comprehensive treatment of field-calibration topics. The most comprehensive
resource to date covering use of FieldCal() and FieldCalStrain() is RTDAQ
software documentation available at www.campbellsci.com
http://www.campbellsci.com. Be aware of the following precautions:
• The CR1000 does not check for out-of-bounds values in mode variables.
• Valid mode variable entries are 1 or 4.
Before, during, and after calibration, one of the following codes will be stored in
the CalMode variable:
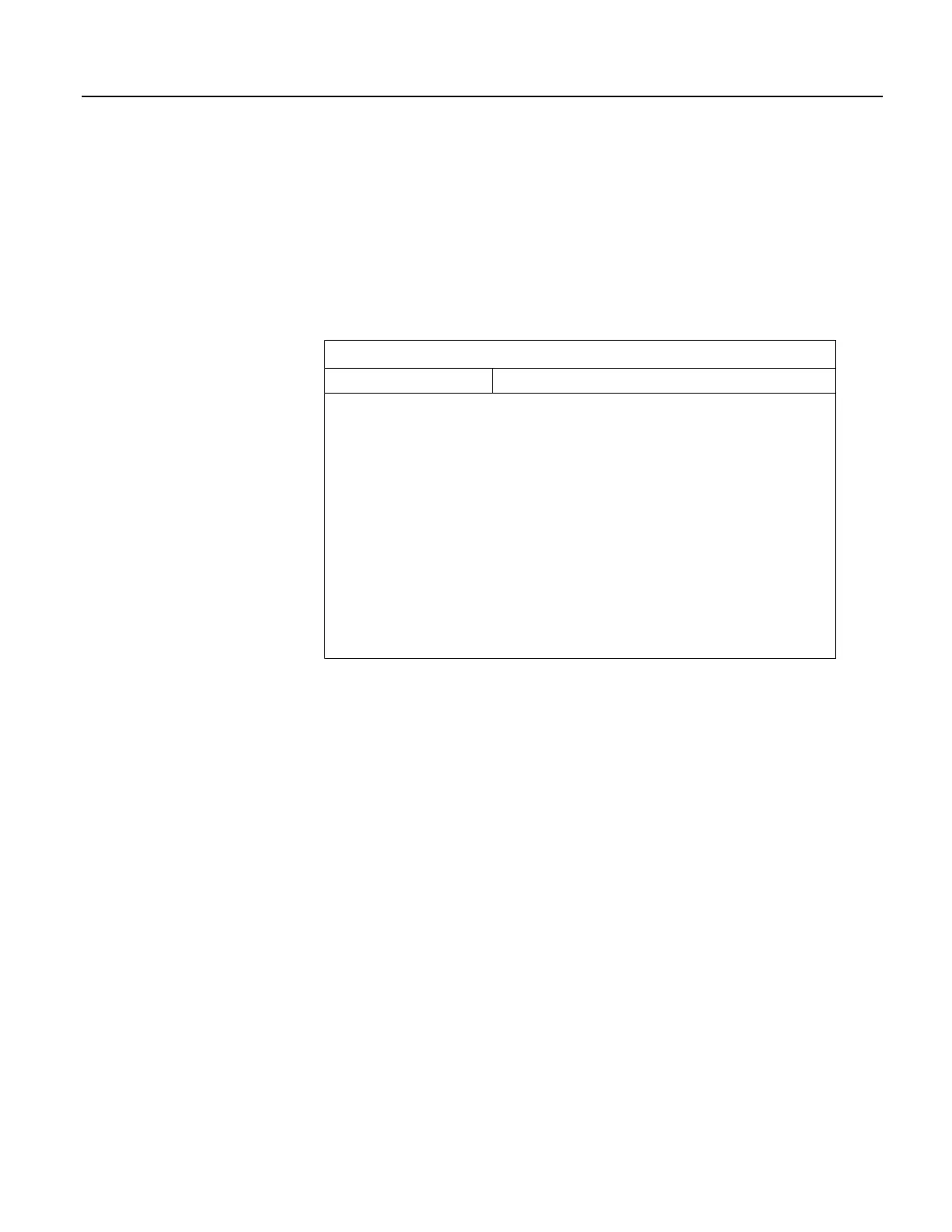
Table 28. FieldCal() Codes
Value Returned State
-1
Error in the calibration setup
-2
Multiplier set to 0 or NAN; measurement = NAN
-3
Reps is set to a value other than 1 or the size of MeasureVar
0
No calibration
1
Ready to calculate (KnownVar holds the first of a two point
calibration)
2
Working
3
First point done (only applicable for two point calibrations)
4
Ready to calculate (KnownVar holds the second of a two-point
calibration)
5
Working (only applicable for two point calibrations)
6
Calibration complete
7.9.12.4.1 One-Point Calibrations (Zero or Offset)
Zero operation applies an offset of equal magnitude but opposite sign. For
example, when performing a zeroing operation on a measurement of 15.3, the
value –15.3 will be added to subsequent measurements.
Offset operation applies an offset of equal magnitude and same sign. For
example, when performing an offset operation on a measurement of 15.3, the
value 15.3 will be added to subsequent measurements.
See FieldCal() Zero or Tare (Opt 0) Example
(p. 214) and FieldCal() Offset (Opt 1)
Example
(p. 216) for demonstration programs:
1. Use a separate FieldCal() instruction and variables for each sensor to be
calibrated. In the CRBasic program , put the FieldCal() instruction
immediately below the associated measurement instruction.
2. Set mode variable = 0 or 6 before starting.
3. Place the sensor into zeroing or offset condition.
4. Set KnownVar variable to the offset or zero value.
5. Set mode variable = 1 to start calibration.
212

 Loading...
Loading...