Section 10. Troubleshooting
10.5.3.3 Data Types, NAN, and ±INF
NAN and ±INF are presented differently depending on the declared-variable data
type. Further, they are recorded differently depending on the final-memory data
type chosen compounded with the declared-variable data type used as the source
(table Variable and FS Data Types with NAN and ±INF
(p. 483) ). For example,
INF, in a variable declared As LONG, is represented by the integer –
2147483648. When that variable is used as the source, the final-memory word
when sampled as UINT2 is stored as 0.
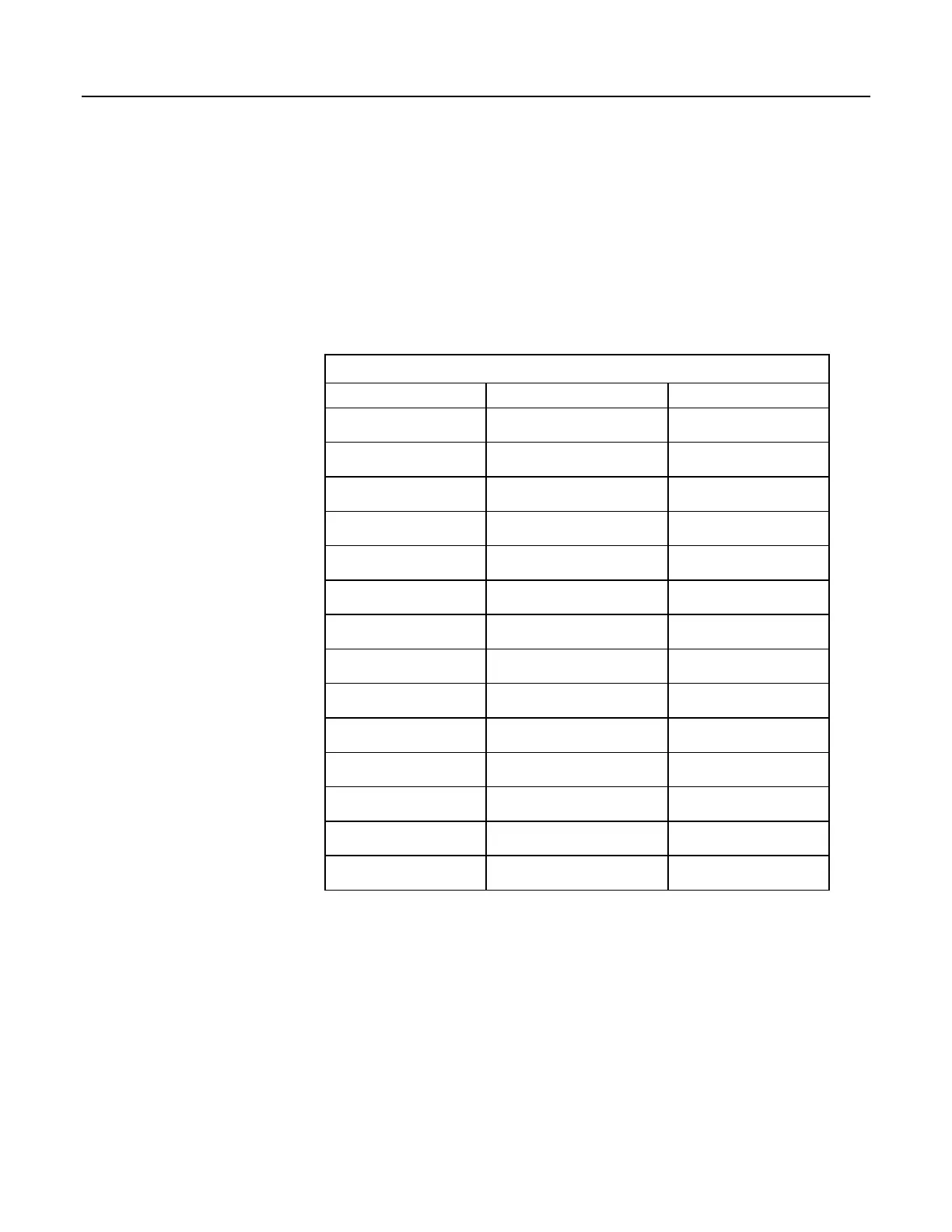
Table 128. Math Expressions and CRBasic Results
Expression CRBasic Expression Result
0 / 0
0 / 0
NAN
∞ – ∞
(1 / 0) - (1 / 0)
NAN
(–1)
∞
-1 ^ (1 / 0)
NAN
0 • –∞
0 • (-1 • (1 / 0))
NAN
±∞ / ±∞
(1 / 0) / (1 / 0)
NAN
1
∞
1 ^ (1 / 0)
NAN
0 • ∞
0 • (1 / 0)
NAN
x / 0
1 / 0
INF
x / –0
1 / -0
INF
-x / 0
-1 / 0
-INF
-x / –0
-1 / -0
-INF
∞
0
(1 / 0) ^ 0
INF
0
∞
0 ^ (1 / 0)
0
0
0
0 ^ 0
1
483

 Loading...
Loading...