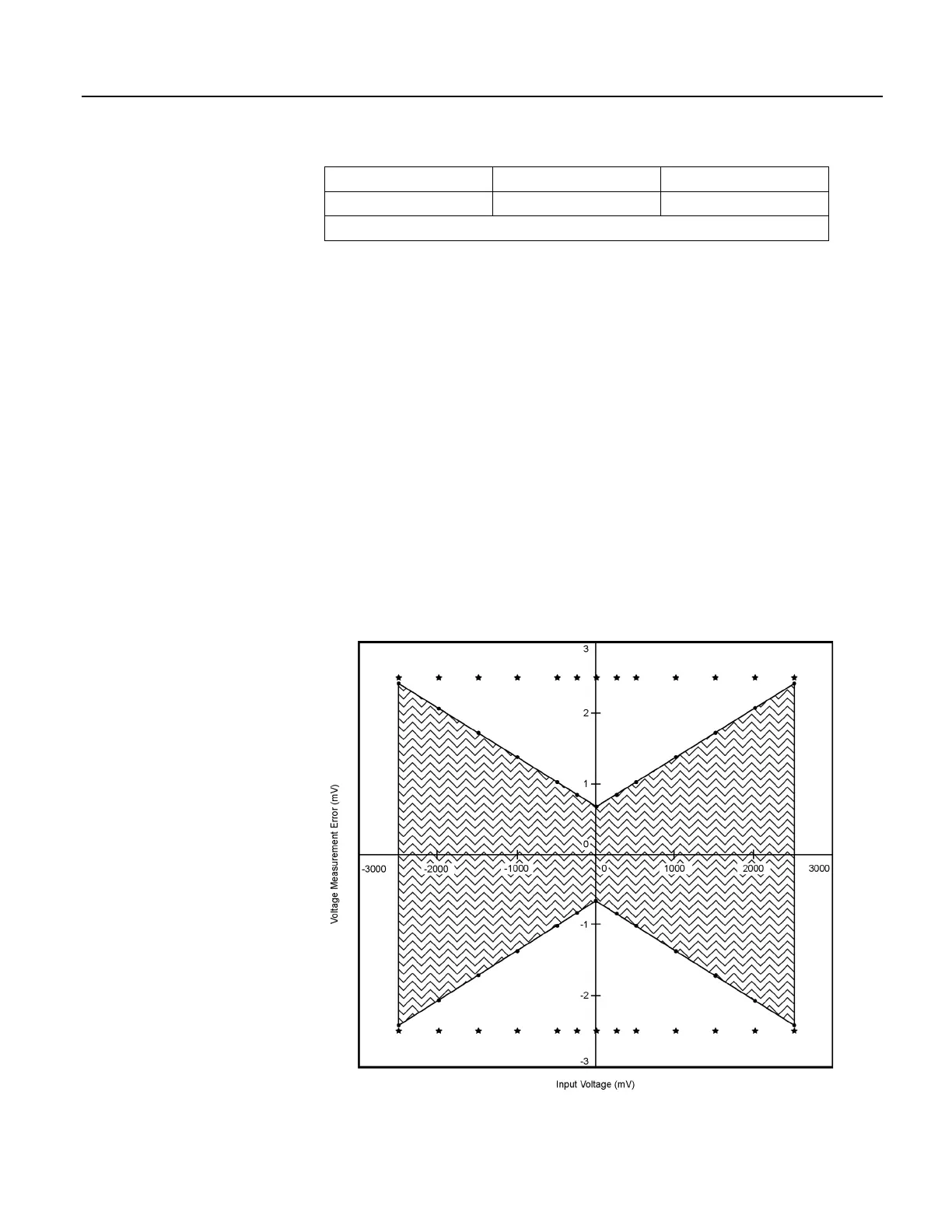
As an example, figure Voltage Measurement Accuracy Band Example (p. 314)
shows changes in accuracy as input voltage changes on the ±2500 input range.
Percent-of-reading is the principle component, so accuracy improves as input
voltage decreases. Offset is small, but could be significant in applications
wherein the sensor-signal voltage is very small, such as is encountered with
thermocouples.
Offset depends on measurement type and voltage-input range. Offsets equations
are tabulated in table Analog Voltage Measurement Offsets
(p. 313). For example,
for a differential measurement with input reversal on the ±5000 mV input range,
the offset voltage is calculated as follows:
offset = 1.5 • Basic Resolution + 1.0 µV
= (1.5 • 667 µV) + 1.0 µV
= 1001.5 µV
where Basic Resolution is the published resolution is taken from the table Analog-
Voltage Measurement Resolution
(p. 313).
Figure 82. Example voltage measurement accuracy band, including the
effects of percent of reading and offset, for a differential measurement
with input reversal at a temperature between 0 to 40 °C.
314

 Loading...
Loading...