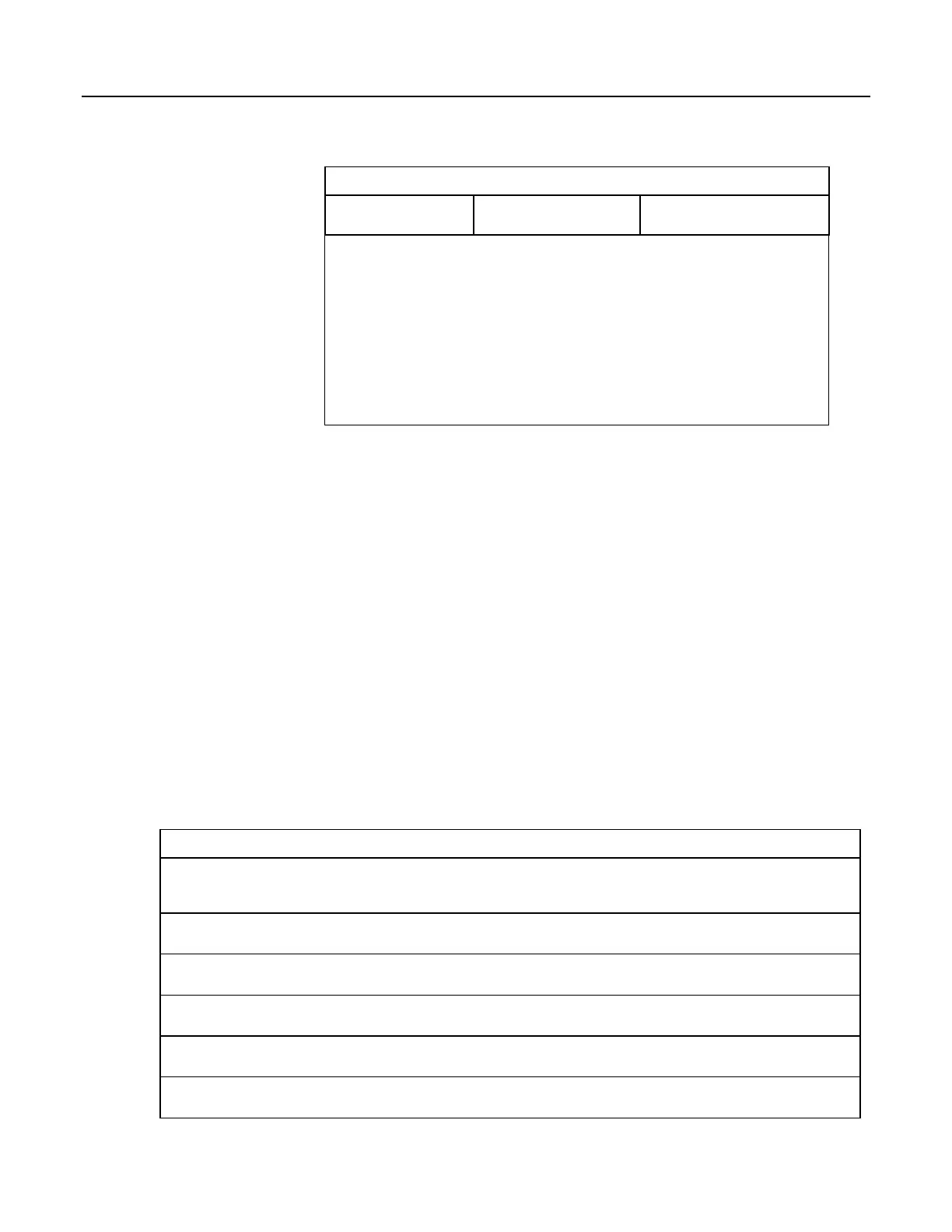
Table 21. Binary Conditions of TRUE and FALSE
Condition
CRBasic Instruction(s)
Used
Memory Location of Binary
Result
Time
TimeIntoInterval()
Variable, System
IfTime()
Variable, System
TimeIsBetween()
Variable, System
Control Port Trigger
WaitDigTrig()
System
Communications
VoiceBeg()
System
ComPortIsActive()
Variable
PPPClose()
Variable
Measurement Event
DataEvent()
System
Using TRUE or FALSE conditions with logic operators such as AND and OR,
logical expressions can be encoded to perform one of the following three general
logic functions. Doing so facilitates conditional processing and control
applications:
1. Evaluate an expression, take one path or action if the expression is true (= –1),
and / or another path or action if the expression is false (= 0).
2. Evaluate multiple expressions linked with AND or OR.
3. Evaluate multiple AND or OR links.
The following commands and logical operators are used to construct logical
expressions. CRBasic example Logical Expression Examples
(p. 165) demonstrate
some logical expressions.
• IF
• AND
• OR
• NOT
• XOR
• IMP
• IIF
Table 22. Logical Expression Examples
If X >= 5 then Y = 0
Sets the variable Y to 0 if the expression "X >= 5" is true, i.e. if X is greater than or equal to 5. The CR1000 evaluates the
expression (X >= 5) and registers in system memory a -1 if the expression is true, or a 0 if the expression is false.
If X >= 5 OR Z = 2 then Y = 0
Sets Y = 0 if either X >= 5 or Z = 2 is true.
If X >= 5 AND Z = 2 then Y = 0
Sets Y = 0 only if both X >= 5 and Z = 2 are true.
If 6 then Y = 0.
If 6 is true since 6 (a non-zero number) is returned, so Y is set to 0 every time the statement is executed.
If 0 then Y = 0.
If 0 is false since 0 is returned, so Y will never be set to 0 by this statement.
Z = (X > Y).
Z equals -1 if X > Y, or Z will equal 0 if X <= Y.
165

 Loading...
Loading...