Note A program can be forced to run in sequential or pipeline mode by placing
the SequentialMode or PipelineMode instruction in the declarations section of
the program.
Some tasks in a program may have higher priorities than others. Measurement
tasks generally take precedence over all others. Task priorities are different for
pipeline mode and sequential mode.
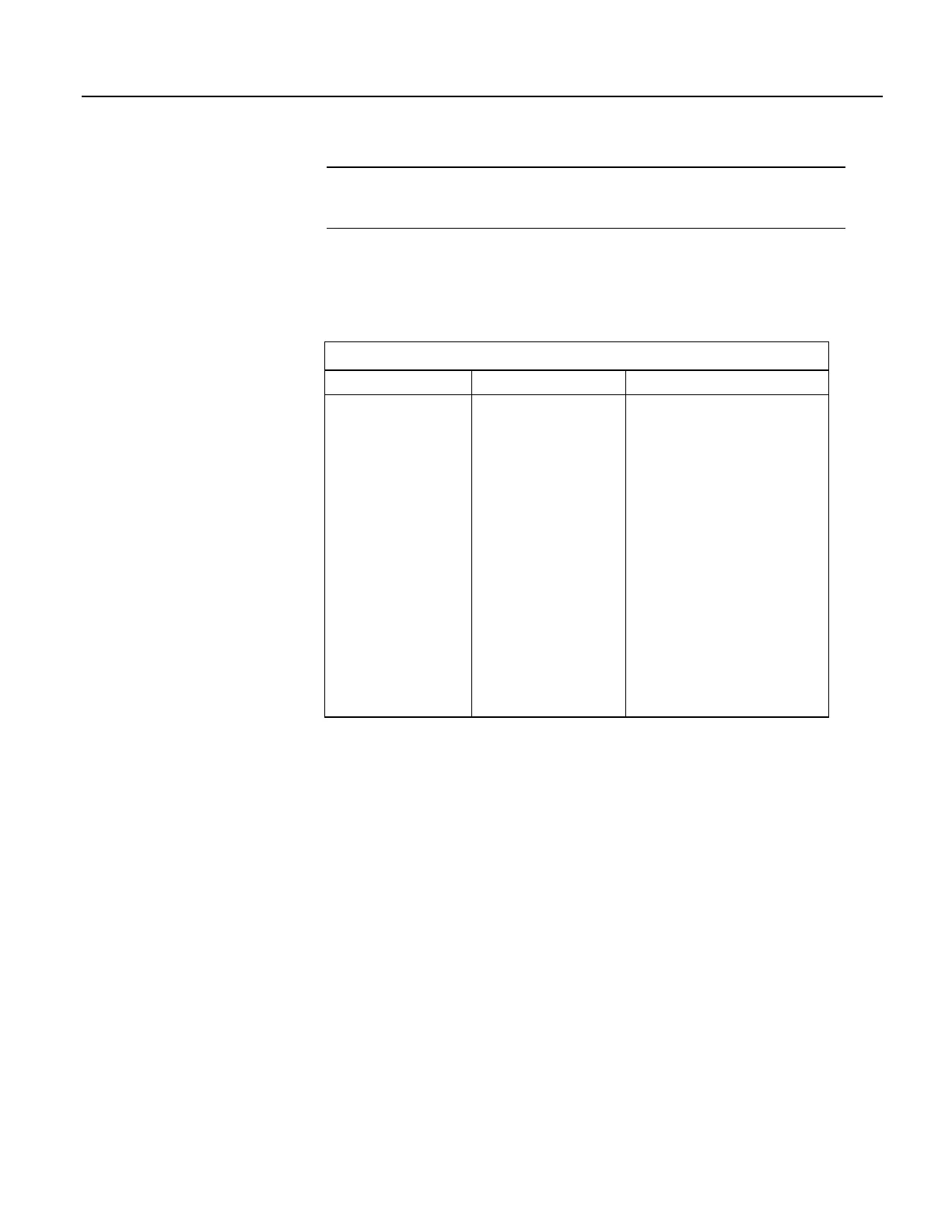
Table 17. Program Tasks
Measurement Task Digital Task Processing Task
• Analog
measurements
• Excitation
• Read pulse
counters
• Read control ports
(GetPort())
• Set control ports
(SetPort())
• VibratingWire()
• PeriodAvg()
• CS616()
• Calibrate()
• SDM instructions,
except SDMSI04()
and SDMI016()
• CDM instructions /
CPI devices.
• Processing
• Output
• Serial I/O
• SDMSIO4()
• SDMIO16()
• ReadIO()
• WriteIO()
• Expression evaluation and
variable setting in
measurement and SDM
instructions
7.8.4.11.1 Pipeline Mode
Pipeline mode handles measurement, most digital, and processing tasks
separately, and possibly simultaneously. Measurements are scheduled to execute
at exact times and with the highest priority, resulting in more precise timing of
measurement, and usually more efficient processing and power consumption.
Pipeline scheduling requires that the program be written such that measurements
are executed every scan. Because multiple tasks are taking place at the same time,
the sequence in which the instructions are executed may not be in the order in
which they appear in the program. Therefore, conditional measurements are not
allowed in pipeline mode. Because of the precise execution of measurement
instructions, processing in the current scan (including update of public variables
and data storage) is delayed until all measurements are complete. Some
processing, such as transferring variables to control instructions, like PortSet()
and ExciteV(), may not be completed until the next scan.
When a condition is true for a task to start, it is put in a queue. Because all tasks
are given the same priority, the task is put at the back of the queue. Every 10 ms
(or faster if a new task is triggered) the task currently running is paused and put at
the back of the queue, and the next task in the queue begins running. In this way,
152

 Loading...
Loading...